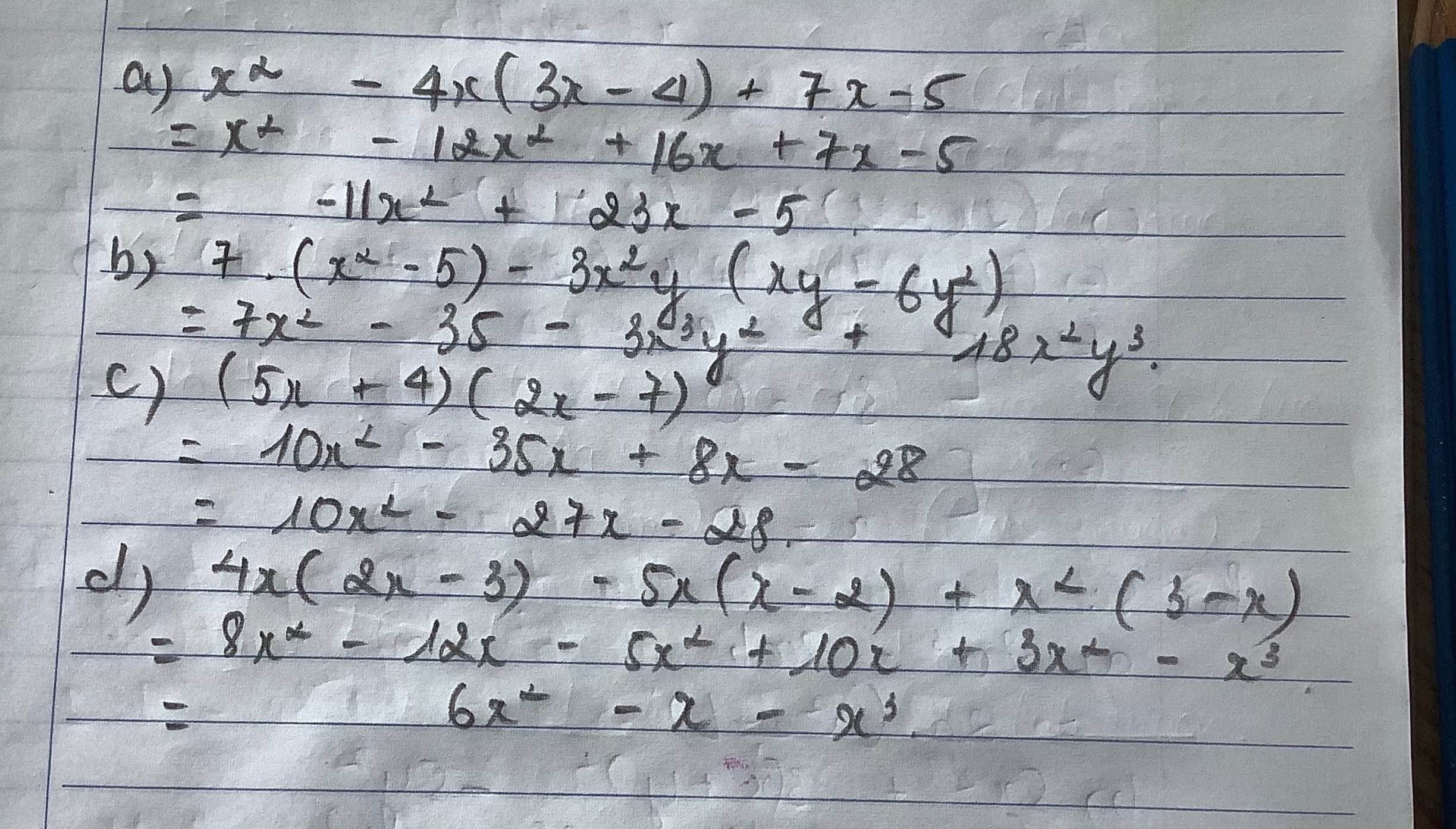ND
Những câu hỏi liên quan
A(2,3x-6,5)(0,1x+2)=0
B(2x+7)(x-5)(5x+1)=0
C(x-1)(2x+7)(x2+2)=0
D(4x-10)(24+5x)=0
E(3,5-7x)(0,1x+2,3)=0
F (5x+2)(x+7)=0
G15 (x+9)(x-3)(x+21)=0
H (x2+1)(×2-4x+4)=0
I(3x-2)(2 (x+3)/9-4x-3/5)=0
\(A.\left(2,3x-6,5\right)\left(0,1x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2,3x-6,5=0\\0,1x+2=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2,3x=6,5\\0,1x=-2\end{cases}}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{6,5}{2,3}\\x=-20\end{cases}}\)
Thu gọn biểu thức a)x^2-4x(3x-4)+7x-5 b)7x(x^2-5)-3x^2y(xy-6y^2) c)(5x+4)(2x-7) d)4x(2x-3)-5x(x-2)+x^2(3-x)
a: Ta có: \(x^2-4x\left(3x-4\right)+7x-5\)
\(=x^2-12x^2+16x+7x-5\)
\(=-11x^2+23x-5\)
b: Ta có: \(7x\left(x^2-5\right)-3x^2y\left(xy-6y^2\right)\)
\(=7x^3-35x-3x^3y^2+18x^2y^3\)
c: Ta có: \(\left(5x+4\right)\left(2x-7\right)\)
\(=10x^2-35x+8x-28\)
\(=10x^2-27x-28\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (2)
bài 7 4x3 + 12 120 b, ( x - 4 )2 64 c, ( x + 1 )3 - 2 52d, 136 - ( x + 5)2 100e, 4x 16f, 7x. 3 - 147 0 g, 2x+3 - 15 17 h, 52x-4. 4 102i, (32 - 4x)(7 - x) 0k, ( 8 - x)(10 - 2x) 0m, 3x + 3x+1 108 n, 5x+2 + 5x+1 750
Đọc tiếp
bài 7
4x3 + 12 = 120
b, ( x - 4 )2 = 64
c, ( x + 1 )3 - 2 = 52
d, 136 - ( x + 5)2 = 100
e, 4x = 16
f, 7x. 3 - 147 = 0
g, 2x+3 - 15 = 17
h, 52x-4. 4 = 102
i, (32 - 4x)(7 - x) = 0
k, ( 8 - x)(10 - 2x) = 0
m, 3x + 3x+1 = 108
n, 5x+2 + 5x+1 = 750
a: \(4x^3+12=120\)
=>\(4x^3=108\)
=>\(x^3=27=3^3\)
=>x=3
