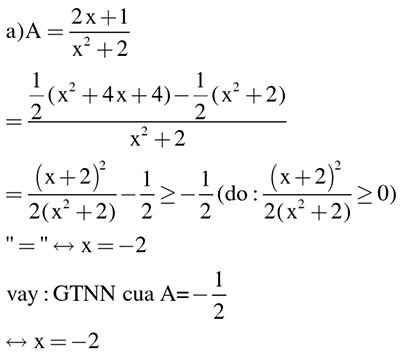Tìm gtnn và gtln của A=2x+1/x^2+2
AP
Những câu hỏi liên quan
a, Tìm GTNN: A = \(\dfrac{x^2-2x+2013}{x^2}\) ; x>0
b, Tìm GTLN và GTNN của: B = \(\dfrac{4x+1}{4x^2+2}\)
a.
\(A=\dfrac{2013}{x^2}-\dfrac{2}{x}+1=2013\left(\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{2013}\right)^2+\dfrac{2012}{2013}\ge\dfrac{2012}{2013}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(x=2013\)
b.
\(B=\dfrac{4x^2+2-4x^2+4x-1}{4x^2+2}=1-\dfrac{\left(2x-1\right)^2}{4x^2+2}\le1\)
\(B_{max}=1\) khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(B=\dfrac{-2x^2-1+2x^2+4x+2}{4x^2+2}=-\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{2x^2+1}\ge-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(B_{max}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\) khi \(x=-1\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Tìm GTLN của Q=\(-2x^2+6x+8\)
Tìm GTLN và GTNN của: A=\(\dfrac{6x+17}{x^2+2}\)
\(Q=-2\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{25}{2}\le\dfrac{25}{2}\)
\(Q_{max}=\dfrac{25}{2}\) khi \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(A=\dfrac{9\left(x^2+2\right)-9x^2+6x-1}{x^2+2}=9-\dfrac{\left(3x-1\right)^2}{x^2+2}\le9\)
\(A_{max}=9\) khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(A=\dfrac{12x+34}{2\left(x^2+2\right)}=\dfrac{-\left(x^2+2\right)+x^2+12x+36}{2\left(x^2+2\right)}=-\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{\left(x+6\right)^2}{2\left(x^2+2\right)}\le-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(A_{min}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\) khi \(x=-6\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm GTNN và GTLN nếu có của các biểu thức
\(A=\dfrac{2x^2-2x+5}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(B=\dfrac{4x^2+x+4}{x^2+x+1}\)
Biểu thức nào em?
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
Tìm GTNN và GTLN của biểu thức P=(2x+1)/(x^2+2)
Nháp:
\(P=\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+2}\) \(\Leftrightarrow P\left(x^2+2\right)=2x+1\) \(\Leftrightarrow Px^2-2x+2P-1=0\) (*)
*Cần chú ý: Với bất kì đa thức bậc hai \(f\left(x\right)=ax^2+bx+c\) nào, muốn \(f\left(x\right)\) có nghiệm thì \(b^2-4ac\ge0\) (Mình không chứng minh ở đây nhé, bạn chỉ cần nhớ để nháp là đủ rồi.)
Do đó để (*) có nghiệm thì \(\left(-2\right)^2-4P\left(2P+1\right)\ge0\) \(\Leftrightarrow4-8P^2+4P\ge0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(2P+1\right)\left(1-P\right)\ge0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-1}{2}\le P\le1\)
\(P=-\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=-2\), \(P=1\Leftrightarrow x=1\).
Ý tưởng:
Từ thông tin ở phần nháp, ta sẽ đưa tử của phân thức P về dạng chứa \(\left(x+2\right)^2\) và \(-\left(x-1\right)^2\) vì P đạt min tại \(x=-2\) và max tại \(x=1\), rồi tìm cách biến đổi các số hạng bên ngoài để ra dạng \(kA^2+c\) (\(k,c\) là các hằng số)
Trình bày:
\(P=\dfrac{-x^2+2x-1+x^2+2}{x^2+2}=\dfrac{-\left(x-1\right)^2}{x^2+2}+1\)
Dễ thấy \(-\left(x-1\right)^2\le0\), \(x^2+2>0\) nên \(\dfrac{-\left(x-1\right)^2}{x^2+2}\le0\) \(\Leftrightarrow P\le1\).
