Mn giúp e nốt phần b ạ :vvvv
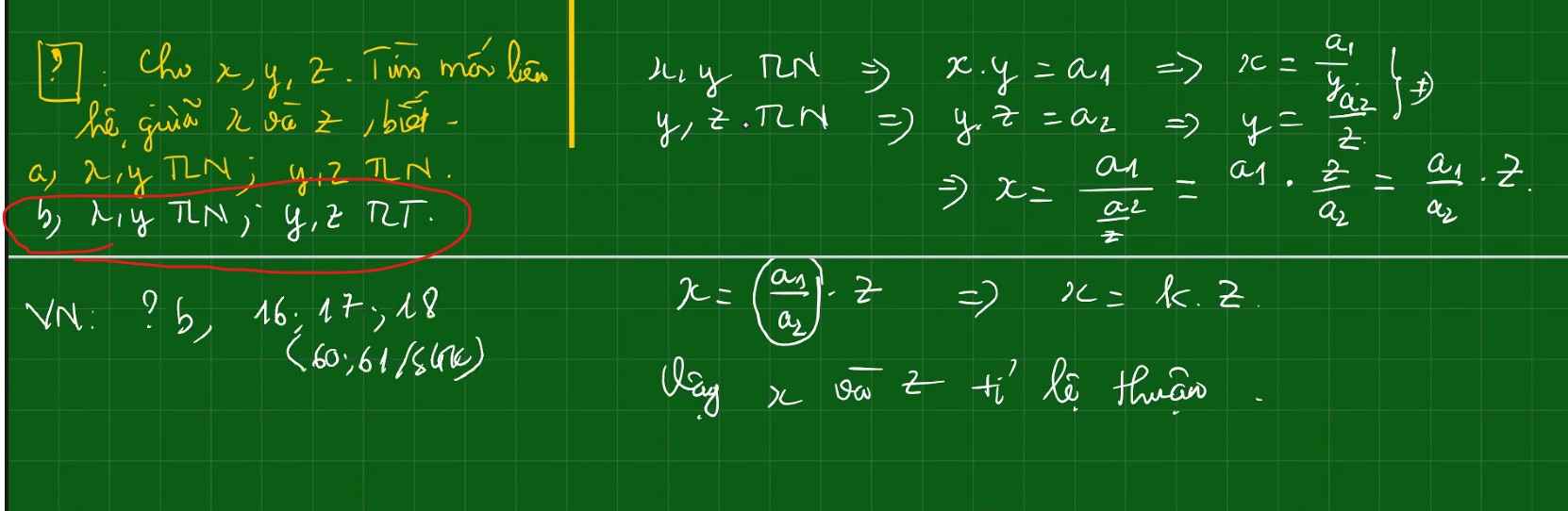
Mn, lm giúp e phần b thôi ạ :)


mn giúp e phần A,B,D,E với ạ, e cảm ơn e đg cần gấp
mong mn giúp nốt bài này ạ

a: Xét ΔABC vuông tại A có \(cosB=\dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
nên \(\widehat{B}=60^0\)
b:
ΔABC vuông tại A
=>\(AB^2+AC^2=BC^2\)
=>\(AC^2=6^2-3^2=27\)
=>\(AC=3\sqrt{3}\left(cm\right)\)
Xét ΔBAC có BD là phân giác
nên \(\dfrac{AD}{AB}=\dfrac{CD}{CB}\)
=>\(\dfrac{AD}{3}=\dfrac{CD}{6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{AD}{1}=\dfrac{CD}{2}\)
Áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau, ta được:
\(\dfrac{AD}{1}=\dfrac{CD}{2}=\dfrac{AD+CD}{1+2}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{3}=\sqrt{3}\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}AD=\sqrt{3}\simeq1,7\left(cm\right)\\CD=2\sqrt{3}\simeq3,5\left(cm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: ΔABC vuông tại A có AH là đường cao
nên \(AH\cdot BC=AB\cdot AC\)
=>\(AH\cdot6=3\cdot3\sqrt{3}=9\sqrt{3}\)
=>\(AH=\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}\left(cm\right)\)
d: ΔABC vuông tại A có AH là đường cao
nên \(BA^2=BH\cdot BC\left(1\right)\)
ΔADB vuông tại A có AE là đường cao
nên \(BE\cdot BD=BA^2\left(2\right)\)
Từ (1),(2) suy ra \(BH\cdot BC=BE\cdot BD\)
=>\(\dfrac{BH}{BD}=\dfrac{BE}{BC}\)
Xét ΔBHE và ΔBDC có
BH/BD=BE/BC
\(\widehat{HBE}\) chung
Do đó: ΔBHE đồng dạng với ΔBDC
Mn giúp mik nốt bài này vs ạ!
1You shouldn't spend a lot of time watching TV
2Antarctica is the coldest place in the world
4A car is not as convenient as a bicycle in towns
5Take a first right
Mn giúp em nốt câu cuối vs ạ :D Cảm ơn mn trc nha

