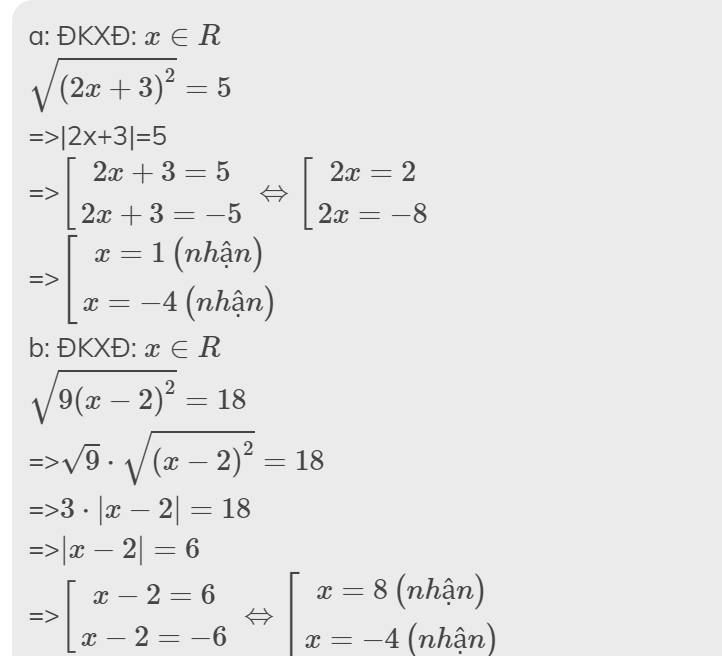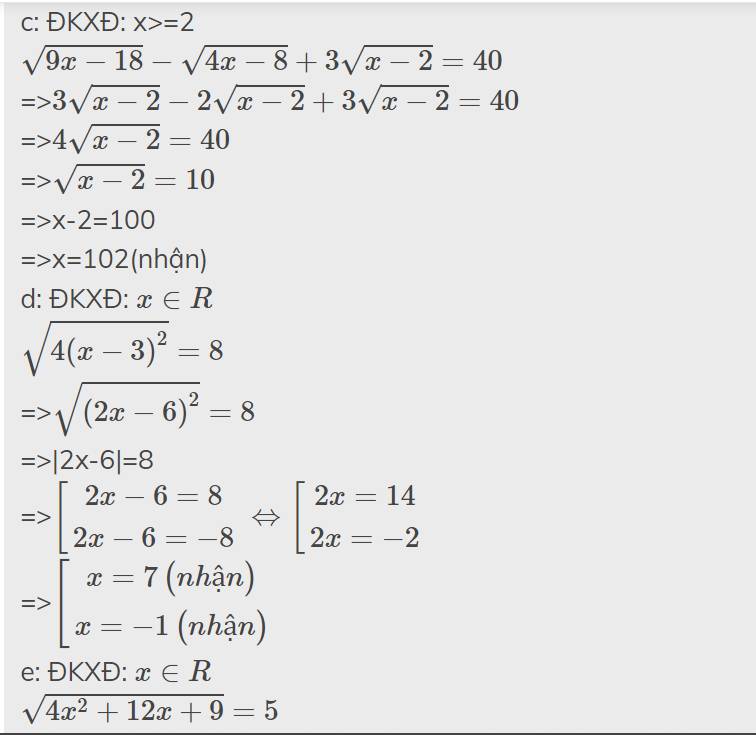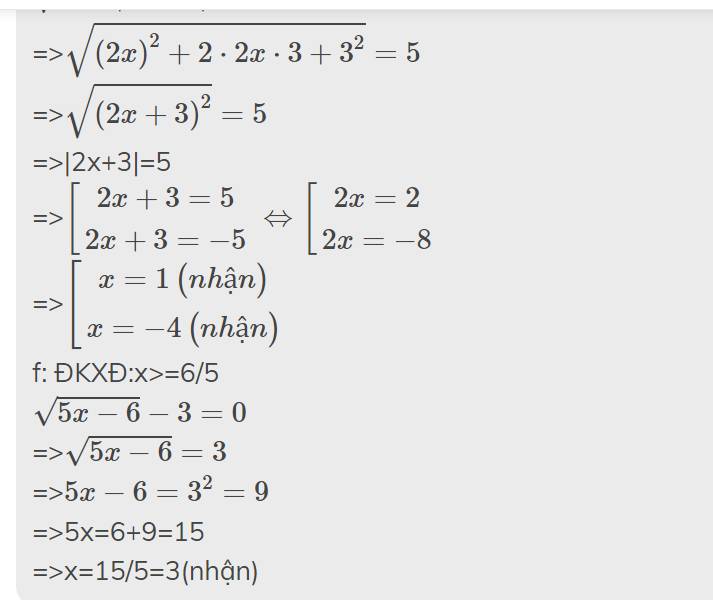giải phương trình\(x^3-2x^2-\sqrt{x^2-2x+5}=2\sqrt{4x-5}-5x-4\)
TN
Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải phương trình:
1. \(5x^2+2x+10=7\sqrt{x^4+4}\)
2. \(\dfrac{4}{x}+\sqrt{x-\dfrac{1}{x}}=x+\sqrt{2x-\dfrac{5}{x}}\)
3. \(\sqrt{x^2+2x}=\sqrt{3x^2+4x+1}-\sqrt{3x^2+4x+1}\)
Bài 1 GIẢI PHƯƠNG TRÌNH:
a) \(\sqrt{x-5}=\sqrt{3-x}\)
b) \(\sqrt{4-5x}=\sqrt{2-5x}\)
c) x2+4x+5=2\(\sqrt{2x+3}\)
d) \(\sqrt{x^2-2x+1}=\sqrt{4x^2-4x+1}\)
\(a,ĐK:\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge5\\x\le3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm
\(b,ĐK:x\le\dfrac{2}{5}\\ PT\Leftrightarrow4-5x=2-5x\\ \Leftrightarrow0x=2\Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\)
\(c,ĐK:x\ge-\dfrac{3}{2}\\ PT\Leftrightarrow x^2+4x+5-2\sqrt{2x+3}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3-2\sqrt{2x+3}+1\right)+\left(x^2+2x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{2x+3}-1\right)^2+\left(x+1\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+3=1\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=-1\left(tm\right)\\ d,PT\Leftrightarrow\left|x-1\right|=\left|2x-1\right|\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=2x-1\\x-1=1-2x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a) \(\sqrt{x-5}=\sqrt{3-x}\)
⇔\(\left(\sqrt{x-5}\right)^2=\left(\sqrt{3-x}\right)^2\)
⇔\(x-5=3-x\)
⇔\(x=4\)
b) \(\sqrt{4-5x}=\sqrt{2-5x}\)
⇔\(\left(\sqrt{4-5x}\right)^2=\left(\sqrt{2-5x}\right)^2\)
⇔\(4-5x=2-5x\)
⇔\(2=0\) (Vô lí)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải bất phương trình sau : a/ 2x ^ 2 + 6x - 8 < 0 x ^ 2 + 5x + 4 >=\ 2) Giải phương trình sau : a/ sqrt(2x ^ 2 - 4x - 2) = sqrt(x ^ 2 - x - 2) c/ sqrt(2x ^ 2 - 4x + 2) = sqrt(x ^ 2 - x - 3) b/ x ^ 2 + 5x + 4 < 0 d/ 2x ^ 2 + 6x - 8 > 0 b/ sqrt(- x ^ 2 - 5x + 2) = sqrt(x ^ 2 - 2x - 3) d/ sqrt(- x ^ 2 + 6x - 4) = sqrt(x ^ 2 - 2x - 7)
2:
a: =>2x^2-4x-2=x^2-x-2
=>x^2-3x=0
=>x=0(loại) hoặc x=3
b: =>(x+1)(x+4)<0
=>-4<x<-1
d: =>x^2-2x-7=-x^2+6x-4
=>2x^2-8x-3=0
=>\(x=\dfrac{4\pm\sqrt{22}}{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình:
a) \(\sqrt{4x^2+4x+3}=8\)
b) \(\sqrt{5x^3+5x^2+7}=9\)
c) \(\dfrac{3}{5}\sqrt{x^5+4x^3+2x^2}=18\)
