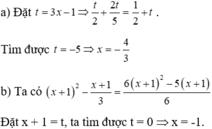Giải các phương trình sau: 3x +2(1-2x)= 5x+1
PB
Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải các phương trình sau bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích
a) 2x(x-5)+4(x-5)=0
b) 3x-15=2x(x-5)
c) (2x+1)(3x-2)=(5x-8)(2x+1)
d) (4x^2-1+(2x+1)(3x-5)
\(a,2x\left(x-5\right)+4\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(2x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\2x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;-2\right\}\)
\(b,3x-15=2x\left(x-5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(x-5\right)-2x\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(-2x+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\-2x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=3\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
\(c,\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)=\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)-\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2-5x+8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(-2x+6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=0\\-2x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-1\\2x=6\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};3\right\}\)
Câu d xem lại đề
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
Giúp mik vs mik cần gấp ạ Đề toán 8 - Ôn tậpCâu 1: Giải các phương trình sau:a. 7x + 21 0b. 3x – 2 2x – 3c. 5x – 2x – 24 0Câu 2: Giải các phương trình sau:a. (2x + 1)(x – 1) 0b. (2x – 3)(-x + 7) 0c. (x + 3)3 – 9(x + 3) 0Câu 3: Giải các phương trình sau:
Đọc tiếp
Giúp mik vs mik cần gấp ạ Đề toán 8 - Ôn tập
Câu 1: Giải các phương trình sau:
a. 7x + 21 = 0
b. 3x – 2 = 2x – 3
c. 5x – 2x – 24 = 0
Câu 2: Giải các phương trình sau:
a. (2x + 1)(x – 1) = 0
b. (2x – 3)(-x + 7) = 0
c. (x + 3)3 – 9(x + 3) = 0
Câu 3: Giải các phương trình sau:

Câu 1:
a) Ta có: 7x+21=0
\(\Leftrightarrow7x=-21\)
hay x=-3
Vậy: S={-3}
b) Ta có: 3x-2=2x-3
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-2-2x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1=0\)
hay x=-1
Vậy: S={-1}
c) Ta có: 5x-2x-24=0
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=24\)
hay x=8
Vậy: S={8}
Câu 2:
a) Ta có: \(\left(2x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-1\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};1\right\}\)
b) Ta có: \(\left(2x-3\right)\left(-x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-3=0\\-x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=3\\-x=-7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{3}{2};7\right\}\)
c) Ta có: \(\left(x+3\right)^3-9\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left[\left(x+3\right)^2-9\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(x+3-3\right)\left(x+3+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+3\right)\left(x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x+3=0\\x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-3\\x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={0;-3;-6}
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:a)
3
x
−
1
2
−
2
−
6
x
5
1
2
+
3
x
−
1
;
b)
x
2...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 3 x − 1 2 − 2 − 6 x 5 = 1 2 + 3 x − 1 ;
b) x 2 + 2 x + 1 − x + 1 3 = 6 x + 1 2 − 5 x − 5 6 .
Giải các phương trình và hệ phương trình sau:1. Phương trình bậc hai và hệ thức vi éta. -3² + 2x + 80b. 5x² - 6x - 10c. -3x² + 14x - 802. Nhẩm nghiệm của các phương trình bậc hai sau:a) 5x² + 3x -20b) -18x² + 7x +110c) x² + 1001x + 1000 0d) -7x² - 8x + 150e) 2x³ - 4x² - 6x 03. Tìm hai số biết tổng và tích của chúng:a) u + v 14, uv40b) u + v -7, uv12c) u + v -5, uv -24
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình và hệ phương trình sau:
1. Phương trình bậc hai và hệ thức vi ét
a. -3² + 2x + 8=0
b. 5x² - 6x - 1=0
c. -3x² + 14x - 8=0
2. Nhẩm nghiệm của các phương trình bậc hai sau:
a) 5x² + 3x -2=0
b) -18x² + 7x +11=0
c) x² + 1001x + 1000 =0
d) -7x² - 8x + 15=0
e) 2x³ - 4x² - 6x =0
3. Tìm hai số biết tổng và tích của chúng:
a) u + v =14, uv=40
b) u + v = -7, uv=12
c) u + v = -5, uv = -24
3:
a: u+v=14 và uv=40
=>u,v là nghiệm của pt là x^2-14x+40=0
=>x=4 hoặc x=10
=>(u,v)=(4;10) hoặc (u,v)=(10;4)
