
Giúp mình câu:
Hãy giải bất phương trình sau: 2x2 + x - 3 > 0, 3x2 - 4x + 1 > 0

Giúp vs ạ
Bài 1 giải các bất phương trình sau
a.x2 - x - 6 = 0
b.2x2 - 7x + 5 < 0
c.3x2 - 9x + 6 ≥ 0
d.2x2 - 5x + 3 < 0
Bài 2 Giải phương trình sau
A.√x2 + x + 5 = √2x2 - 4x + 1
B.√11x2 -14x - 12 = √3x2 + 4x - 7
Bài 2:
a: =>2x^2-4x+1=x^2+x+5
=>x^2-5x-4=0
=>\(x=\dfrac{5\pm\sqrt{41}}{2}\)
b: =>11x^2-14x-12=3x^2+4x-7
=>8x^2-18x-5=0
=>x=5/2 hoặc x=-1/4
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 5 − 2 x 2 + 4 x − 10 = 8 ;
b) x 2 + 2 x + 3 x 2 + 2 x + 1 = 3 ;
c) x x − 1 x 2 − x + 1 − 6 = 0 .
Giải phương trình bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích :
3x2 + 2x - 1 = 0
x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
3x2 + 7x + 2 = 0
x2 - 4x + 1 = 0
2x2 - 6x + 1 = 0
3x2 + 4x - 4 = 0
3x2 + 2x - 1 = 0
=> 3x2 + 3x - x - 1 = 0
=> 3x(x + 1) - (x + 1) = 0
=> (3x - 1)(x + 1) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-1=0\\x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{3}\\x=-1\end{cases}}\)
x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
=> x2 - 2x - 3x + 6 = 0
=> x(x - 2) - 3(x - 2) = 0
=> (x - 3)(x - 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
3x2 + 7x + 2 = 0
=> 3x2 + 6x + x + 2 = 0
=> 3x(x + 2) + (x + 2) = 0
=> (3x + 1)(x + 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x+1=0\\x+2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{1}{3}\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)
1, \(3x^2+2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+3x-x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
2, \(x^2-5x+6=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\x-3=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=3\end{cases}}}\)
3, \(3x^2+7x+2=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+6x+x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+2\right)+\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+2=0\\3x+1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=-\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
\(x^2-4x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\sqrt{3}+2;x=2-\sqrt{3}\)
\(2x^2-6x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-12x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right)^2=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{\sqrt{7}+3}{2};x=\frac{3-\sqrt{7}}{2}\)
\(3x^2+4x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-2x+6x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2;x=\frac{2}{3}\)
Bài 7: Giải phương trình : a)( x- 2x + 3 ) ( 2x - x+6 ) =18
b) 3x3 + 6x2 –4x = 0
c) 3x2 – 5x = 0
d) – 2x2 + 8 = 0
a: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(-x+3\right)\left(x+6\right)=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^2-6x+3x+18-18=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x\left(x+3\right)=0\)
=>x=0 hoặc x=-3
b: \(\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x^2+6x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\3x^2+6x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x^2+2x-\dfrac{4}{3}=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\\left(x+1\right)^2=\dfrac{7}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{0;\dfrac{\sqrt{21}}{3}-1;\dfrac{-\sqrt{21}}{3}-1\right\}\)
c: =>x(3x-5)=0
=>x=0 hoặc x=5/3
d: =>(x-2)(x+2)=0
=>x=2 hoặc x=-2
Giải các phương trình sau bằng máy tính bỏ túi (làm tròn kết quả đến chữ số thập phân thứ ba)
a) 2x2 - 5x - 4 = 0 ; b) -3x2 + 4x + 2 = 0
c) 3x2 + 7x + 4 = 0 ; d) 9x2 - 6x - 4 = 0.
Giải phương trình bằng cách đặt ẩn phụ:
a ) 2 x 2 − 2 x 2 + 3 x 2 − 2 x + 1 = 0 b ) x + 1 x 2 − 4 ⋅ x + 1 x + 3 = 0
a) 2 x 2 − 2 x 2 + 3 x 2 − 2 x + 1 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 – 2 x = t ,
(1) trở thành : 2 t 2 + 3 t + 1 = 0 ( 2 ) .
Giải (2) :
Có a = 2 ; b = 3 ; c = 1
⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có nghiệm t 1 = - 1 ; t 2 = - c / a = - 1 / 2 .
+ Với t = -1 ⇒ x 2 − 2 x = − 1 ⇔ x 2 − 2 x + 1 = 0 ⇔ ( x − 1 ) 2 = 0 ⇔ x = 1
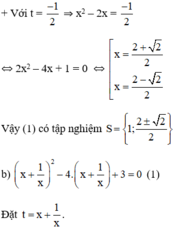
(1) trở thành: t 2 – 4 t + 3 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2):
Có a = 1; b = -4; c = 3
⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có nghiệm t 1 = 1 ; t 2 = c / a = 3 .
+ t = 1 ⇒ x + 1/x = 1 ⇔ x 2 + 1 = x ⇔ x 2 – x + 1 = 0
Có a = 1; b = -1; c = 1 ⇒ Δ = ( - 1 ) 2 – 4 . 1 . 1 = - 3 < 0
Phương trình vô nghiệm.

giải bất phương trình
a,-2x2+3x-7>0
b,3x2-4x+4
a) BPT \(\Leftrightarrow-2\left(x^2-\dfrac{3}{2}x+\dfrac{7}{2}\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2\left(x^2-2x\cdot\dfrac{3}{4}+\dfrac{9}{16}+\dfrac{47}{16}\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{47}{8}-2\left(x-\dfrac{3}{4}\right)^2>0\) (Vô lý)
b) Bạn xem lại đề !
Giải bất phương trình sau:
x 2 - x - 2 x 2 - x - 1 ≥ 0
A. 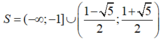
B. ![]()
C. 
D. 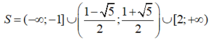
Chọn D
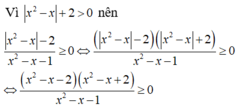
Bảng xét dấu
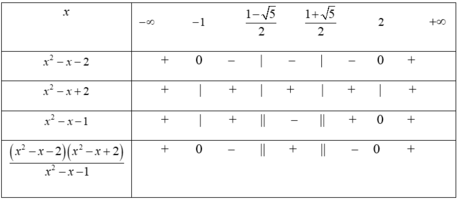
Dựa vào bảng xét dấu, ta có tập nghiệm của bất phương trình đã cho là
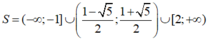
Giải các phương trình sau: 1) 4x2 - 9 = 0; 2) - 2x2 + 50 = 0;3) 3x2 + 11 = 0