Mng giúp mình bài 3.1 đc ko mik cảm ơn
H24
Những câu hỏi liên quan
Mọi ng cho mik hỏi bài 3.1 đc ko ạ mik cảm ơn 
Gọi CTHH của oxit sắt cần tìm là FexOy
Khử toàn bộ oxit sắt bằng khí CO ta có phương trình sau
(1)\(Fe_xO_y+yCO\underrightarrow{t^o}xFe+yCO_2\uparrow\)
\(\Rightarrow\)Hỗn hợp khí A là CO dư và CO2.Chất rắn B là Fe
Dẫn toàn bộ khí A vào dd Ca(OH)2 ta có phương trình sau:
\(\left(2\right)CO_2+Ca\left(OH\right)_2\rightarrow CaCO_3+H_2O\)
Đặt n\(CO_2\)=a(mol) ,theo (2)\(n_{CO_2}=n_{CaCO_3}=0,12\left(mol\right)\)
Ta có:\(m_{CaCO_3}-m_{CO_2}=100a-44a=6,72\left(g\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a=0,12\left(mol\right)\)
Ta lại có:\(n_{O\left(trõngoxit\right)}=n_{CO_2}=0,12\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m_{Fe}=m_{Fe_xO_y}-m_{O\left(trongoxit\right)}=6,96-0,12.16=5,04\left(g\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow n_{Fe}=\dfrac{5,04}{56}=0,09\left(mol\right)\)
Ta thấy \(n_{Fe}:n_O=0,09:0,12=3:4\)
\(\Rightarrow\)Oxit sắt cần tìm là Fe3O4
Cho chất rắn B và dd hỗn hơp hai muối AgNO3 và Cu(NO3)2 ta có các phương trình hóa học sau:
\(\left(3\right)Fe+2AgNO_3\rightarrow2Ag\downarrow+Fe\left(NO_3\right)_2\)
\(\left(4\right)Fe+Cu\left(NO_3\right)_2\rightarrow Cu\downarrow+Fe\left(NO_3\right)_2\)
Ta có:\(n_{AgNO_3}=1,2.0,1=0,12\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{Cu\left(NO_3\right)_2}=0,6.0,1=0,06\left(mol\right)\)
Giả sử Fe dư trong phản ứng (3) ta có
Theo\(\left(3\right)n_{Fe\left(3\right)}=\dfrac{1}{2}n_{AgNO_3}=0,06\left(mol\right)\)<\(0,09\left(mol\right)=n_{Fe\left(có\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow\)Giả sử đúng,\(n_{Fe\left(dư\right)}=0,09-0,06=0,03\left(mol\right)\)
Giả sử Fe hết trong phản ứng (4)
Theo(4)\(n_{Cu\left(NO_3\right)_2\left(4\right)}=n_{Fe\left(dư\right)}=0,03\left(mol\right)< 0,06\left(mol\right)=n_{Cu\left(NO_3\right)_2\left(có\right)}\)
⇒Giả sử đúng,m(g) chất rắn thu đc sau phản ứng gồm Ag và Cu
Theo(3)\(n_{Ag}=n_{AgNO_3}=0,12\left(mol\right)\)
Theo(4)\(n_{Cu}=n_{Cu\left(NO_3\right)_2\left(4\right)}=0,03\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow m=m_{Ag}+m_{Cu}=108.0,12+64.0,03=14,88\left(g\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Mng giải giúp mình bài này nha,mik đang cần gấp á!Mng giúp mình nhé!!Mik xin cảm ơn
Đọc tiếp


Mng giải giúp mình bài này nha,mik đang cần gấp á!![]()
Mng giúp mình nhé!!![]()
Mik xin cảm ơn![]()
IX
2. j
3. i
4. f
5. c
6. a
7. h
8. e
9. g
10. d
XI
2. part => parts
3. a => an
4. a => an
5. a => the
6. are => will be (không chắc lắm)
7. taking => take
8. are => is
C.
