Cho x2 - 4x + 1 = 0. Tính giá trị biểu thức A = \(\frac{x^4+x^2+1}{x^2}\)
NH
Những câu hỏi liên quan
.Cho biểu thức A ( x - 5 ) ( x2 + 5x + 25) - ( x – 2)(x+ 2) + x.(x2 + x + 4)
a) Rút gọn biểu thức A
b) Tính giá trị biểu thức A biết x -2
b) Tính giá trị biểu thức A biết x2 – 1 0
Đọc tiếp
.Cho biểu thức A = ( x - 5 ) ( x2 + 5x + 25) - ( x – 2)(x+ 2) + x.(x2 + x + 4)
a) Rút gọn biểu thức A
b) Tính giá trị biểu thức A biết x = -2
b) Tính giá trị biểu thức A biết x2 – 1 = 0
a) A = (x - 5)(x² + 5x + 25) - (x - 2)(x + 2) + x(x² + x + 4)
= x³ - 125 - x² + 4 + x³ + x² + 4x
= (x³ + x³) + (-x² + x²) + 4x + (-125 + 4)
= 2x³ + 4x - 121
b) Tại x = -2 ta có:
A = 2.(-2)³ + 4.(-2) - 121
= 2.(-8) - 8 - 121
= -16 - 129
= -145
c) x² - 1 = 0
x² = 1
x = -1; x = 1
*) Tại x = -1 ta có:
A = 2.(-1)³ + 4.(-1) - 121
= 2.(-1) - 4 - 121
= -2 - 125
= -127
*) Tại x = 1 ta có:
A = 2.1³ + 4.1 - 121
= 2.1 + 4 - 121
= 2 - 117
= -115
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho biểu thức :
P
x
2
-
2
x
2
x
2
+
8
-
2
x
2
8...
Đọc tiếp
Cho biểu thức : P = x 2 - 2 x 2 x 2 + 8 - 2 x 2 8 - 4 x + 2 x 2 - x 3 1 - 1 x - 2 x 2 x ≠ 0 , x ≠ 2
a) Rút gọn biểu thức P
b) Tính giá trị biểu thức P với x = 1/2
a) Ta có: 2x2 + 8 = 2(x2 + 4).
8 – 4x + 2x2 – x3
= (8 – x3) - ( 4x - 2x2)
= (2 – x).(4 + 2x + x2) - 2x.(2 - x)
= (2 – x).(4 + 2x + x2 – 2x)
= (2 - x). (4 + x2 )
* Do đó:
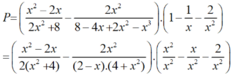
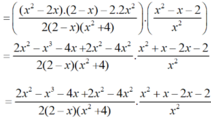
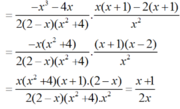
b) Tại x = 1 2 hàm số đã cho xác định nên thay x = 1 2 vào biểu thức rút gọn của P ta được:
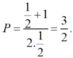
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho biểu thức A=\(\left(\frac{4x}{x^2-4}+\frac{2x-4}{x+2}\right).\frac{x+2}{2x}+\frac{2}{2-x}\)
a)Rút gọn biểu thức A
b)Tính giá trị của biếu thức A với x=4
c)tìm giá trị nguyên của x để biểu thức A nhận giá trị nguyên
đk:x khác 0,+-2,2
cho biểu thức A= \(\frac{2x^2+4x}{x^3-4x}+\frac{x^2-4}{x^2+2x}+\frac{2}{2-x}\) (với x \(\ne\)0; x\(\ne\)-2; x\(\ne\)2
a) Rút gọn biểu thức A
b) Tính giá trị biểu thức A khi x=4
c) Tìm giá trị nguyên của x để biểu thức A nhận giá trị nguyên.
