x2-2x-8
Thực hiện phép tính:
a)x2/2x-10 + 25-10x/2x-10
b)2x/x2+2x + -8/x2-4 + 2/x-2
c,
\(\dfrac{x^2}{2x-10}+\dfrac{25-10x}{2x-10}\\ =\dfrac{x^2-10x+5^2}{2\left(x-5\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-5\right)\left(x-5\right)}{2\left(x-5\right)}\\ =\dfrac{x-5}{2}\)
d,
\(=\dfrac{2x}{x\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{8}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{2}{x-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2-4x}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{8x}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{2x^2+4x}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2-4x-8x+2x^2+4x}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{4x^2-8x}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x\left(x-2\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{4x}{x\left(x+2\right)}\)
Hãy giải các phương trình sau đây :
1, x2 - 4x + 4 = 0
2, 2x - y = 5
3, x + 5y = - 3
4, x2 - 2x - 8 = 0
5, 6x2 - 5x - 6 = 0
6,( x2 - 2x )2 - 6 (x2 - 2x ) + 5 = 0
7, x2 - 20x + 96 = 0
8, 2x - y = 3
9, 3x + 2y = 8
10, 2x2 + 5x - 3 = 0
11, 3x - 6 = 0
1) Ta có: \(x^2-4x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2=0\)
hay x=2
Vậy: S={2}
Tìm x, biết
b) x2 - 2x + 1 = 4
c) x2 - 4x + 4 = 9
d) 4x2 - 4x + 1 = 4
e) x2 - 2x - 8 = 0
f) 9x2 - 6x - 8 = 0
b)x2-2x+1=4
⇔(x-1)2=4
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=2\\x-1=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
c)x2-4x+4=9
⇔ (x-2)2=9
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=3\\x-2=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
d)4x2-4x+1=4
⇔ (2x-1)2=4
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=4\\2x-1=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=\dfrac{-3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
e)x2-2x-8=0
⇔ x2-4x+2x-8=0
⇔ x(x-4)+2(x-4)=0
⇔(x-4)(x+2)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
f)9x2-6x-8=0
⇔ 9x2-12x+6x-8=0
⇔ 3x(3x-4)+2(3x-4)=0
⇔ (3x-4)(3x+2)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{4}{3}\\x=\dfrac{-2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thực hiện phép tính: (x3 – 8) : (x – 2)
A. x2 + 2 B. x2 – 2x + 4
C. x2 – 4 D. x3 + 2x + 4
Tìm x
1. x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
2. (x + 4)2 - (3x - 1)2 = 0
3, x2 - 2x + 24 = 0
4, 9x2 - 4 = 0
5, x2 + 2x - 8 = 0
1.
\(x^2-5x+6=0\\ \Rightarrow x^2-2x-3x+6=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x^2-2x\right)-\left(3x-6\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow x\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x-2\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
2.
\(\left(x+4\right)^2-\left(3x-1\right)^2=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x+4-3x+1\right)\left(x+4+3x-1\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(-2x+5\right)\left(4x+3\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-2x+5=0\\4x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{3}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
3.
\(x^2-2x+24=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+23=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2+23=0\)
Vì (x-1)2≥0
23>0
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2+23>0\)
Vậy x vô nghiệm
4.
\(9x^2-4=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(3x-4\right)\left(3x+4\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-4=0\\3x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{4}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
5.
\(x^2+2x-8=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x^2+2x+1\right)-9=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2-3^2=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tìm giá trị nguyên lớn nhất của m để: x 2 - 2 x - 3 + 8 + 2 x - x 2 > m , ( * ) có nghiệm
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Điều kiện: 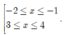
Đặt t= x2- 2x; t’ = 2x- 2 và t’ =0 khi x= 1.
Bảng biến thiên
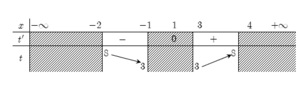
Dựa vào bảng biến thiên suy ra tập giá trị của t là [ 3; 8].
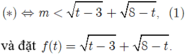
Để (* ) có nghiệm khi và chỉ khi ( 1) có nghiệm
![]()
Xét hàm số
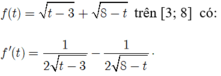
Cho f’ (t) =0 khi nên
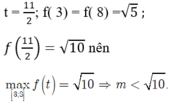
Vậy m ∈ (-∞; √10) sẽ thỏa mãn yêu cầu bài toán.
Chọn D.
a, -x2 + 2x + 3
b, x2 - 2x + 4y2 - 4y + 8 c, -x2 - y2 + xy + 2x + 2y + 4 d, x2 + 5y2 - 4xy - 2y + 2015 e, 2x2 + y2 + 6x + 2y + 2xy + 2018A= -x2+2x+3
=>A= -(x2-2x+3)
=>A= -(x2-2.x.1+1+3-1)
=>A=-[(x-1)2+2]
=>A= -(x+1)2-2
Vì -(x+1)2 ≤0=> A≤-2
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi
-(x+1)2=0 => x=-1
Vây A lớn nhất= -2 khi x= -1
B=x2-2x+4y2-4y+8
=> B= (x2-2x+1)+(4y2-4y+1)+6
=> B=(x-1)2+(2y+1)2+6
=> B lớn nhất=6 khi x=1 và y=-1/2
Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a) x 2 +2x-8; b) x 2 +5x + 6;
c) 4 x 2 -12x + 8; d) 3 x 2 +8xy + 5 y 2 .
Sử dụng hằng đẳng thức để thực hiện phép chia:
a) ( x 2 - 2x + l) :(x - 1);
b) (8 x 3 +27): (2x + 3);
c) ( x 6 - 6 x 4 + 12 x 2 - 8): (2 - x 2 ).
a) Biến đổi x 2 – 2x + 1 = ( x – 1 ) 2 ; thực hiện chia được kết quả x – 1.
b) Biến đổi 8 x 3 + 27 = (2x + 3)(4 x 2 – 6x + 9); thực hiện phép chia được kết quả 4 x 2 – 6x + 9.
c) Phân thích x 6 – 6 x 4 + 12 x 2 – 8 = ( x 2 – 2)( x 4 – 4 x 2 + 4); thực hiện phép chia được kết quả - x 4 + 4 x 2 – 4.
1) x3-x2+2x-2 4) ax-2x-a2+2a 7) x2-6xy-25z2+9y2
2) x2-y2+2x+2y 5) 2xy +3z+6y+xz 8) x3-2x2+x
3) x2/4+2xy+4y2-25 6) x2y2+yz+y3+zx2 9) x4+4