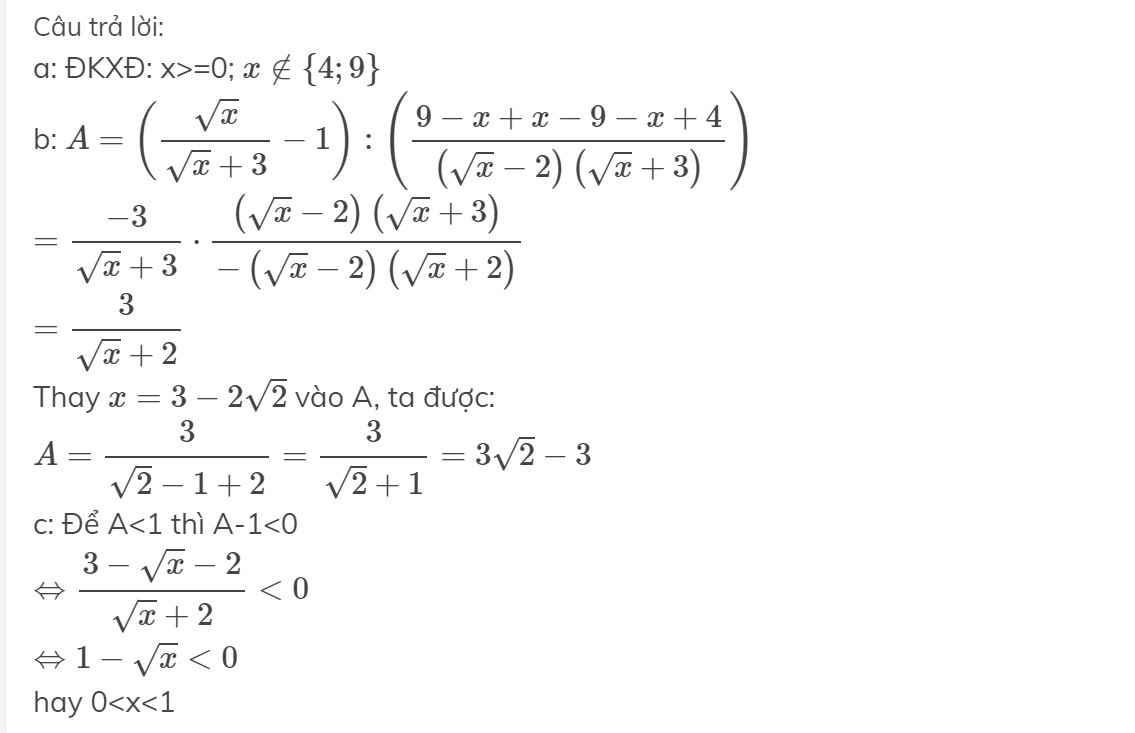Điều nào sau đây là sai khi nói về công suất
a. công thức tính công suất là P=\(\dfrac{A}{t}\)
b. P (J/s; W) là công suất
c. A (J) là công thực hiện
d. t (h) là thời gian thực hiện công
Gọi (A )là công của một máy thực hiện được trong thời gian(t) giây. Công suất(P) của máy đc tính bằng công thức
A.P=A/t
B.P=A.t
C.P=10A.t
D.P=F.v
Xem chi tiết
Gọi (A )là công của một máy thực hiện được trong thời gian(t) giây. Công suất(P) của máy đc tính bằng công thức A.P=A/t B.P=A.t C.P=10A.t D.P=F.v
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Trường hợp nào dưới đây không phải công thức tính công suất điện?
