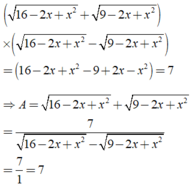(2x-1)2-9=16
AD
Những câu hỏi liên quan
Cho \(\sqrt{16-2x+x^2}-\sqrt{9-2x+x^2}=1\)
Tính A = \(\sqrt{16-2x+x^2}+\sqrt{9-2x+x^2}\)
\(\sqrt{16-2x+x^2}-\sqrt{9-2x+x^2}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{16-2x+x^2}-\sqrt{9-2x+x^2}\right)\left(\sqrt{16-2x+x^2}+\sqrt{9-2x+x^2}\right)}{\sqrt{16-2x+x^2}+\sqrt{9-2x+x^2}}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{16-2x+x^2-9+2x-x^2}{\sqrt{16-2x+x^2}+\sqrt{9-2x+x^2}}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{7}{\sqrt{16-2x+x^2}+\sqrt{9-2x+x^2}}=1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{7}{A}=1\Rightarrow A=7\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho \(\sqrt{16-2x+x^2}-\sqrt{9-2x+x^2}=1\)
Tính \(A=\sqrt{16-2x+x^2}+\sqrt{9-2x+x^2}\)
Có: \(\sqrt{16-2x+x^2}-\sqrt{9-2x+x^2}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)^2+15}-\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)^2+8}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x-1\right)^2+23-2\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)^4+23\left(x-1\right)^2+120}=1\)
Đặt \(t=\left(x-1\right)^2\left(t\ge0\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow2t+23-2\sqrt{t^2+23t+120}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t+11=\sqrt{t^2+23t+120}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2+22t+121=t^2+23t+120\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t=1\left(TM\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0;2\right\}\)
Thay x=0 vào A, ta có:
\(A=\sqrt{16-2.0+0^2}+\sqrt{9-2.0+0^2}=7\)
Thay x=2 vào A, ta có:
\(A=\sqrt{16-2.1+1^2}+\sqrt{9-2.1+1^2}=\sqrt{15}+2\sqrt{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (2)
Ta có \(\left(\sqrt{16-2x+x^2}-\sqrt{9-2x+x^2}\right)\left(\sqrt{16-2x+x^2}+\sqrt{9-2x+x^2}\right)=16-2x+x^2-\left(9-2x+x^2\right)=16-2x+x^2-9+2x-x=7\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{16-2x+x^2}-\sqrt{9-2x+x^2}\right)\left(\sqrt{16-2x+x^2}+\sqrt{9-2x+x^2}\right)=7\Leftrightarrow1.A=7\Leftrightarrow A=7\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 2: Tìm x biết:1,x^2+4x+4252,(5-2x)^2-1603,(x-3)^3-(x-3)(x^2+3x+9)+9(x+1)^2154,3(x+2)^2+(2x-1)^2-7(x-3)9x+3)365,(x-3)(x^2+3x+9)+x(x+2)(2-x)16,(2x+1)^2-4(x+2)^297,(x+3)^{^{ }2}-(x-4)(x+8)1
Đọc tiếp
Bài 2: Tìm x biết:
1,x\(^2\)+4x+4=25
2,(5-2x)\(^2\)-16=0
3,(x-3)\(^3\)-(x-3)(x\(^2\)+3x+9)+9(x+1)\(^2\)=15
4,3(x+2)\(^2\)+(2x-1)\(^2\)-7(x-3)9x+3)=36
5,(x-3)(x\(^2\)+3x+9)+x(x+2)(2-x)=1
6,(2x+1)\(^2\)-4(x+2)\(^2\)=9
7,(x+3)\(^{^{ }2}\)-(x-4)(x+8)=1
1: =>x^2+4x-21=0
=>(x+7)(x-3)=0
=>x=3 hoặc x=-7
2: =>(2x-5-4)(2x-5+4)=0
=>(2x-9)(2x-1)=0
=>x=9/2 hoặc x=1/2
3: =>x^3-9x^2+27x-27-x^3+27+9(x^2+2x+1)=15
=>-9x^2+27x+9x^2+18x+9=15
=>18x=15-9-27=-21
=>x=-7/6
6: =>4x^2+4x+1-4x^2-16x-16=9
=>-12x-15=9
=>-12x=24
=>x=-2
7: =>x^2+6x+9-x^2-4x+32=1
=>2x+41=1
=>2x=-40
=>x=-20
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tính giá trị biểu thức
A=căn của 16-2x+x2 +căn của 9-2x+x2 biết căn của 16-2x+x2 -căn của 9-2x+x2=1
16(x-1)^2-9(2x 1)^2=0
Sửa đề: \(16\left(x-1\right)^2-9\left(2x+1\right)^2=0\)
=>\(\left[4\left(x-1\right)\right]^2-\left[3\left(2x+1\right)\right]^2=0\)
=>\(\left(4x-4\right)^2-\left(6x+3\right)^2=0\)
=>\(\left(4x-4-6x-3\right)\left(4x-4+6x+3\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(-2x-7\right)\left(10x-1\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(2x+7\right)\left(10x-1\right)=0\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+7=0\\10x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-7\\10x=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=\dfrac{1}{10}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
(2x+1)^2-16=9
\(\left(2x+1\right)^2=25=5^2=\left(-5\right)^2\\ \left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=5\\2x+1=-5\end{matrix}\right.\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=6\\2x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (3)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=5\\2x+1=-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
tìm x biết
a) (2x-3)(2x+3)=0
b) x^2-1=0
c) x^2-9=0
d) 4^2-16=0
e) 25x^2-9=0
a) \(\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(x^2-1=0\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(x^2-9=0\Rightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) \(\Rightarrow\left(2x-4\right)\left(2x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
2) \(\Rightarrow\left(5x-3\right)\left(5x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{5}\\x=-\dfrac{3}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Cho
16
-
2
x
+
x
2
-
9
-
2
x
+
x
2
1
.Tính giá trị của biểu thức
A
16
-
2
x
+
x
2
+
9
-
2
x...
Đọc tiếp
Cho 16 - 2 x + x 2 - 9 - 2 x + x 2 = 1 .Tính giá trị của biểu thức A = 16 - 2 x + x 2 + 9 - 2 x + x 2
A. A = 6
B. A = 3
C. A = 5
D. A = 7
Bài 2: Tìm x, biết: a) (x+2)(x² -2x+4)-x(x²+2)=15 b) (x-2)³-(x-4)(x² + 4x+16) + 6(x+1)=49 c) (x - 1)³ + (2 - x)(4 + 2x + x²)+ 3x(x + 2) = 16 d) (x - 3)³ - (x - 3)(x² + 3x + 9) + 9(x + 1)² = 15
a: Ta có: \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-x\left(x^2+2\right)=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+8-x^3-2x=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-7\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\)
b: Ta có: \(\left(x-2\right)^3-\left(x-4\right)\left(x^2+4x+16\right)+6\left(x+1\right)^2=49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-6x^2+12x-8-x^3+64+6\left(x+1\right)^2=49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x^2+12x+56+6x^2+12x+6=49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow24x=-13\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{13}{24}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)