Cho biểu thức A left(dfrac{4x}{x+2}+dfrac{8x^2}{4-x^2}right):left(dfrac{x-1}{x^2-2x}-dfrac{2}{x}right)(x+24x+4−x28x2):(x2−2xx−1−x2)
a) Tìm x để giá trị của biểu thức biểu thức A được xác định.
b) Rút gọn A.
c) Tìm giá trị của A biết x2 + 2x 15
d) Tìm x biết |A| A
Đọc tiếp
Cho biểu thức A =
a) Tìm x để giá trị của biểu thức biểu thức A được xác định.
b) Rút gọn A.
c) Tìm giá trị của A biết x2 + 2x = 15
d) Tìm x biết |A| > A
Cho biểu thức: \(P=\left(\frac{4x-x^3}{1-4x^2}-x\right):\left(\frac{x^4-4x^2}{4x^2-1}+1\right)\)
a, Rút gọn biểu thức
b, Tìm giá trị của x để P > 0.
Cho các biểu thức sau
A = \(\dfrac{4}{x+2}+\dfrac{2}{x-2}+\dfrac{5x-6}{4-x^2}\)
B = \(\dfrac{x+1}{x^2+3x+2}\)
a. Rút gọn A, B
b. tính giá trị của A biết x2 + x = 0
Tính giá trị của B biết x2 + 2x = 0
\(a,ĐK:x\ne\pm2\\ A=\dfrac{4x-8+2x+4-5x+6}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{x+2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{1}{x-2}\\ ĐK:x\ne-1;x\ne-2\\ B=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{1}{x+2}\\ b,x^2+x=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(tm\right)\\x=-1\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ \forall x=0\Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{1}{0-2}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\ \forall x=-1\Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{1}{-1-2}=-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(x^2+2x=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(tm\right)\\x=-2\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow B=\dfrac{1}{0+2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Đúng 6
Bình luận (0)
Cho \(x^2-4x+1=0\)
Tính giá trị của biểu thức ////;
\(A=\frac{x^4+x^2+1}{x^2}\)
Ta có
\(x^2-4x+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-x+1=3x\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{x^2-x+1}{x}=3\) (1)
\(A=\frac{x^4+x^2+1}{x^2}=\frac{x^2-x+1}{x}.\frac{x^2+x+1}{x}\)
\(=3.\frac{x^2+x+1}{x}\)
Mà \(\frac{x^2+x+1}{x}=\frac{x^2-x+1}{x}+\frac{2x}{x}=3+2=5\)
Vậy \(A=3.5=15\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho biểu thức:
\(A=x-\left(\frac{16x-x^2}{x^2-4}+\frac{3+2x}{2-x}-\frac{2-3x}{x+2}\right):\frac{x-1}{x^3+4x^2+4x}\)
1) Rút gọn biểu thức A.
2) Tính giá trị của biểu thức A với các giá trị x thỏa mãn:\(|x^2-3|=3-x\)
Cho biểu thức: A= 1/x-1 - 1/x+1 + 4x+2/x2-1 a, Rút gọn A b, Tính x để A=4/2015 c, tìm x nguyên để A có giá trị nguyên d, Tính giá trị của A khi x=-1/2 Làm giúp em với ạ
a. \(A=\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}+\dfrac{4x+2}{x^2-1}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{4x+2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)-\left(x-1\right)+4x+2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x+1-x+1+4x+2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{4x+4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{4\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{4}{x-1}\)
b) Ta có: \(A=\dfrac{4}{x-1}=\dfrac{4}{2015}\) (ĐK: \(x\ne\pm1\) )
\(\Leftrightarrow8060=4\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8060=4x-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8064=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{8064}{4}=2016\left(tm\right)\)
c) Ta có: \(\dfrac{4}{x-1}\left(x\ne1\right)\)
Để \(\dfrac{4}{x-1}\) nhận giá trị nguyên thì \(4:\left(x-1\right)\Leftrightarrow x-1\in\text{Ư}\left(4\right)=\left\{1;4;2\right\}\)
Vậy với x ∈ {2; 5; 3; 0; -1; -3} thì biểu thức \(\dfrac{4}{x-1}\) nhận giá trị nguyên
d) Thay \(x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\) vào biểu thức A ta được:
\(\dfrac{4}{-\dfrac{1}{2}-1}=-3\)
Vậy biểu thức A có giá trị -3 tại \(x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)



