Cho hàm số: f x = x 3 - 3 m x 2 + 3 2 m - 1 + 1 (m là tham số).
Với giá trị nào của tham số m thì hàm số có một cực đại và một cực tiểu?
Đạo hàm y 0 = −3x 2 + 6x + m − 1. Hàm số đã cho đồng biến trên khoảng (0; 3) khi và chỉ khi y 0 > 0, ∀x ∈ (0; 3). Hay −3x 2 + 6x + m − 1 > 0, ∀x ∈ (0; 3) ⇔ m > 3x 2 − 6x + 1, ∀x ∈ (0; 3) (∗). Xét hàm số f(x) = 3x 2 − 6x + 1 trên đoạn [0; 3] có f 0 (x) = 6x − 6; f 0 (x) = 0 ⇔ x = 1. Khi đó f(0) = 1, f(3) = 10, f(1) = −2, suy ra max [0;3] f(x) = f(3) = 10. Do đó (∗) ⇔ m > max [0;3] f(x) ⇔ m > 10. Vậy với m > 10 thì hàm số đã cho đồng biến trên khoảng (0; 3).
1/ Cho hàm số \(f\)(\(x\))=\(\dfrac{1}{3}\)\(x\)\(^3\)+\(x \)\(^2\)-(\(m\)+1)\(x\)-\(m\)+3. Với \(m\) là tham số. Có bao nhiêu số nguyên \(m\) thuộc đoạn [-10;10] để \(f\)'(\(x\)) ≥ 0, ∀\(x\) ϵ \(R\)
2/ Cho hàm số \(y\) = \(\dfrac{mx+4}{x+m}\). Với \(m\) là tham số. Có bao nhiêu số nguyên m thuộc đoạn [-5;2023] để \(y\)' > 0, ∀\(x\) ϵ (0;+∞).
1: \(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{3}\cdot3x^2+2x-\left(m+1\right)=x^2+2x-m-1\)
\(\Delta=2^2-4\left(-m-1\right)=4m+8\)
Để f'(x)>=0 với mọi x thì 4m+8<=0 và 1>0
=>m<=-2
=>\(m\in\left\{-10;-9;...;-2\right\}\)
=>Có 9 số
Cho hàm số y = f(x) xác định trên tập số thực R và có đạo hàm f'(x) = (x - sinx)(x- m- 3)(x- \(\sqrt{9-m^2}\) )3 ∀x∈ R (m là tham số). Có bao nhiêu giá trị nguyên của m để hàm số y =f(x) đạt cực tiểu tại x = 0
\(f'\left(x\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-sinx=0\\x-m-3=0\\x-\sqrt{9-m^2}=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=m+3\\x=\sqrt{9-m^2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do hệ số bậc cao nhất của x dương nên:
- Nếu \(m=-3\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=0\) có nghiệm bội 3 \(x=0\) \(\Rightarrow x=0\) là cực tiểu (thỏa mãn)
- Nếu \(m=3\Rightarrow x=0\) là nghiệm bội chẵn (không phải cực trị, ktm)
- Nếu \(m=0\Rightarrow x=3\) là nghiệm bội chẵn và \(x=0\) là nghiệm bội lẻ, đồng thời \(x=0\) là cực tiểu (thỏa mãn)
- Nếu \(m\ne0;\pm3\) , từ ĐKXĐ của m \(\Rightarrow-3< m< 3\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+3>0\\\sqrt{9-m^2}>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi đó \(f'\left(x\right)=0\) có 3 nghiệm pb trong đó \(x=0\) là nghiệm nhỏ nhất
Từ BBT ta thấy \(x=0\) là cực tiểu
Vậy \(-3\le m< 3\)
1. Cho hàm số \(y=x^3-3mx^2+3\left(2m-1\right)x+1\) . Với giá trị nào của m thì \(f'\left(x\right)-6x>0\) với mọi x>2
A. m > 1/2 B. m < -1/2 C. m >1 D. m ≤ 0
2. Cho hai hàm số f(x) và g(x) đều có đạo hàm trên R và thỏa mãn :
\(f^3\left(2-x\right)-2f^2\left(2+3x\right)+x^2g\left(x\right)+36x=0\) với mọi x thuộc R.
Tính \(A=3f\left(2\right)+4f'\left(2\right)\)
3. Biết hàm số f(x) - f(2x) có đạo hàm bằng 18 tại x=1 và đạo hàm bằng 2000 tại x=2. Tính đạo hàm của hàm số f(x) - f(4x) tại x=1
1.
\(f'\left(x\right)=3x^2-6mx+3\left(2m-1\right)\)
\(f'\left(x\right)-6x=3x^2-3.2\left(m+1\right)x+3\left(2m-1\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2\left(m+1\right)x+2m-1>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-1>2m\left(x-1\right)\)
Do \(x>2\Rightarrow x-1>0\) nên BPT tương đương:
\(\dfrac{x^2-2x-1}{x-1}>2m\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2-2}{x-1}>2m\)
Đặt \(t=x-1>1\Rightarrow\dfrac{t^2-2}{t}>2m\Leftrightarrow f\left(t\right)=t-\dfrac{2}{t}>2m\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(t\right)\) với \(t>1\) : \(f'\left(t\right)=1+\dfrac{2}{t^2}>0\) ; \(\forall t\Rightarrow f\left(t\right)\) đồng biến
\(\Rightarrow f\left(t\right)>f\left(1\right)=-1\Rightarrow\) BPT đúng với mọi \(t>1\) khi \(2m< -1\Rightarrow m< -\dfrac{1}{2}\)
2.
Thay \(x=0\) vào giả thiết:
\(f^3\left(2\right)-2f^2\left(2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow f^2\left(2\right)\left[f\left(2\right)-2\right]=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}f\left(2\right)=0\\f\left(2\right)=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đạo hàm 2 vế giả thiết:
\(-3f^2\left(2-x\right).f'\left(2-x\right)-12f\left(2+3x\right).f'\left(2+3x\right)+2x.g\left(x\right)+x^2.g'\left(x\right)+36=0\) (1)
Thế \(x=0\) vào (1) ta được:
\(-3f^2\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)-12f\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)+36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f^2\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)+4f\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)-12=0\) (2)
Với \(f\left(2\right)=0\) thế vào (2) \(\Rightarrow-12=0\) ko thỏa mãn (loại)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(2\right)=2\)
Thế vào (2):
\(4f'\left(2\right)+8f'\left(2\right)-12=0\Leftrightarrow f'\left(2\right)=1\)
\(\Rightarrow A=3.2+4.1\)
3.
Đặt \(g\left(x\right)=f\left(x\right)-f\left(2x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow g'\left(x\right)=f'\left(x\right)-2f'\left(2x\right)\)
Thay \(x=1\Rightarrow18=f'\left(1\right)-2f'\left(2\right)\) (1)
Thay \(x=2\Rightarrow2000=f'\left(2\right)-2f'\left(4\right)\Rightarrow4000=2f'\left(2\right)-4f'\left(4\right)\) (2)
Cộng vế (1) và (2):
\(f'\left(1\right)-4f'\left(4\right)=4018\)
Đặt \(h\left(x\right)=f\left(x\right)-f\left(4x\right)\Rightarrow h'\left(x\right)=f'\left(x\right)-4f'\left(4x\right)\)
Thay \(x=1\Rightarrow h'\left(1\right)=f'\left(1\right)-4f'\left(4\right)=4018\)
Cho hàm số y=f(x) có đạo hàm f'(x)= x ( x - 1 ) 2 ( x 2 + m x + 9 ) . Có bao nhiêu số nguyên dương m để hàm số y=f(3-x) đồng biến trên khoảng ( 3 ; + ∞ ) .
A. 6.
B. 8.
C. 5.
D. 7.
cho hàm số y= f(x)=(m-3)x + m-2 a)tìm m để hàm số trên là hàm số đồng biến b) tìm m biết f(-1)=1
a: Để hàm số đồng biến thì m-3>0
hay m>3
b: Thay x=-1 và y=1 vào (d), ta được:
-m+3+m-2=1
hay 1=1(đúng)
bài 1: a/ cho hàm số \(y=\frac{3}{2}x\) . điểm E ( -4;m ) là 1 điểm thuộc đồ thị của hàm số trên. tìm m.
b/ cho hàm số y=I\(m+\frac{1}{2}\)I . x-3 đi qua điểm B ( 2;-1).
c/ cho hàm số y=f(x)=(2a + 3).x + . tìm a biết f(1)=-4
bài 2: cho hàm số y=f(x)=\(-x^2\)+3x. tính f(-2), f(\(\frac{2}{3}\)).
Cho hàm số y=f(x) có đạo hàm trên ℝ . Đồ thị hàm số y=f'(x) như hình vẽ bên dưới
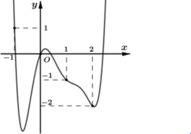
Tìm m để bất phương trình m - x ≥ 2 f x + 2 + 4 x + 3 nghiệm đúng với mọi x ∈ - 3 ; + ∞
A. m ≥ 2 f ( 0 ) - 1
B. m ≤ 2 f ( 0 ) - 1
C. m ≤ 2 f ( - 1 )
D. m ≥ 2 f ( - 1 )
Đáp án B
![]()
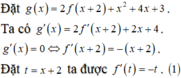
(1) là phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của đồ thị f'(t) và đường thẳng d : y = -t (hình vẽ)
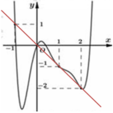
Dựa vào đồ thị của f'(t) và đường thẳng y =-t ta có



cho hàm số y=f(x)=(x+4)|x+2| tìm m để hàm số y=f(x) cắt đường thẳng y=m tại 3 điểm phân biệt
Cho các hàm số \(f\left(x\right)=x^2-4x+m\) và \(g\left(x\right)=\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x^2+2\right)^2\left(x^2+3\right)^3\) . Tìm tập hợp tất cả các giá trị của tham số m để hàm số \(g\left(f\left(x\right)\right)\) đồng biến trên \(\left(3;+\infty\right)\) .
\(g'\left(x\right)=0\Rightarrow x=0\)
Ta thấy \(g\left(x\right)\) đồng biến trên \(\left(0;+\infty\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow g\left(f\left(x\right)\right)\) đồng biến khi \(f\left(x\right)\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow g\left(f\left(x\right)\right)\) đồng biến trên \(\left(3;+\infty\right)\) khi \(f\left(x\right)\ge0\) ; \(\forall x>3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x\ge-m\) ; \(\forall x>3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-m\le\min\limits_{x>3}\left(x^2-4x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow-m\le-3\Rightarrow m\ge3\)