Bài 1
1. C
2. B
3. C
4. B
(Nên double-check trước khi chép)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Mng giúp mik vs bn của mik lm sai, các bạn có thể sửa lại và chọn đáp án đúng nhất đc ko ạ? Lm ơn giúp mik, cảm ơn.
Đọc tiếp
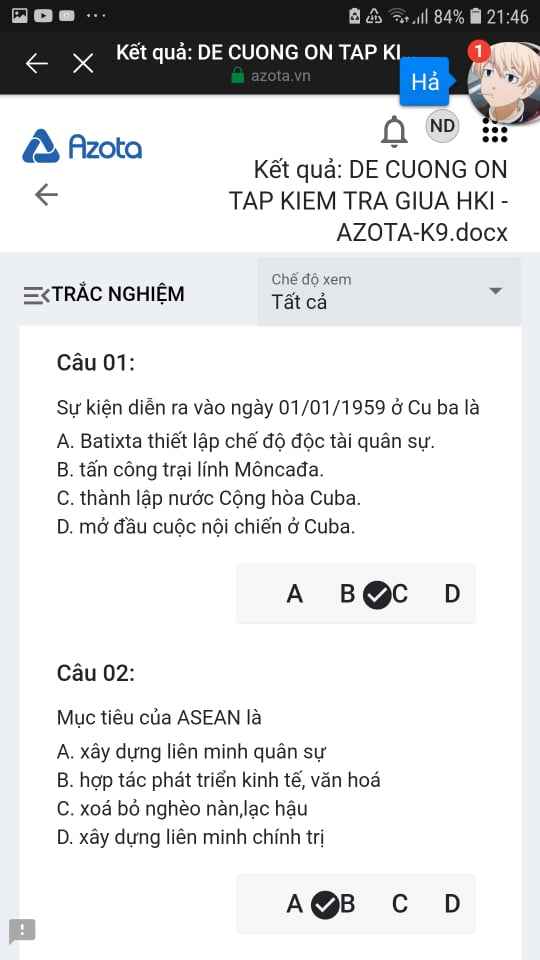
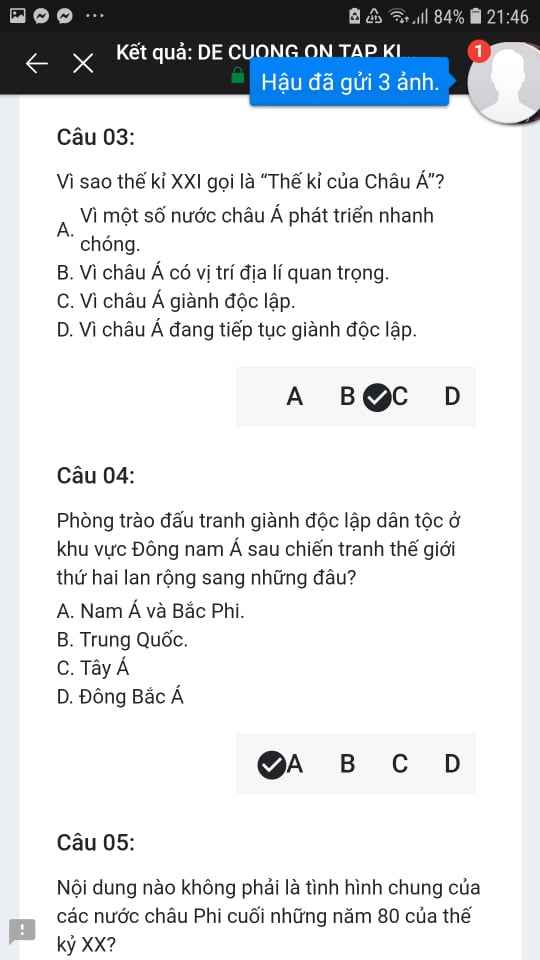
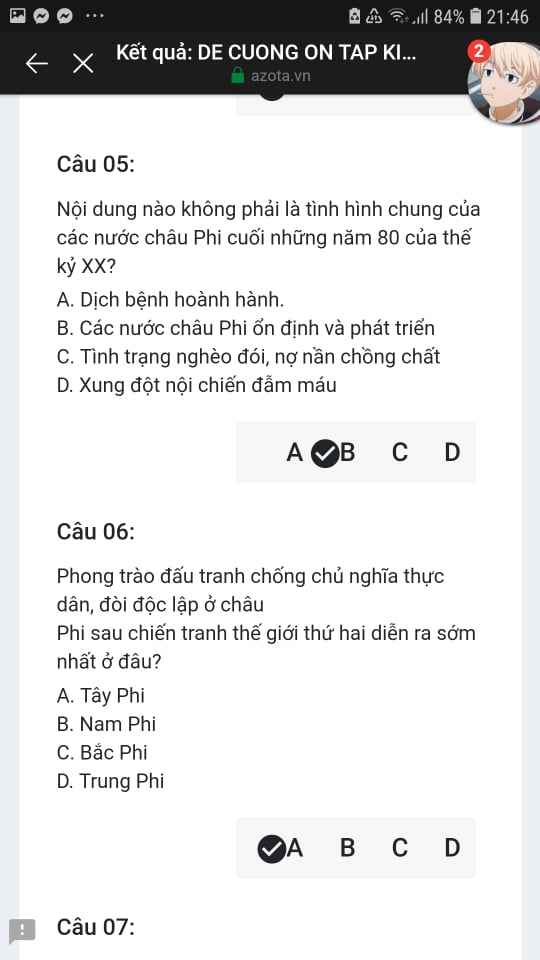
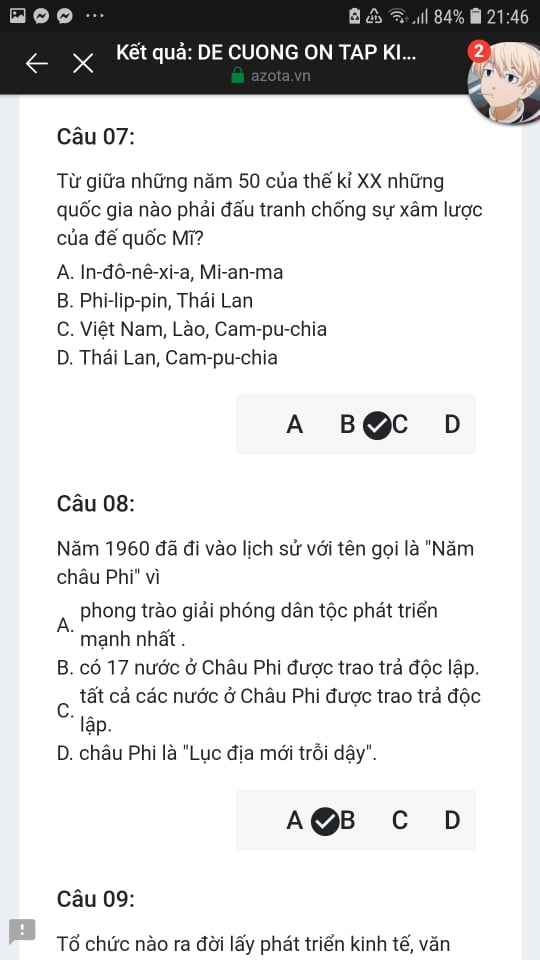

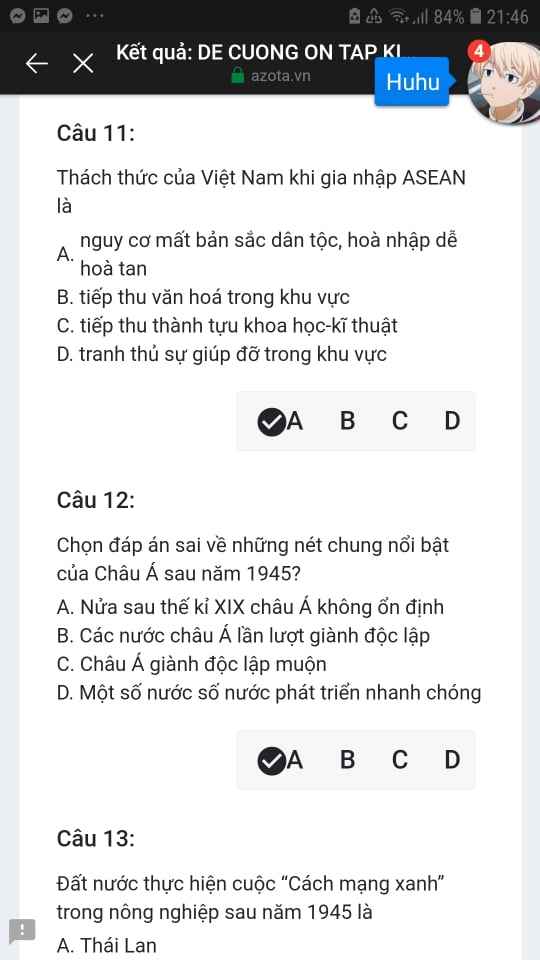
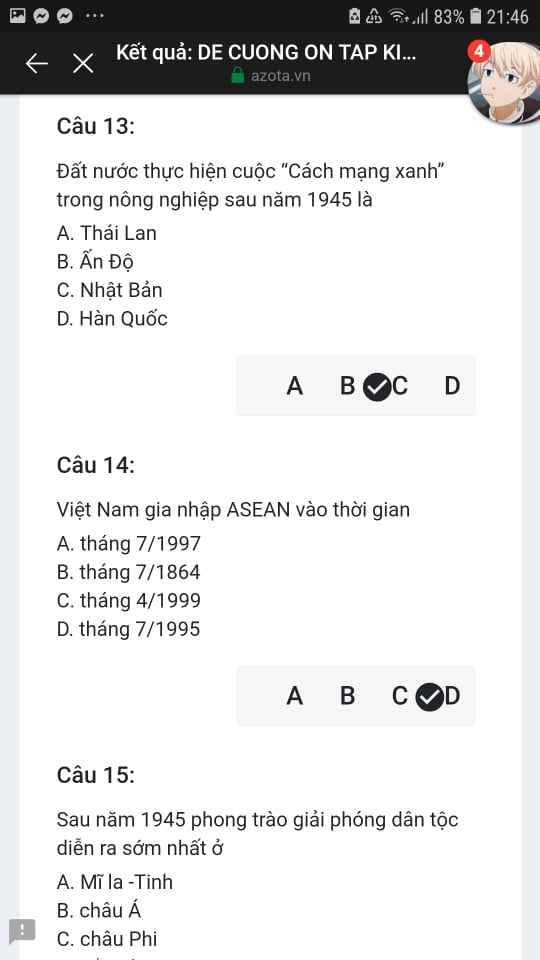
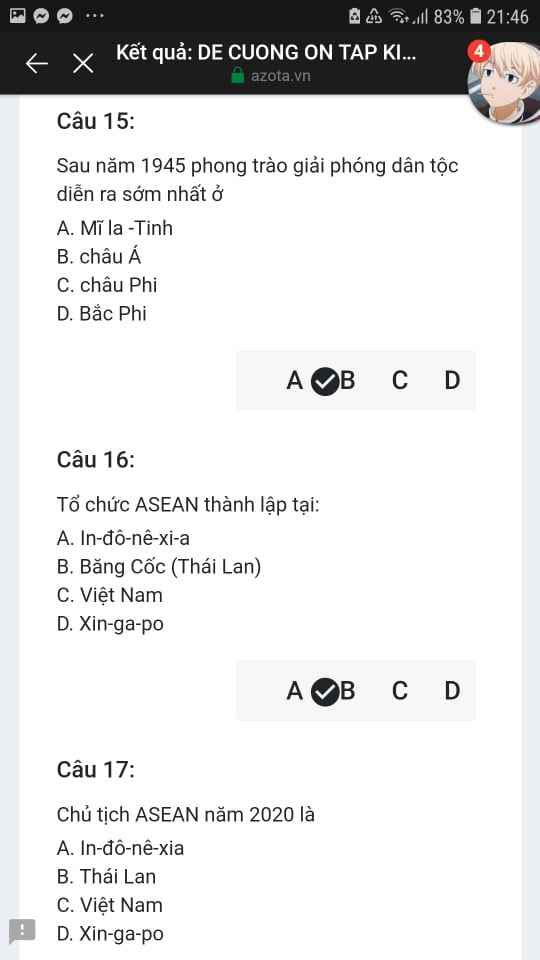


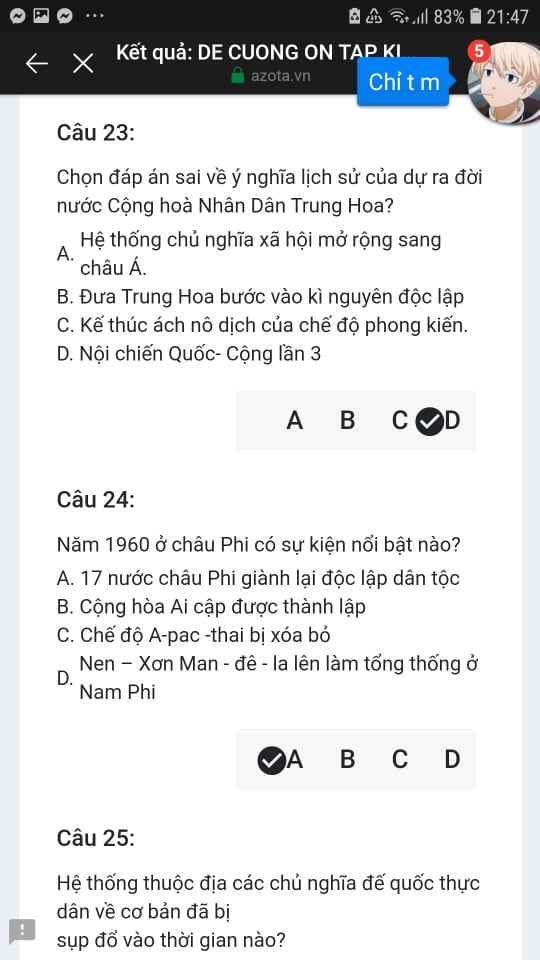
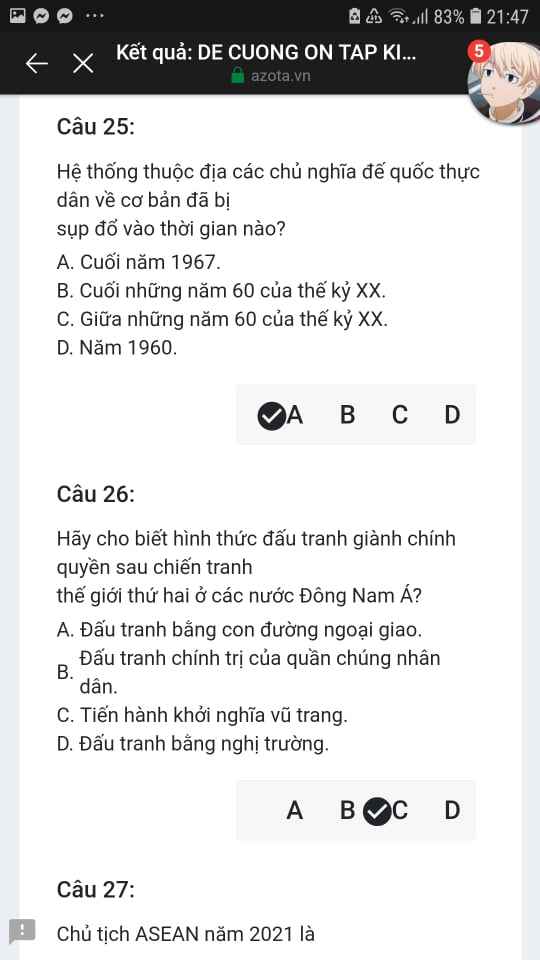
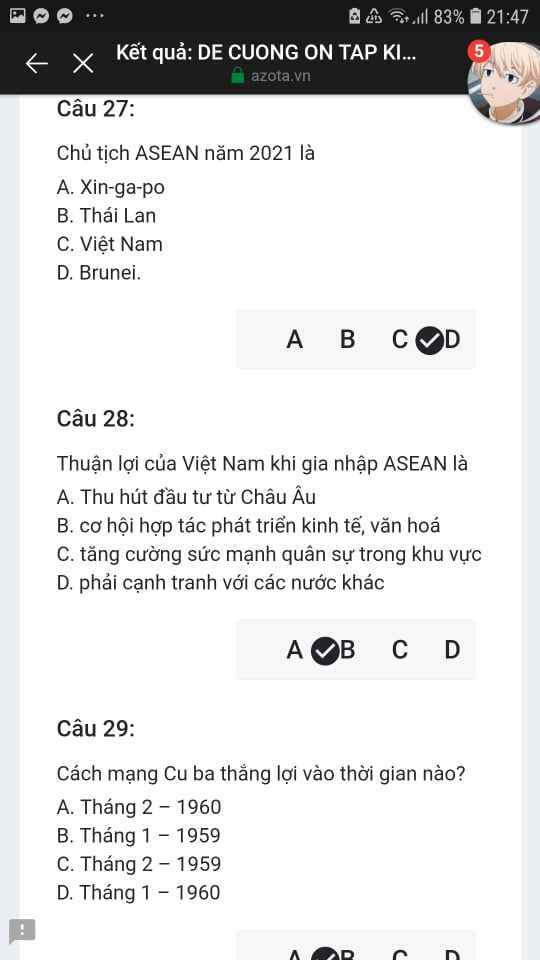
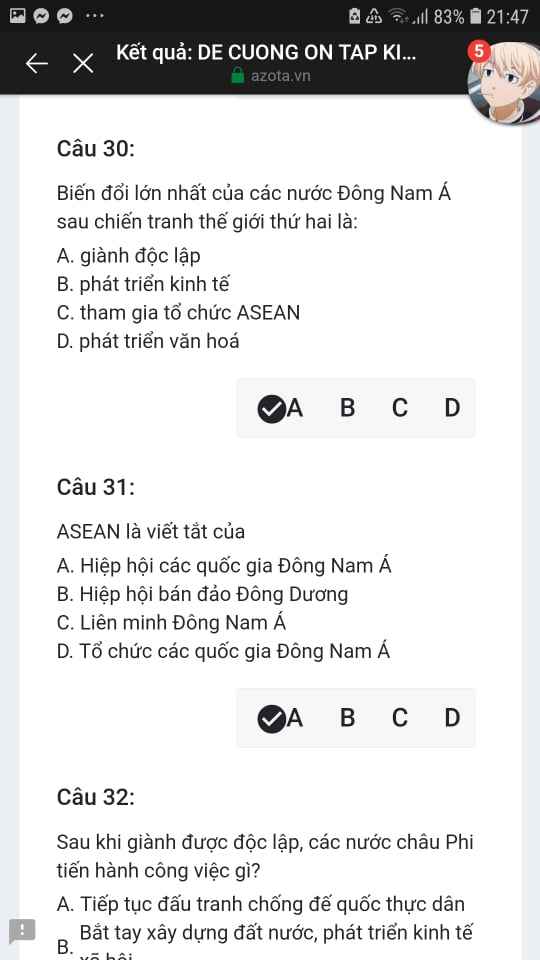
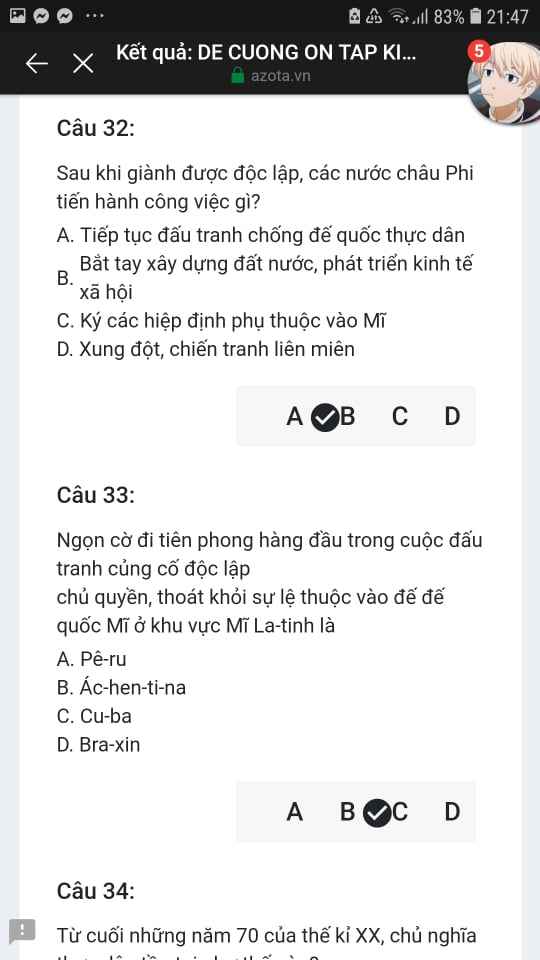


Mng giúp mik vs bn của mik lm sai, các bạn có thể sửa lại và chọn đáp án đúng nhất đc ko ạ? Lm ơn giúp mik, cảm ơn.![]()