b: \(\left(x-4\right)^2=64\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4=8\\x-4=-8\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=12\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: (x+1)^3-2=5^2
=>\(\left(x+1\right)^3=25+2=27\)
=>x+1=3
=>x=2
d: 136-(x+5)^2=100
=>(x+5)^2=36
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+5=6\\x+5=-6\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-11\end{matrix}\right.\)
e: \(4^x=16\)
=>\(4^x=4^2\)
=>x=2
f: \(7^x\cdot3-147=0\)
=>\(3\cdot7^x=147\)
=>\(7^x=49\)
=>x=2
g: \(2^{x+3}-15=17\)
=>\(2^{x+3}=32\)
=>x+3=5
=>x=2
h: \(5^{2x-4}\cdot4=10^2\)
=>\(5^{2x-4}=\dfrac{100}{4}=25\)
=>2x-4=2
=>2x=6
=>x=3
i: (32-4x)(7-x)=0
=>(4x-32)(x-7)=0
=>4(x-8)*(x-7)=0
=>(x-8)(x-7)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-8=0\\x-7=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\\x=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
k: (8-x)(10-2x)=0
=>(x-8)(x-5)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-8=0\\x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
m: \(3^x+3^{x+1}=108\)
=>\(3^x+3^x\cdot3=108\)
=>\(4\cdot3^x=108\)
=>\(3^x=27\)
=>x=3
n: \(5^{x+2}+5^{x+1}=750\)
=>\(5^x\cdot25+5^x\cdot5=750\)
=>\(5^x\cdot30=750\)
=>\(5^x=25\)
=>x=2
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình
1) 16-8x=0
2) 7x+14=0
3) 5-2x=0
4) 3x-5=7
5) 8-3x=6
6) 8=11x+6
7)-9+2x=0
8) 7x+2=0
9) 5x-6=6+2x
10) 10+2x=3x-7
11) 5x-3=16-8x
12)-7-5x=8+9x
13) 18-5x=7+3x
14) 9-7x=-4x+3
15) 11-11x=21-5x
16) 2(-7+3x)=5-(x+2)
17) 5(8+3x)+2(3x-8)=0
18) 3(2x-1)-3x+1=0
19)-4(x-3)=6x+(x-3)
20)-5-(x+3)=2-5x
20) -5-(x + 3) = 2 - 5x ⇔ -5 - x - 3 = 2 -5x ⇔ 4x = 10 ⇔ x = \(\frac{5}{2}\)
Vậy...
