x-3-(48-24):2+6-3=0
giúp mình với ạ:(
c) (x2 + 1). (x + 2) > 0
d) (x + 4). (x – 3) < 0
e) ( x2 + 2). (x2 + 5) < 0
f) (x + 6). (x – 4) > 0
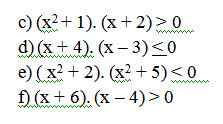 Giúp mình với, mình cần gấp ạ
Giúp mình với, mình cần gấp ạ
Hai bài bị trùng nhau nên các bạn nhìn ảnh hay văn bản đều như nhau ạ
c: =>x+2>0
hay x>-2
d: =>-4<=x<=3
e: =>\(x\in\varnothing\)
f: \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>4\\x< -6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài1: giải các pt sau:
a, 3-4x+24+6x= x+27+3x
b, 5-(6-x)=4(3-2x)
c, x-(x+1)/3 = (2x+1)/5
d,(2x-1)/3 - (5x+2)/7 = x+13
Bài 2:
a, (x-1)(3x+1)=0
b, (x-5)(7-x)=0
c, ( x-1)(x+5)(-3x+8)=0
d, x(x^2 - 1 )=0
Giúp mình 2 bài này với , mình đang cần gấp , CẢM ƠN M.N ạ><
2:
a: =>x-1=0 hoặc 3x+1=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=-1/3
b: =>x-5=0 hoặc 7-x=0
=>x=5 hoặc x=7
c: =>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x+5=0\\3x-8=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{1;-5;\dfrac{8}{3}\right\}\)
d: =>x=0 hoặc x^2-1=0
=>\(x\in\left\{0;1;-1\right\}\)
(1 - x)2 + (x - x2) + 3 = 0
Giúp mình với, mình cảm ơn nhiều ạ !
Ta có: \(\left(1-x\right)^2+\left(x-x^2\right)+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1+x-x^2+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4-x=0\)
hay x=4
Vậy: S={4}
$⇔x^2-2x+1+x-x^2+3=0$
$⇔-x=-4$
$⇔x=4$
Vậy phương trình đã cho có tập nghiệm S={4}
Cho A= x^3 -2x+n B=x-2 Tìm n để A chia hết cho B
(x-3)^2-2x+6=0
x^2-5x+6=0
Giúp mình nhanh vs ạ
\(A=x^3-2x+n\)
\(B=n-2\)
\(A\text{⋮}B\) ⇒ \(\left(x^3-2x+n\right)\text{⋮}\left(n-2\right)\)
⇒ \(\left[\left(x^3-2x^2\right)+\left(2x^2-4x\right)+\left(2x-4\right)+\left(n+4\right)\right]\text{⋮}\left(n-2\right)\)
⇒ \(\left[x^2\left(x-2\right)+2x\left(x-2\right)+2\left(x-2\right)+\left(n+4\right)\right]\text{⋮}\left(n-2\right)\)
⇒ \(\left[\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+2\right)+\left(n+4\right)\right]\text{⋮}\left(x-2\right)\)
Vì \(\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+2\right)\text{⋮}\left(n-2\right)\)
Để \(A\text{⋮}B\)
⇒ \(n+4=0\)
⇒ \(n=-4\)
a) (x\(^2\)+ 3x - 3)\(^2\) - 12x\(^2\) - 36x + 36 = 0
b) x\(^3\) + 1 + 3(x\(^2\) - x +1) = 0
c) x\(^3\) - 2x\(^2\) + 4x - 8 = 0
Giúp mình với ạ
a) 1-(5/3/8+x-7/5/24)=16/2/3=0
Giúp mình nha mình đg cần gấp
\(a,1-\left(\dfrac{\dfrac{5}{3}}{8}+x-\dfrac{\dfrac{7}{5}}{24}\right)-\dfrac{\dfrac{16}{2}}{3}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow1-\left(\dfrac{5}{24}+x-\dfrac{7}{120}\right)=\dfrac{8}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{20}+x=1-\dfrac{8}{3}=-\dfrac{5}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{5}{3}-\dfrac{3}{20}=-\dfrac{109}{60}\)
Ta có: \(1-\left(\dfrac{5}{\dfrac{3}{8}}+\dfrac{x-7}{\dfrac{5}{24}}\right)-\dfrac{16}{\dfrac{2}{3}}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{40}{3}+\dfrac{24\left(x-7\right)}{5}=23\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-7\right)\cdot\dfrac{24}{5}=\dfrac{29}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-7=\dfrac{145}{72}\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{649}{72}\)