mng giúp mik bài này được ko? mik đang cần gấp . cảm ơn bạn nhiều 
a: =>x>=0 và x^2+x=x^2
=>x=0
a: =>x>=1 và 1-x^2=x^2-2x+1
=>-2x^2+2x=0 và x>=1
=>x=1
a: =>x>=1 và 1-2x^2=x^2-2x+1
=>-3x^2+2x=0 và x>=1
=>\(x\in\varnothing\)
a: ĐKXĐ: x<=2 và x^2-2x=x^2-4x+4
=>x=2
a: =>căn x^2-4=x-2
=>x>=2 và x^2-4=x^2-4x+4
=>x>=2 và 4x=8
=>x=2
b: =>x>=0 và x^2-4x+1=x^2
=>-4x+1=0 và x>=0
=>x=1/4
b: =>x>=-1 và x^2+x+1=x^2+2x+1
=>x=0
c: =>x>=1 và 4x^2-8x+1=x^2-2x+1
=>x>=1 và 3x^2-6x=0
=>x=2
b: =>x>=-1 và 5x^2-2x+2=x^2+2x+1
=>x>=-1 và 4x^2-4x+1=0
=>x=1/2
b: =>căn 4x^2-x+1=2x+3
=>x>=-3/2 và 4x^2-x+1=(2x+3)^2=4x^2+12x+9
=>x>=-3/2 và -13x=8
=>x=-8/13
Đúng 1
Bình luận (2)
1) \(\sqrt{x^2+x}=x\) (Thỏa mẵn với mọi x)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x=x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Vậy \(x=0\)
