Giải phương trình: cos 2 x - 3 cos x = 4 cos 2 x 2

![]()


giải phương trình sin^2 x − 4√3 sin x · cos x + cos^2 x = −2.
Với \(cosx=0\) ko phải nghiệm
Với \(cosx\ne0\) chia 2 vế cho \(cos^2x\)
\(\Rightarrow tan^2x-4\sqrt{3}tanx+1=-2\left(1+tan^2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3tan^2x-4\sqrt{3}tanx+3=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tanx=\sqrt{3}\\tanx=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\\x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải phương trình
(1+cos(x))*(2+4^cos(x)) = 3 * 4^cos(x)
mn giúp mình với !!!! HELP !
Học cái viết đề đi b. Đọc không có ra
đề nè
\(\left(1+cosx\right)\cdot\left(1+4^{cosx}\right)=3\cdot4^{cosx}\)
Giải phương trình :
\(3^{\cos x}-2^{\cos x}=\cos x\)
Xét hàm số \(f\left(t\right)=t^{\cos\alpha}-t\cos\alpha\)
Ta có : \(f'\left(x\right)=\left(t^{\cos\alpha}-1\right)\cos\alpha\)
Khi đó \(f\left(3\right)=f\left(2\right)\) và \(f\left(1\right)\) khả vi liên tục trên \(\left[2;3\right]\) Theo định lí Lagrange thì tồn tại \(c\in\left[2;3\right]\) sao cho :
\(f'\left(c\right)=\frac{f\left(3\right)-f\left(2\right)}{3-2}\) hay \(\left(c^{\cos\alpha-1}-1\right)\cos\alpha\)
Từ đó suy ra :
\(\begin{cases}\cos\alpha=0\\\cos\alpha=1\end{cases}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}\alpha=\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\\\alpha=k\pi\end{cases}\) \(\left(k\in Z\right)\)
Thử lại ta thấy các giá trị này đều thỏa mãn
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là \(x=\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi;x=k\pi\) và \(\left(k\in Z\right)\)
Giải phương trình \(\cos2x+2\cos x+2\sqrt{2}\cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)+3=0\)
Giải các phương trình sau :
a) \(2\sin^2x+\sin x\cos x-3\cos^2x=0\)
b) \(3\sin^2-4\sin x\cos x+5\cos^2x=2\)
c) \(\sin^2x+\sin2x-2\cos^2+5\cos^2x=2\)
d) \(2\cos^2x-3\sqrt{3}\sin2x-4\sin^2x=-4\)
a) Dễ thấy cosx = 0 không thỏa mãn phương trình đã cho nên chiaw phương trình cho cos2x ta được phương trình tương đương 2tan2x + tanx - 3 = 0.
Đặt t = tanx thì phương trình này trở thành
2t2 + t - 3 = 0 ⇔ t ∈ {1 ; ![]() }.
}.
Vậy ![]()
b) Thay 2 = 2(sin2x + cos2x), phương trình đã cho trở thành
3sin2x - 4sinxcosx + 5cos2x = 2sin2x + 2cos2x
⇔ sin2x - 4sinxcosx + 3cos2x = 0
⇔ tan2x - 4tanx + 3 = 0
⇔ ![]()
⇔ x = ![]() + kπ ; x = arctan3 + kπ, k ∈ Z.
+ kπ ; x = arctan3 + kπ, k ∈ Z.
c) Thay sin2x = 2sinxcosx ; ![]() =
= ![]() (sin2x + cos2x) vào phương trình đã cho và rút gọn ta được phương trình tương đương
(sin2x + cos2x) vào phương trình đã cho và rút gọn ta được phương trình tương đương
![]() sin2x + 2sinxcosx -
sin2x + 2sinxcosx - ![]() cos2x = 0 ⇔ tan2x + 4tanx - 5 = 0 ⇔
cos2x = 0 ⇔ tan2x + 4tanx - 5 = 0 ⇔ ![]()
⇔ x = ![]() + kπ ; x = arctan(-5) + kπ, k ∈ Z.
+ kπ ; x = arctan(-5) + kπ, k ∈ Z.
d) 2cos2x - 3√3sin2x - 4sin2x = -4
⇔ 2cos2x - 3√3sin2x + 4 - 4sin2x = 0
⇔ 6cos2x - 6√3sinxcosx = 0 ⇔ cosx(cosx - √3sinx) = 0
⇔ 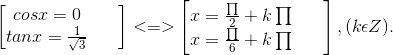
Giải phương trình :
\(2^{\cos2x}\cos x+2\cos^2x=2^{\cos2x-1}+4\cos^3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2^{\cos2x-1}\left(2\cos x-1\right)=2\cos^2x\left(2\cos x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2\cos x-1\right)\left(2^{\cos2x}-2\cos^2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}\cos x=\frac{1}{2}\\2^{\cos2x}=\cos2x+1\end{array}\right.\)
* Với \(\cos x=\frac{1}{2}\) ta có \(x=\frac{\pi}{3}=k2\pi,k\in Z\)
* Với \(2^{\cos2x}=\cos2x+1\) (*), đặt \(t=\cos2x;t\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
Phương trình trở thành \(2^t-t-1=0\)
Xét hàm số \(f\left(t\right)=2^t-t-1,t\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
Có \(f'\left(t\right)=2^t\ln2-1,t\in\left[-1;1\right];f'\left(t\right)=0\) có đúng 1 nghiệm nên phương trình \(f\left(t\right)=0\) có tối đa 2 nghiệm. Mà \(f\left(0\right)=f\left(1\right)=0\) nên \(t=0;t=1\) là tất cả các nghiệm của phương trình \(f\left(t\right)=0\)
Do đó phương trình (*) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}\cos2x=0\\\cos2x=1\end{array}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x=\frac{\pi}{4}+k\frac{\pi}{2}\\x=k\pi\end{array}\right.\) \(k\in Z\)
Vậy phương trình đã cho có 3 nghiệm là :
\(x=\frac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi;x=\frac{\pi}{4}+k\frac{\pi}{2};x=k\pi;k\in Z\)
Giải các phương trình sau :
a) \(\cos^2x+2\sin x\cos x+5\sin^2x=2\)
b) \(3\cos^2x-2\sin2x+\sin^2x=1\)
c) \(4\cos^2x-3\sin x\cos x+3\sin^2x=1\)
Giải phương trình sau:
a) $\tan ^2x+4\cos ^2x+7=4\tan x+8\cot x$
b) $6\sin ^2x+2\cos ^2x-2\sqrt{3}\sin 2x=14\sin \left(x-\frac{\pi }{6}\right)$
Giải phương trình sau: \(\sin^22x-2\cos x+\dfrac{3}{4}=0\)