\(\dfrac{-1}{8}\le\dfrac{x}{72}\le\dfrac{-1}{36}\)
\(\dfrac{-9}{72}\le\dfrac{x}{72}\le\dfrac{-2}{72}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) \(x\in\) {\(-9;-8;-7;-6;-5;-4;-3;-2\)}
Phần Vl , mn xem giúp e làm đúng ko ạ và sửa e vs giúp e vài câu e ko bt làm ạ ( đây là đề ôn ạ )
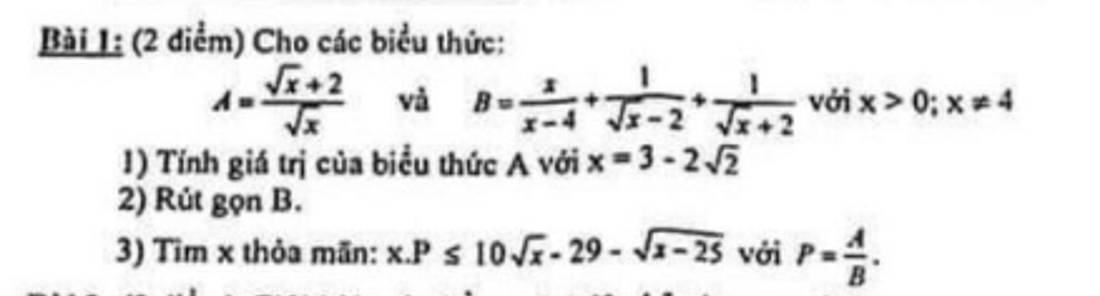
mn giúp e phần c vs ạ
e cảm ơnn
1: Khi x=3-2 căn 2 thì \(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1+2}{\sqrt{2}-1}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}+1}{\sqrt{2}-1}=3+2\sqrt{2}\)
2: \(B=\dfrac{x+\sqrt{x}+2+\sqrt{x}-2}{x-4}=\dfrac{x+2\sqrt{x}}{x-4}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
3: \(P=A:B=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}}:\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}=\dfrac{x-4}{x}\)
\(x\cdot P< =10\sqrt{x}-29-\sqrt{x-25}\)
=>\(x-4< =10\sqrt{x}-29-\sqrt{x-25}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-4-10\sqrt{x}+29< =-\sqrt{x-25}\)
=>\(x-10\sqrt{x}+25< =-\sqrt{x-25}\)
=>(căn x-5)^2<=-căn x-25
=>x-25=0
=>x=25
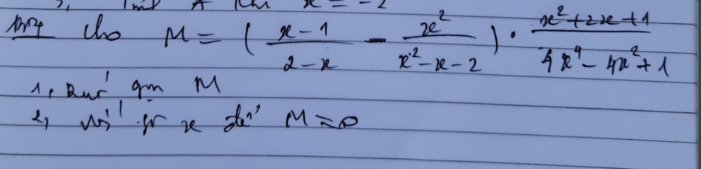
mn ơi giúp mik nốt câu này dc ko ạ plssss
1
Với \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne2\\x\ne-1\\x\ne\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{2}}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(M=\left(\dfrac{x-1}{2-x}-\dfrac{x^2}{x^2-x-2}\right)\left(\dfrac{x^2+2x+1}{4x^4-4x^2+1}\right)\\ =\left(\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(2-x\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{x^2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(2-x\right)}\right)\left(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(2x^2-1\right)^2}\right)\\ =\dfrac{x^2-1+x^2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(2-x\right)}\left(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(2x^2-1\right)^2}\right)\\ =\dfrac{\left(2x^2-1\right)\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(2-x\right)\left(2x^2-1\right)^2}\\ =\dfrac{x+1}{\left(2-x\right)\left(2x^2-1\right)}\)
2
Để M = 0 thì \(\dfrac{x+1}{\left(2-x\right)\left(2x^2-1\right)}=0\Rightarrow x+1=0\Rightarrow x=-1\) (loại)
Vậy không có giá trị x thỏa mãn M = 0
1) \(M=\left(\dfrac{x-1}{2-x}-\dfrac{x^2}{x^2-x-2}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x^2+2x+1}{4x^4-4x^2+1}\) (ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne2\\x\ne-1\\x\ne\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{2}}\end{matrix}\right.\))
\(M=\left(\dfrac{-\left(x-1\right)}{x-2}-\dfrac{x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right)\cdot\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(2x^2-1\right)^2}\)
\(M=\left(\dfrac{-\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right)\cdot\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(2x^2-1\right)^2}\)
\(M=\left(\dfrac{-\left(x^2-1\right)-x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right)\cdot\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(2x^2-1\right)^2}\)
\(M=\left(\dfrac{-x^2+1-x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right)\cdot\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(2x^2-1\right)^2}\)
\(M=\dfrac{-2x^2+1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(2x^2-1\right)^2}\)
\(M=\dfrac{-\left(2x^2-1\right)\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(2x^2-1\right)^2}\)
\(M=\dfrac{-\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(2x^2-1\right)}\)
2) Ta có: \(M=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{-\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(2x^2-1\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\left(ktm\right)\)
1: \(M=\left(\dfrac{-x+1}{x-2}-\dfrac{x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right)\cdot\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(2x^2-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{-x^2+1-x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(2x^2-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{1-2x^2}{\left(x-2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+1}{\left(1-2x^2\right)^2}=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(1-2x^2\right)}\)
2: M=0
=>x+1=0
=>x=-1(loại)
Mn giúp e phần bài tập tham khảo với ạ , đc e sẽ hậu tạ ạ