https://i.imgur.com/PCDykdb.jpg
1) 16 - 8x = 0 ⇔ 8(2 - x) = 0⇔ 2 - x = 0 ⇔ x = 2
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là x = 2
Xem thêm câu trả lời
1) 2x^4-7x^2-4=0
2)(x62+5x^2)-2(x^2+5x)-24=0
3)x^2-2x-3(x-1)+3=0
4)(x+1/x)^2+2(x+1/x)-8=0
5)x(x+1)(x+2)(2x+3)-18=0
7)(x^2+4x+7)=(x+4)nhân vs căn bậc hai cua x^2 +2
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 3x ^ 2 - 5x + 2 = 0
d) - 4x ^ 2 + 25 = 0
b) 11x - 2x ^ 2 = 0
e) sqrt(x ^ 2 - x + 9) = 2x + 1
c) x ^ 2 + 5x + 7 = 0
f) 6x ^ 4 - 7x ^ 2 + 1 = 0
a: =>3x^2-3x-2x+2=0
=>(x-1)(3x-2)=0
=>x=2/3 hoặc x=1
b: =>2x^2=11
=>x^2=11/2
=>\(x=\pm\dfrac{\sqrt{22}}{2}\)
c: Δ=5^2-4*1*7=25-28=-3<0
=>PTVN
f: =>6x^4-6x^2-x^2+1=0
=>(x^2-1)(6x^2-1)=0
=>x^2=1 hoặc x^2=1/6
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\pm1\\x=\pm\dfrac{\sqrt{6}}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
d: =>(5-2x)(5+2x)=0
=>x=5/2 hoặc x=-5/2
e: =>4x^2+4x+1=x^2-x+9 và x>=-1/2
=>3x^2+5x-8=0 và x>=-1/2
=>3x^2+8x-3x-8=0 và x>=-1/2
=>(3x+8)(x-1)=0 và x>=-1/2
=>x=1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a,4x-10=0 b, 7-3x=9-x c, 2x-(3-5x) = 4(x+3)
d, 5-(6-x)=4(3-2x) e, 4(x+3)=-7x+17 f, 5(x-3) - 4=2(x-1)+7
g, 5(x-3)-4=2(x-1)+7 h,4(3x-2)-3(x-4)=7x+20
`a,4x-10=0 `
`<=> 4x=10`
`<=>x=10/4`
`<=>x=5/2`
`b, 7-3x=9-x `
`<=>-3x+x=9-7`
`<=>-2x=2`
`<=>x=-1`
`c, 2x-(3-5x) = 4(x+3)`
`<=>2x-3+5x=4x+12`
`<=>2x+5x-4x=12+3`
`<=>3x=15`
`<=>x=5`
`d, 5-(6-x)=4(3-2x) `
`<=>5-6+x=12-8x`
`<=>x+8x=12-5+6`
`<=>9x=13`
`<=>x=13/9`
`e, 4(x+3)=-7x+17 `
`<=>4x+12=-7x+17`
`<=>4x+7x=17-12`
`<=>11x=5`
`<=>x=5/11`
`f, 5(x-3) - 4=2(x-1)+7`
`<=>5x-15-4=2x-2+7`
`<=>5x-2x=15+4-2+7`
`<=>3x=24`
`<=>x=8`
`g, 5(x-3)-4=2(x-1)+7 `
`<=>5x-15-4=2x-2+7`
`<=>5x-2x=15+4-2+7`
`<=>3x=24`
`<=>x=8`
`h,4(3x-2)-3(x-4)=7x+20`
`<=>12x-8-3x+12=7x+20`
`<=>12x-3x-7x=20+8+12`
`<=>2x=40`
`<=>x=20`
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
tìm x biết
a, 3-2 | 4x - 5 | = 2 phần 6
b, | 4 - 7x | - 3 phần 2 : 5 = giá trị tuyệt đối -1 và 1 phần 3
c, ( 7-3x ) ( 2x+1 ) = 0
d, 2x ( 5-3x ) > 0
e, ( 4-2x ) ( 5x + 3 ) < 0
g, | 3x+ 1 | + | 1-3x | =0
a: 3-2|4x-5|=2/6
=>2|4x-5|=3-1/3=8/3
=>|4x-5|=4/3
=>4x-5=4/3 hoặc 4x-5=-4/3
=>4x=19/3 hoặc 4x=11/3
=>x=19/12 hoặc x=11/12
c: (7-3x)(2x+1)=0
=>2x+1=0 hoặc -3x+7=0
=>x=-1/2 hoặc x=-7/3
d: 2x(5-3x)>0
=>x(3x-5)<0
=>0<x<5/3
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình bậc 3:
a)2x^3+5x^2-3x-10=0
b)x^3-2x^2+7x+66=0
c)x^3+3x-4=0
d)x^3+7x^2-48=0
e)4x^3+4x^2-x+14=0
f)3x^3-4x^2+5x+500=0