2) \(\sqrt{1-x^2}=x-1\) (ĐK: \(x\le1\) )
\(\Leftrightarrow1-x^2=\left(x-1\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-x^2=x^2-2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^2-x^2+2x=1-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x^2+2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-2x=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(tm\right)\\x=1\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{0;1\right\}\)
\(\sqrt{1-2x^2}=x-1\) (ĐK: \(x\le\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{2}}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow1-2x^2=\left(x-1\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-2x^2=x^2-2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x^2-x^2+2x=1-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x^2+2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-x=0\\3x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(tm\right)\\x=\dfrac{2}{3}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{0;\dfrac{2}{3}\right\}\)
\(\sqrt{x^2-2x}=2-x\) (ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\le0\\x\ge2\end{matrix}\right.\) )
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x=\left(2-x\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x=4-4x+x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x^2-2x+4x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy: \(x=2\)
\(\sqrt{x^2-4}-x+2=0\) (ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\le-2\\x\ge2\end{matrix}\right.\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2-4}=x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4=\left(x-2\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4=x^2-4x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x^2+4x=4+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy: \(x=2\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Mng giúp mik bài này được ko? Mik đang cần gấp. Cảm ơn bạn nhiều 🤩
Giải phương trình:
1) \(\sqrt{x^2+x}\)=\(x\)
2) \(\sqrt{1-x^2}\)=\(x-1\)
mng giúp mik 2 câu này đc ko. cảm ơn bạn nhiều
1) \(\sqrt{x^2-x}=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x=x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Vậy: \(x=0\)
2) \(\sqrt{1-x^2}=x-1\) (ĐK: \(x\le1\))
\(\Leftrightarrow1-x^2=\left(x-1\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-x^2=x^2-2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