ĐTXR \(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Mặt khác, \(P=\dfrac{\dfrac{x^2}{2}+2x+2-\dfrac{x^2}{2}-1}{x^2+2}\)\(=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}\left(x+2\right)^2-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(x^2+2\right)}{x^2+2}\) \(=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{2\left(x^2+2\right)}-\dfrac{1}{2}\). Do \(\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{x^2+2}\ge0\) \(\Leftrightarrow P\ge-\dfrac{1}{2}\). ĐTXR \(\Leftrightarrow x=-2\).
Vậy GTNN, GTLN của P lần lượt là \(-\dfrac{1}{2};1\), lần lượt xảy ra khi \(x=-2;x=1\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Lời giải:
$P=\frac{2x+1}{x^2+2}$
$\Rightarrow P(x^2+2)=2x+1$
$\Rightarrow Px^2-2x+(2P-1)=0(*)$
Vì $P$ tồn tại nên PT $(*)$ có nghiệm.
$\Rightarrow \Delta'=1-P(2P-1)\geq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2P^2-P-1\leq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow (P-1)(2P+1)\leq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{-1}{2}\leq P\leq 1$
Vậy $P_{\min}=\frac{-1}{2}$ và $P_{\max}=1$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm GTNN hoặc GTLN của:
a) A=|2x-1|-4 (GTLN)
b) B = 1,5-|2-x| (GTLN)
c) C = |x-3|(GTNN)
d)D = 10-4|x-2|(GTLN)
a) Sửa đề: Tìm GTNN
A = |2x - 1| - 4
Ta có:
|2x - 1| ≥ 0 với mọi x ∈ R
⇒ |2x - 1| - 4 ≥ -4 với mọi x ∈ R
Vậy GTNN của A là -4 khi x = 1/2
b) B = 1,5 - |2 - x|
Ta có:
|2 - x| ≥ 0 với mọi x ∈ R
⇒ -|2 - x| ≤ 0 với mọi x ∈ R
⇒ 1,5 - |2 - x| ≤ 1,5 với mọi x ∈ R
Vậy GTLN của B là 1,5 khi x = 2
c) C = |x - 3| ≥ 0 với mọi x ∈ R
Vậy GTNM của C là 0 khi x = 3
d) D = 10 - 4|x - 2|
Ta có:
|x - 2| ≥ 0 với mọi x ∈ R
⇒ 4|x - 2| ≥ 0 với mọi x ∈ R
⇒ -4|x - 2| ≤ 0 với mọi x ∈ R
⇒ 10 - 4|x - 2| ≤ 10 với mọi x ∈ R
Vậy GTLN của D là 10 khi x = 2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm GTLN và GTNN của biểu thức sau : 4x+1/ x^2+2x+2
là \(4x+\dfrac{1}{x^2}+2x+2\) hay là \(\dfrac{4x+1}{x^2+2x+2}\) cái neog:0
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
\(P=\dfrac{4x+1}{x^2+2x+2}=\dfrac{x^2+2x+2-x^2+2x-1}{x^2+2x+2}=1-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{x^2+2x+2}\le1\)
"=" xảy ra <=> x - 1 = 0 <=> x = 1
Vậy Max P = 1 <=> x = 1
P = \(\dfrac{4x+1}{x^2+2x+2}=\dfrac{-4x^2-8x-8+4x^2+12x+9}{x^2+2x+2}=-4+\dfrac{\left(2x+3\right)^2}{x^2+2x+2}\)
\(\ge-4\)
"=" xảy ra <=> 2x + 3 = 0 <=> x = -1,5
Vậy Min P = -4 <=> x = -1,5
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
tìm gtln và gtnn của biểu thức p=(x^2-2x-2)/(x^2+x+1)
\(P=\dfrac{x^2-2x-2}{x^2+x+1}=\dfrac{2\left(x^2+x+1\right)-\left(x^2+4x+4\right)}{x^2+x+1}=2-\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}}\le2\)
\(P_{max}=2\) khi \(x=-2\)
\(P=\dfrac{x^2-2x-2}{x^2+x+1}=\dfrac{-2\left(x^2+x+1\right)+3x^2}{x^2+x+1}=-2+\dfrac{3x^2}{\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}}\ge-2\)
\(P_{min}=-2\) khi \(x=0\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Dự đoán: $Px^2+Px +P-x^2+2x+2=0\\\to x^2(P-1) +x(P+2)+(P+2)=0$ $\Delta =(P+2)^2-4(P-1)(P+2)=(P+2)(P+2-4P+4)=(P+2)(6-3P)\ge 0$ giải BPT Ta được: $-2\le P \le 2$ $\to P_{min}=-2,P_{max}=2$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm GTNN và GTLN của :