b: u+v=-7 và uv=12
=>u,v là các nghiệm của pt:
x^2+7x+12=0
=>x=-3 hoặc x=-4
=>(u,v)=(-3;-4) hoặc (u,v)=(-4;-3)
c; u+v=-5 và uv=-24
=>u,v là các nghiệm của phương trình:
x^2+5x-24=0
=>x=-8 hoặc x=3
=>(u,v)=(-8;3) hoặc (u,v)=(3;-8)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải các phương trình sau : a) 6x2 - 5x+ 3 2x - 3x(3- 2x) b) (3x - 1)(4x+3) 2(3x-1)
Đọc tiếp
giải các phương trình sau : a) 6x2 - 5x+ 3= 2x - 3x(3- 2x) b) (3x - 1)(4x+3) = 2(3x-1)
\(a,6x^2-5x+3=2x-3x\left(3-2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-5x+3=2x-9x+6x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-6x^2-5x-2x+9x=-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(b,\left(3x-1\right)\left(4x+3\right)=2\left(3x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(4x+3\right)-2\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(4x+3-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=0\\4x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(6x^2-5x+3=2x-3x\left(3-2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-5x+3=2x-9x+6x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-5x+3-2x+9x-6x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{-3}{2}\)
\(\text{Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là }S=\left\{\dfrac{-3}{2}\right\}\)
\(\left(3x-1\right)\left(4x+3\right)=2\left(3x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(4x+3\right)-2\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(4x+3-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(4x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=0\\4x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x=1\\4x=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\text{Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là }S=\left\{\dfrac{1}{3};\dfrac{1}{4}\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình sau bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích: (2x + 1)(3x – 2) = (5x – 8)(2x + 1)
(2x + 1)(3x – 2) = (5x – 8)(2x + 1)
⇔ (2x + 1)(3x – 2) – (5x – 8)(2x + 1) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1).[(3x – 2) – (5x – 8)] = 0
⇔ (2x + 1).(3x – 2 – 5x + 8) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1)(6 – 2x) = 0
⇔ 2x + 1 = 0 hoặc 6 – 2x = 0
+ 2x + 1 = 0 ⇔ 2x = -1 ⇔ x = -1/2.
+ 6 – 2x = 0 ⇔ 6 = 2x ⇔ x = 3.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 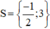
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau
\(1)\sqrt{3x+1}+\sqrt{5x+4}=3x^2-x+3\)
\(2)\left(4x-1\right)\sqrt[3]{2-8x^3}=2x\)
1.
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-3x+\left(x+1-\sqrt{3x+1}\right)+\left(x+2-\sqrt{5x+4}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x^2-x\right)+\dfrac{x^2-x}{x+1+\sqrt{3x+1}}+\dfrac{x^2-x}{x+2+\sqrt{5x+4}}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x\right)\left(3+\dfrac{1}{x+1+\sqrt{3x+1}}+\dfrac{1}{x+2+\sqrt{5x+4}}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
2.
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=a\\\sqrt[3]{2-8x^3}=b\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta được hệ:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(2a-1\right)b=a\\a^3+b^3=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=2ab\\\left(a+b\right)^3-3ab\left(a+b\right)=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow8\left(ab\right)^3-6\left(ab\right)^2=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(ab-1\right)\left[4\left(ab\right)^2+ab+1\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow ab=1\Rightarrow a+b=2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=2\\ab=1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow a=b=1\)
\(\Rightarrow2x=1\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:a)
2
x
3
x
−
2
3
x
−
1
3
x
−
2
;
b)
2
x
−
5
x
+...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 2 x 3 x − 2 = 3 x − 1 3 x − 2 ;
b) 2 x − 5 x + 2 = x 2 − 5 x ;
c) x − 1 2 x + 1 + 2 x = 2 ;
d) x + 2 3 − 9 x + 2 = 0 .
Giải các phương trình sau: 2x –(5x + 3) = 4(3x – 1) -7.
2x –(5x + 3) = 4(3x – 1) -7 ⇔ 2x – 5x – 3 = 12x- 4 – 7 ⇔ - 15x = -8 ⇔ x = 8/15
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = 8/15.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)