TÌM x
1, (3 – x)2 + (2x + 1)2 – (2 – x)2 – (2x + 1)2 = 0
2, (1 – 2x)2 – 3(x – 1)2 + (x + 1)2 – (1 – x)2 – (x – 1)2 = 0
GIÚP MÌNH VỚI, THANKS NHÌU NHÌU Ạ !!!^^
1: Ta có: \(\left(3-x\right)^2+\left(2x+1\right)^2-\left(2-x\right)^2-\left(2x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2-\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3+x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\)
2: Ta có: \(\left(1-2x\right)^2-3\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(x+1\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1-3x^2+6x-3+\left(x+1\right)^2-2\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-2+x^2+2x+1-2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+4x+1-2x^2+4x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
f(x)=-2x+6
f(x)=x2 -6x+5
f(x)=(x+3)(4-x)
f(x)=-x2 +4/x2-2x+1
bài 2 giải bpt sau
a (x-2)(x2+2x-3)>/=0
b x2-9/-x+5<0
giúp mình với ạ
\(a)\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x-3\right)\ge0.\)
Đặt \(f\left(x\right)=\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x-3\right).\)
Ta có: \(x-2=0.\Leftrightarrow x=2.\\ x^2+2x-3=0.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1.\\x=-3.\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bảng xét dấu:
x \(-\infty\) -3 1 2 \(+\infty\)
\(x-2\) - | - | - 0 +
\(x^2+2x-3\) + 0 - 0 + | +
\(f\left(x\right)\) - 0 + 0 - 0 +
Vậy \(f\left(x\right)\ge0.\Leftrightarrow x\in\left[-3;1\right]\cup[2;+\infty).\)
\(b)\dfrac{x^2-9}{-x+5}< 0.\)
Đặt \(g\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x^2-9}{-x+5}.\)
Ta có: \(x^2-9=0.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3.\\x=-3.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(-x+5=0.\Leftrightarrow x=5.\)
Bảng xét dấu:
x \(-\infty\) -3 3 5 \(+\infty\)
\(x^2-9\) + 0 - 0 + | +
\(-x+5\) + | + | + 0 -
\(g\left(x\right)\) + 0 - 0 + || -
Vậy \(g\left(x\right)< 0.\Leftrightarrow x\in\left(-3;3\right)\cup\left(5;+\infty\right).\)
(2x-1)^3-8x+4=0
Giúp mình nhanh với ạ!
(2x - 1)³ - 8x + 4 = 0
(2x - 1)³ - 4x(2x - 1) = 0
(2x - 1)[(2x - 1)² - 4x] = 0
(2x - 1)[(2x - 1)(2x - 1) - 4x] = 0
(2x - 1)[2x(2x - 1) - 1.(2x - 1) - 4x] = 0
(2x - 1)(4x² - 2x - 2x + 1 - 4x) = 0
(2x - 1)(4x² + 1) = 0
⇒ 2x - 1 = 0 hoặc 4x² + 1 = 0
*) 2x - 1 = 0
2x = 1
x = 1/2
*) 4x² + 1 = 0
4x² = -1 (vô lý vì 4x² ≥ 0 với mọi x)
Vậy x = 1/2
`(2x-1)^3-8x+4=0`
`-> (2x-1)^3 - 4(2x-1)=0`
`-> (2x-1)^2*(2x-1)-4(2x-1)=0`
`-> (2x-1)* [(2x-1)^2-4]=0`
`->` TH1: `2x-1=0`
`-> 2x=1`
`-> x=1/2`
TH2: `(2x-1)^2-4=0`
`-> (2x-1)^2=4`
`-> (2x-1)^2=(+-2)^2`
`->`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=2\\2x-1=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
`->`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=3\\2x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
`->`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy, `x={1/2; 3/2; -1/2}`.