D= 2x +1 / x^2 +2
Tìm GTLN GTNN của A=\(\dfrac{\text{ 2x+1}}{\text{x^2+2 }}\)
\(A=\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow Ax^{2\:}+2A=2x+1\)
+) \(A=0\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
+) \(A\ne0\)
\(Ax^2+2A=2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow Ax^{2\:}-2x=1-2A\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2.\dfrac{x}{A}=\dfrac{1-2A}{A}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2.x.\dfrac{1}{A}+\dfrac{1}{A^2}=\dfrac{1-2A}{A}+\dfrac{1}{A^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{1}{A}\right)^2=\dfrac{A-2A^2+1}{A^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{1}{A}\right)^2=\dfrac{\left(1-A\right)\left(2A+1\right)}{A^2}\)
Vì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-\dfrac{1}{A}\right)^2\ge0\left(\forall x,A\ne0\right)\\A^2\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇒ \(\left(1-A\right)\left(2A+1\right)\ge0\)
⇒ \(-\dfrac{1}{2}\le A\le1\)
Còn lại tụ làm nha
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
\(A=\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+2}=\dfrac{x^2+2-x^2-2+2x+1}{x^2+2}\\ =1-\dfrac{-\left(x-1\right)^2}{x^2+2}\\ Do\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\Rightarrow\dfrac{-\left(x-1\right)^2}{x^2+2}\ge0\\ \Rightarrow\dfrac{-\left(x-1\right)^2}{x^2+2}=0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-\left(x-1\right)^2}{x^2+2}+1\le1\)
\(Dấu"="\Leftrightarrow A=1\\ \Leftrightarrow x-1=0\Rightarrow x=1\\ Vậy.P_{max}=1.khi.x=1\\ A=\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+2}\rightarrow2A+1=\dfrac{2.\left(2x+1\right)}{x^2+2}+1\\ =\dfrac{4x+2+x^2+2}{x^2+2}=\dfrac{x^2+4x+2}{x^2+2}=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{x^2+2}\\ Do\left(x+2\right)^2\ge0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{x^2+2}\ge0\)
\(Dấu"="\Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{1}{2}khi.x=-2\\ \Rightarrow2A+1\ge0\Rightarrow2A\ge-1\Rightarrow A>-\dfrac{1}{2}\\ Vậy.MinA=-\dfrac{1}{2}.khi.x=-2\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1. tìm GTNN của A= x(x+2)(x+4)(x+6)+8
2. tìm GTLN của B=5+(1-x)(x+2)(x+3)(x+6)3
3.tìm GTNN của C=(x+3)4 + (x-7)4
4. Cho x>0. Tìm GTNN của P=\(\dfrac{4x^2+1}{2x}\)
1.
$x(x+2)(x+4)(x+6)+8$
$=x(x+6)(x+2)(x+4)+8=(x^2+6x)(x^2+6x+8)+8$
$=a(a+8)+8$ (đặt $x^2+6x=a$)
$=a^2+8a+8=(a+4)^2-8=(x^2+6x+4)^2-8\geq -8$
Vậy $A_{\min}=-8$ khi $x^2+6x+4=0\Leftrightarrow x=-3\pm \sqrt{5}$
Đúng 4
Bình luận (0)
2.
$B=5+(1-x)(x+2)(x+3)(x+6)=5-(x-1)(x+6)(x+2)(x+3)$
$=5-(x^2+5x-6)(x^2+5x+6)$
$=5-[(x^2+5x)^2-6^2]$
$=41-(x^2+5x)^2\leq 41$
Vậy $B_{\max}=41$. Giá trị này đạt tại $x^2+5x=0\Leftrightarrow x=0$ hoặc $x=-5$
Đúng 4
Bình luận (0)
3.
Đặt $x+3=a; 7-x=b$ thì $a+b=10$
$C=a^4+b^4$
Áp dụng BĐT Bunhiacopxky:
$(a^4+b^4)(1+1)\geq (a^2+b^2)^2$
$\Rightarrow C\geq \frac{(a^2+b^2)^2}{2}$
$(a^2+b^2)(1+1)\geq (a+b)^2=100$
$\Rightarrow a^2+b^2\geq 50$
$\Rightarrow C\geq \frac{50^2}{2}=1250$
Vậy $C_{\min}=1250$
Giá trị này đạt tại $a=b=5\Leftrightarrow x=2$
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời