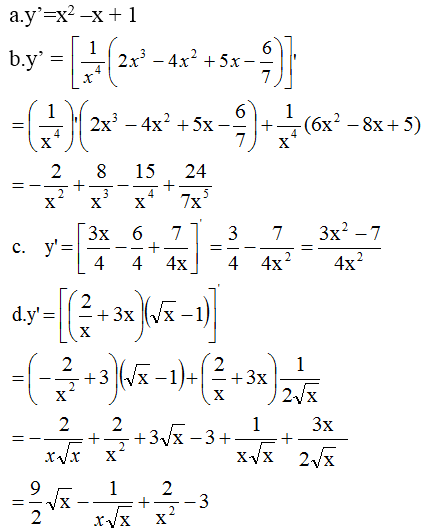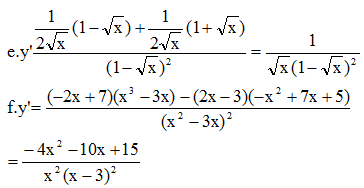Hàm số y= \(\dfrac{x^2-7x+8}{x^2-3x+1}\) có tập xđ D = R\{a,b}; a khác b Tính gtri biểu thức Q = \(a^3+b^3-4ab\) Mn giúp em với ạ
TK
Những câu hỏi liên quan
Câu 25. Cho hàm số \(y = \dfrac{x + 1}{x - 1}, y = -x^3+x^2-3x+1, y = x^4 + 2x^2 +2.\) Trong các hàm số trên, có bao nhiêu hàm số đơn điệu trên \(R\)?
A. 1. B. 3. C. 0. D. 2.
\(y'_1=-\dfrac{2}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\) nghịch biến trên R/{1}
\(y'_2=-3x^2+2x-3\) có nghiệm khi y' = 0
\(y'_3=4x^3+4x\) có nghiệm khi y' = 0
Vậy không có hàm số đơn điệu trên R.
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
Tìm m để các hàm số sau có tập xác định là R (hay luôn xác định trên R):
a. \(y=f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{3x+1}{x^2+2\left(m-1\right)x+m^2+3m+5}\)
b. \(y=f\left(x\right)=\sqrt{x^2+2\left(m-1\right)x+m^2+m-6}\)
c. \(y=f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{3x+5}{\sqrt{x^2-2\left(m+3\right)x+m+9}}\)
a.
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2\left(m-1\right)x+m^2+3m+5\ne0\) ; \(\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=\left(m-1\right)^2-\left(m^2+3m+5\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5m-4< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m>-\dfrac{4}{5}\)
b.
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2\left(m-1\right)x+m^2+m-6\ge0\) ;\(\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=\left(m-1\right)^2-\left(m^2+m-6\right)\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3m+7\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow m\ge\dfrac{7}{3}\)
c.
\(x^2-2\left(m+3\right)x+m+9>0\) ;\(\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=\left(m+3\right)^2-\left(m+9\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2+5m< 0\Rightarrow-5< m< 0\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Tìm đạo hàm của các hàm số sau :
a) ydfrac{x^3}{3}-dfrac{x^2}{2}+x-5
b) ydfrac{2}{x}-dfrac{4}{x^2}+dfrac{5}{x^3}-dfrac{6}{7x^4}
c) ydfrac{3x^2-6x+7}{4x}
d) yleft(dfrac{2}{x}+3xright)left(sqrt{3}-1right)
e) ydfrac{1+sqrt{x}}{1-sqrt{x}}
f) ydfrac{-x^2+7x+5}{x^2-3x}
Đọc tiếp
Tìm đạo hàm của các hàm số sau :
a) \(y=\dfrac{x^3}{3}-\dfrac{x^2}{2}+x-5\)
b) \(y=\dfrac{2}{x}-\dfrac{4}{x^2}+\dfrac{5}{x^3}-\dfrac{6}{7x^4}\)
c) \(y=\dfrac{3x^2-6x+7}{4x}\)
d) \(y=\left(\dfrac{2}{x}+3x\right)\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)\)
e) \(y=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{x}}{1-\sqrt{x}}\)
f) \(y=\dfrac{-x^2+7x+5}{x^2-3x}\)
Tìm đạo hàm của các hàm số sau :
a) \(y=\dfrac{x-1}{5x-2}\)
b) \(y=\dfrac{2x+3}{7-3x}\)
c) \(y=\dfrac{x^2+2x+3}{3-4x}\)
d) \(y=\dfrac{x^2+7x+3}{x^2-3x}\)
a) =
=
.
b) =
=
.
c) =
=
.
d) y' =\(\dfrac{\left(x^2+7x+3\right)'\left(x^2-3x\right)-\left(x^2+7x+3\right)\left(x^2-3x\right)'}{\left(x^2-3x\right)^2}\)=\(\dfrac{\left(2x+7\right)\left(x^2-3x\right)-\left(x^2+7x+3\right)\left(2x-3\right)}{\left(x^2-3x\right)^2}\)=\(\dfrac{-2x^2-6x+9}{\left(x^2-3x\right)^2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tập xác định của hàm số y = \(\dfrac{x-1}{x^2-x+3}\) là:
A. ∅
B. R
C. R\{1}
D. R\{0;1}
\(y=\dfrac{\sqrt{4-x}}{\left(x-1\right)\sqrt{x^2+2x+1}}\)
Tìm tập xđ của hàm số trên mn giúp mk vs
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4-x\ge0\\x-1\ne0\\x^2+2x+1\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\le4\\x\ne1\\\left(x+1\right)^2\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tập xác định: D=(\(-\infty;4\) ] \ {1}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau
a, y=\(-\dfrac{3x^4}{8}+\dfrac{2x^3}{5}-\dfrac{x^2}{2}+5x-2021\)
b, y= \(\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}\)
c, y=\(\sqrt[3]{3x-2}\)
d, y=(2x-1)\(\sqrt{x+2}\)
e, y=\(sin^3\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-5x\right)\)
g, y=\(cot^{^4}\left(\dfrac{\pi}{6}-3x\right)\)
a.
\(y'=-\dfrac{3}{2}x^3+\dfrac{6}{5}x^2-x+5\)
b.
\(y'=\dfrac{\left(x^2+4x+5\right)'}{2\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}}=\dfrac{2x+4}{2\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}}=\dfrac{x+2}{\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}}\)
c.
\(y=\left(3x-2\right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}\Rightarrow y'=\dfrac{1}{3}\left(3x-2\right)^{-\dfrac{2}{3}}=\dfrac{1}{3\sqrt[3]{\left(3x-2\right)^2}}\)
d.
\(y'=2\sqrt{x+2}+\dfrac{2x-1}{2\sqrt{x+2}}=\dfrac{6x+7}{2\sqrt{x+2}}\)
e.
\(y'=3sin^2\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-5x\right).\left[sin\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-5x\right)\right]'=-15sin^2\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-5x\right).cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-5x\right)\)
g.
\(y'=4cot^3\left(\dfrac{\pi}{6}-3x\right)\left[cot\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-3x\right)\right]'=12cot^3\left(\dfrac{\pi}{6}-3x\right).\dfrac{1}{sin^2\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-3x\right)}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1. Tập hợp xác định của hàm số
y = (3x+10 )/(x^2+14x+45) là:
A.R
B.R \ {3; -5; 9}
C.R \ {-5; -9}
D. R \ {5; 9}
2.Hàm số y = √(x+7) + 2/(x^2 + 6x - 16) có tập xác định D bằng
A. [7;+∞)
B. (-7;+∞) \ {-8;2}
C. [-7; 7] \ {2}
D. [-7;+∞) \ {2}
Giúp e nha mọi người
1.Ý C
Hàm số có nghĩa khi \(x^2+14x+45\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne\left\{-5;-9\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow D=R\backslash\left\{-5;-9\right\}\)
2. Ý D
Hàm số có nghĩa khi \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+7\ge0\\x^2+6x-16\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge-7\\x\ne\left\{2;-8\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow D=\)\([-7;+ \infty) \)\(\backslash\left\{2\right\}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
ĐK : \(x^2+14x+45\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne-5\\x\ne-9\end{cases}}\)
\(TXĐ:D=R\backslash\left\{-5;-9\right\}\)
Chọn C
ĐK : \(\hept{\begin{cases}x+7\ge0\\x^2+6x-16\ne0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge-7\\x\ne-8\\x\ne2\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge-7\\x\ne2\end{cases}}\)
\(TXĐ:D=\left(-7;+\infty\right)\backslash\left\{2\right\}\)
Chọn D
Tìm tập xác định của các hàm số sau: a) y2x^3+3x+1;b) ydfrac{x-1}{x^2-3x+2} ;��−1�2−3�+c) ysqrt{x+1}+sqrt{1-x}.
Đọc tiếp
Tìm tập xác định của các hàm số sau:
a) \(y=2x^3+3x+1\);
b) \(y=\dfrac{x-1}{x^2-3x+2}\) ;
c) \(y=\sqrt{x+1}+\sqrt{1-x}\).
a) Hàm \(y = 2{x^3} + 3x + 1\) là hàm đa thức nên có tập xác định \(D = \mathbb{R}\)
b) Biểu thức \(\frac{{x - 1}}{{{x^2} - 3x + 2}}\)có nghĩa khi \({x^2} - 3x + 2 \ne 0 \Leftrightarrow x \ne 1\)và \(x \ne 2\)
Vậy tập xác định của hàm số đã cho là \(D = \mathbb{R}/\left\{ {1;2} \right\}\)
c) Biểu thức \(\sqrt {x + 1} + \sqrt {1 - x} \) có nghĩa khi \(x + 1 \ge 0\) và \(1 - x \ge 0\), tức là \( - 1 \le x \le 1\)
Vậy tập xác định của hàm số đã cho là \(D = \left[ { - 1;1} \right]\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)