a: Ta có: \(\sqrt{4x^2+4x+3}=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+4x+1+2-64=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+4x-61=0\)
\(\Delta=4^2-4\cdot4\cdot\left(-61\right)=992\)
Vì Δ>0 nên phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-4-4\sqrt{62}}{8}=\dfrac{-1-\sqrt{62}}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{-4+4\sqrt{62}}{8}=\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{62}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
1) Giải hệ phương trìnhleft{{}begin{matrix}3x^2+xy-4x+2y2xleft(x+1right)+yleft(y+1right)4end{matrix}right.2) Giải phương trìnhsqrt{x^2-5x+4}+2sqrt{x+5}2sqrt{x-4}+sqrt{x^2+4x-5}3) Tính giá trị của biểu thứcA2x^3+3x^2-4x+2Với xsqrt{2+sqrt{dfrac{5+sqrt{5}}{2}}}+sqrt{2-sqrt{dfrac{5+sqrt{5}}{2}}}-sqrt{3-sqrt{5}}-14) Cho x, y thỏa mãn:sqrt{x+2014}+sqrt{2015-x}-sqrt{2014-x}sqrt{y+2014}+sqrt{2015-y}-sqrt{2014-y}Chứng minh xy
Đọc tiếp
1) Giải hệ phương trình
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x^2+xy-4x+2y=2\\x\left(x+1\right)+y\left(y+1\right)=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
2) Giải phương trình
\(\sqrt{x^2-5x+4}+2\sqrt{x+5}=2\sqrt{x-4}+\sqrt{x^2+4x-5}\)
3) Tính giá trị của biểu thức
\(A=2x^3+3x^2-4x+2\)
Với \(x=\sqrt{2+\sqrt{\dfrac{5+\sqrt{5}}{2}}}+\sqrt{2-\sqrt{\dfrac{5+\sqrt{5}}{2}}}-\sqrt{3-\sqrt{5}}-1\)
4) Cho x, y thỏa mãn:
\(\sqrt{x+2014}+\sqrt{2015-x}-\sqrt{2014-x}=\sqrt{y+2014}+\sqrt{2015-y}-\sqrt{2014-y}\)
Chứng minh \(x=y\)
Câu 4:
Giả sử điều cần chứng minh là đúng
\(\Rightarrow x=y\), thay vào điều kiện ở đề bài, ta được:
\(\sqrt{x+2014}+\sqrt{2015-x}-\sqrt{2014-x}=\sqrt{x+2014}+\sqrt{2015-x}-\sqrt{2014-x}\) (luôn đúng)
Vậy điều cần chứng minh là đúng
Đúng 7
Bình luận (3)
2) \(\sqrt{x^2-5x+4}+2\sqrt{x+5}=2\sqrt{x-4}+\sqrt{x^2+4x-5}\)
⇔ \(\sqrt{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-1\right)}-2\sqrt{x-4}+2\sqrt{x+5}-\sqrt{\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}=0\)
⇔ \(\sqrt{x-4}.\left(\sqrt{x-1}-2\right)-\sqrt{x+5}\left(\sqrt{x-1}-2\right)=0\)
⇔ \(\left(\sqrt{x-4}-\sqrt{x+5}\right)\left(\sqrt{x-1}-2\right)=0\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-4}-\sqrt{x+5}=0\\\sqrt{x-1}-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-4}=\sqrt{x+5}\\\sqrt{x-1}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\in\varnothing\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ x = 5