^2-x^2-2x=1-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x^2-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-2x=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(tm\right)\\x=-1\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{0;-1\right\}\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
1: =>x^2+x=x^2 và x>=0
=>x=0
2: =>1-x^2=x^2-2x+1 và x>=1
=>x^2-2x+1-1+x^2>=0 và x>=1
=>2x^2-2x=0 và x>=1
=>x=1
Đúng 1
Bình luận (2)
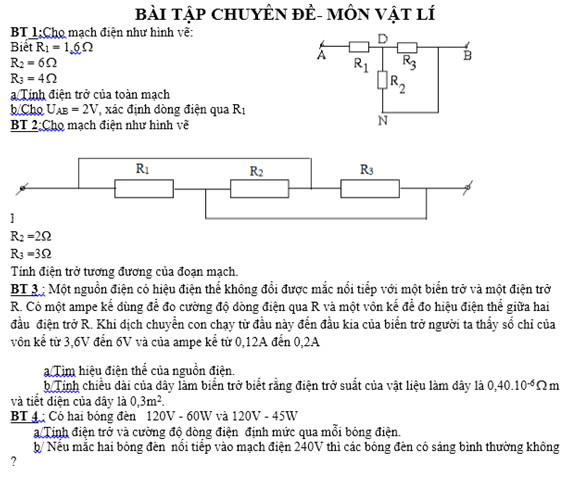 mng giúp mik bài 1 vs bài 3 vs, mik cần gấp lắm, cảm ơn mng.
mng giúp mik bài 1 vs bài 3 vs, mik cần gấp lắm, cảm ơn mng.
 ai giúp mik bài này đc ko ạ, mik cảm ơn!
ai giúp mik bài này đc ko ạ, mik cảm ơn!
1: =>x^2-5x+6-x^2-5x-6=x^2+1-x^2+9
=>-10x=10
=>x=-1(nhận)