Vậy S = {5}
Đúng 4
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1:
ĐKĐB suy ra $x(x+1)+y(y+1)=3x^2+xy-4x+2y+2$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2+x(y-5)+(y-y^2+2)=0$
Coi đây là PT bậc 2 ẩn $x$
$\Delta=(y-5)^2-4(y-y^2+2)=(3y-3)^2$Do đó:
$x=\frac{y+1}{2}$ hoặc $x=2-y$. Thay vào một trong 2 phương trình ban đầu ta thu được:
$(x,y)=(\frac{-4}{5}, \frac{-13}{5}); (1,1)$
Đúng 4
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) \(\sqrt {3{x^2} - 4x - 1} = \sqrt {2{x^2} - 4x + 3} \)
b) \(\sqrt {{x^2} + 2x - 3} = \sqrt { - 2{x^2} + 5} \)
c) \(\sqrt {2{x^2} + 3x - 3} = \sqrt { - {x^2} - x + 1} \)
d) \(\sqrt { - {x^2} + 5x - 4} = \sqrt { - 2{x^2} + 4x + 2} \)
a) \(\sqrt {3{x^2} - 4x - 1} = \sqrt {2{x^2} - 4x + 3} \)
Bình phương hai vế của phương trình ta được:
\(\begin{array}{l}3{x^2} - 4x - 1 = 2{x^2} - 4x + 3\\ \Leftrightarrow {x^2} = 4\end{array}\)
\( \Leftrightarrow x = 2\) hoặc \(x = - 2\)
Thay lần lượt các giá trị này vào phương trình đã cho, ta thấy cả 2 giá trị x=2; x=-2 thỏa mãn
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(S = \left\{ { - 2;2} \right\}\)
b) \(\sqrt {{x^2} + 2x - 3} = \sqrt { - 2{x^2} + 5} \)
Bình phương hai vế của phương trình ta được:
\(\begin{array}{l}{x^2} + 2x - 3 = - 2{x^2} + 5\\ \Leftrightarrow 3{x^2} + 2x - 8 = 0\end{array}\)
\( \Leftrightarrow x = - 2\) hoặc \(x = \frac{4}{3}\)
Thay lần lượt các giá trị này vào phương trình đã cho, ta thấy chỉ có giá trị \(x = \frac{4}{3}\) thỏa mãn
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(x = \frac{4}{3}\)
c) \(\sqrt {2{x^2} + 3x - 3} = \sqrt { - {x^2} - x + 1} \)
Bình phương hai vế của phương trình ta được:
\(\begin{array}{l}2{x^2} + 3x - 3 = - {x^2} - x + 1\\ \Leftrightarrow 3{x^2} + 4x - 4\end{array}\)
\( \Leftrightarrow x = - 2\) hoặc \(x = \frac{2}{3}\)
Thay lần lượt các giá trị này vào phương trình đã cho, ta thấy cả 2 giá trị đều không thỏa mãn.
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm
d) \(\sqrt { - {x^2} + 5x - 4} = \sqrt { - 2{x^2} + 4x + 2} \)
Bình phương hai vế của phương trình ta được:
\(\begin{array}{l} - {x^2} + 5x - 4 = - 2{x^2} + 4x + 2\\ \Leftrightarrow {x^2} + x - 6 = 0\end{array}\)
\( \Leftrightarrow x = - 3\) hoặc \(x = 2\)
Thay lần lượt các giá trị này vào phương trình đã cho, ta thấy x=2 thỏa mãn.
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là x = 2.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình
a, \(\sqrt{x^2+2x}+\sqrt{2x-1}=\sqrt{3x^2+4x+1}\)
b, \(\sqrt{5x^2+14x+9}-\sqrt{x^2-x-20}=5\sqrt{x+1}\)
a. ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2+2x}=a>0\\\sqrt{2x-1}=b\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow a+b=\sqrt{3a^2-b^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a+b\right)^2=3a^2-b^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2-ab-b^2=0\Leftrightarrow\left(a-\dfrac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}b\right)\left(a+\dfrac{\sqrt{5}-1}{2}b\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}b\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2+2x}=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\sqrt{2x-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2}\left(2x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-\left(\sqrt{5}+1\right)x+\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{\sqrt{5}+1}{2}\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}+1}{2}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
b. ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{5x^2+14x+9}=\sqrt{x^2-x-20}+5\sqrt{x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x^2+14x+9=x^2-x-20+25\left(x+1\right)+10\sqrt{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-5\right)\left(x+4\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-5x+2=5\sqrt{\left(x^2-4x-5\right)\left(x+4\right)}\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2-4x-5}=a\ge0\\\sqrt{x+4}=b>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow2a^2+3b^2=5ab\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-b\right)\left(2a-3b\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2-4x-5}=\sqrt{x+4}\\2\sqrt{x^2-4x-5}=3\sqrt{x+4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-4x-5=x+4\\4\left(x^2-4x-5\right)=9\left(x+4\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải Phương Trình
\(\sqrt{\left(2x+3\right)^2}=5\)
\(\sqrt{9\left(x-2\right)^2}=18\)
\(\sqrt{9x-18}-\sqrt{4x-8}+3\sqrt{x-2}=40\)
\(\sqrt{4.\left(x-3\right)^2}=8\)
\(\sqrt{5x-6}-3=0\)
giải phương trình :
a, \(\dfrac{4x-1}{\sqrt{4x-3}}+\dfrac{11-2x}{\sqrt{5-x}}=\dfrac{15}{2}\)
b, \(\left(\sqrt{5x-1}+\sqrt{x-1}\right)\left(3x-1-\sqrt{5x^2-6x+1}\right)=4x\)