2: \(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-15x-x^2+2x-2x^2=0\)
=>-13x=0
=>x=0
3: \(\Leftrightarrow13\left(x+3\right)+x^2-9=12x+42\)
=>x^2-9+13x+39-12x-42=0
=>x^2+x-12=0
=>(x+4)(x-3)=0
=>x=3(loại) hoặc x=-4(nhận)
4: \(\Leftrightarrow-2+x^2-5x+4=x^2+x-6\)
=>-5x-2=x-6
=>-6x=-4
=>x=2/3
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
mng làm nhanh giúp mik nha.Làm bao nhiêu bào cx đc ah(lm hết càng tốt nhé).Cảm ơn mng gất nhìu
Bài 1:
a. $\frac{x}{2}=\frac{3,6}{1,2}=3$
$x=3.2=6$
b.
$\frac{8}{2x+1}=\frac{4}{3}$
$2x+1=\frac{8.3}{4}=6$
$2x=6-1=5$
$x=\frac{5}{2}$
c. $\frac{x}{4}=\frac{9}{x}$
$x^2=9.4=36=6^2=(-6)^2$
$\Rightarrow x=\pm 6$
d.
$\frac{x+1}{2}=\frac{32}{x+1}$
$(x+1)^2=32.2=64=8^2=(-8)^2$
$\Rightarrow x+1=8$ hoặc $x+1=-8$
$\Rightarrow x=7$ hoặc $x=-9$
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)