A: P = U.I
B: P= \(\dfrac{U^2}{R}\)
C: P = I\(^2\).R
D: P = A.t
Xem thêm câu trả lời
tóm tắt
v=15m/s
t=6s
S=?m
ta có công thức v=v0+a.t ,suy ra a.t=v-v0 thế số vào ta có a.6=15-0 hay a.16=15 suy ra a=\(\dfrac{15}{6}\)
ta có công thức S=v0.t+\(\dfrac{a.t^2}{2}\)=0.6+\(\dfrac{\dfrac{15}{6}.6^2}{2}\)=45 (m)
Trong mạch điện gồm R,L,C mắc nối tiếp.\(R=30\Omega\) ,\(L=\dfrac{0,5}{\pi}mH\),\(C=\dfrac{50}{\pi}MF\)
\(u=100\sqrt{2}cos\left(100\pi t+\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
a,Tính hệ số công suất b,Tính biểu thức i
xét biểu thức A=\(\dfrac{a^2+\sqrt{a}}{a-\sqrt{a}+1}-\dfrac{2a+\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{a}+1}\)
a.Tìm ĐKXĐ
b.rút gọn a
c.biết a>1 .Hãy so sánh A với giá trị tuyệt đối của A
d. tìm a để A=2
e.tìm GTNN của A
Câu a : ĐKXĐ : \(a\ge0\)
\(A=\dfrac{a^2+\sqrt{a}}{a-\sqrt{a}+1}-\dfrac{2a+\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{a}+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)\left(a^2+\sqrt{a}\right)-\left(2a+\sqrt{a}\right)\left(a-\sqrt{a}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)\left(a-\sqrt{a}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{a^2\sqrt{a}+a+a^2+\sqrt{a}-2a^2+2a\sqrt{a}-2a-a\sqrt{a}+a-\sqrt{a}}{\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)\left(a-\sqrt{a}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{a^2\sqrt{a}-a^2+a\sqrt{a}}{\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)\left(a-\sqrt{a}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{a\sqrt{a}\left(a-\sqrt{a}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)\left(a-\sqrt{a}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{a\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{a}+1}\)
Câu c : Vì \(a>1\Rightarrow\left|\dfrac{a\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{a}+1}\right|=\dfrac{a\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{a}+1}\)
Câu d : \(\dfrac{a\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{a}+1}=2\Leftrightarrow a\sqrt{a}-2\sqrt{a}-2=0\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{a}=x\Leftrightarrow x^3-2x-2=0\) Tự giải ra nha bạn!
Câu e : \(A=\dfrac{a\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{a}+1}\ge\dfrac{0}{\sqrt{0}+1}=0\)
Vậy GTNN của A là 0 khi \(a=0\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (4)
Cho biểu thức:
A = \(\left(\dfrac{x-3\sqrt{x}}{x-9}-1\right):\left(\dfrac{9-x}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-3}{\sqrt{x}-2}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}+3}\right)\)
a.Tìm x để A có nghĩa
b.Rút gọn A.Tính A khi x = \(3-2\sqrt{2}\)
c.Tìm x để A < 1
Cho biểu thức A = \(\dfrac{x+2}{x+3}-\dfrac{5}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
a.Tìm điều kiện để biểu thức có nghĩa
b.Rút gọn biểu thức
c.Tính giá trị của A tại |x| = 2
d.Tìm x ∈ Z để A nguyên
a) (x-2)(x+3)≠ 0 ⇔x ≠-2 và x≠-3
=> ĐKXĐ x ≠-2 và x≠-3
b) \(A=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{5}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
=\(\dfrac{x^2-4-5}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-9}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{x-3}{x-2}\)
c)|x|=2
th1 x=2 thay vào A ta có
=> \(A=\dfrac{2-3}{2-2}=-\dfrac{1}{1}=-1\)
th2 x=-2 thay vào A ta có
A=\(\dfrac{-2-3}{-2-2}=-\dfrac{5}{-4}=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
để A nguyên thì (x-3) ⋮ (x-2)
vì (x-2) ⋮ (x-2)
=> (x-3)-(x-2) ⋮ (x-2)
<=> (x-3-x+2) ⋮ (x-2)
<=> -1 ⋮ (x-2)
=> (x-2) ∈ Ư(-1)={-1;1}
=> x ∈{1;3}
vậy x ∈{1;3} thì A nguyên
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1.Cho biểu thức A dfrac{x^2-y^2}{5x-5y}
a.Tìm điều kiện xác định của A
b. Rút gọn A
2.Cho biểu thức A dfrac{2x^2+4x}{x^3-4x}+dfrac{x^2-4}{x^2+2x}+dfrac{2}{2-x} (x ≠ 0; x ≠ -2 ; x ≠ 2)
a.Rút gọn biểu thức A
b.Tính A khi x 4
c.Tìm giá trị nguyên của x để A nhận giá trị nguyên
3.Cho 2 đa thức
A 2x3 + 5x2 - 2x + a
B 2x2 - x + 1
a.Tính giá trị của B tại x -1
b.Tìm a để A ⋮ B
c.Tìm x để B 1
Đọc tiếp
1.Cho biểu thức A = \(\dfrac{x^2-y^2}{5x-5y}\)
a.Tìm điều kiện xác định của A
b. Rút gọn A
2.Cho biểu thức A = \(\dfrac{2x^2+4x}{x^3-4x}+\dfrac{x^2-4}{x^2+2x}+\dfrac{2}{2-x}\) (x ≠ 0; x ≠ -2 ; x ≠ 2)
a.Rút gọn biểu thức A
b.Tính A khi x = 4
c.Tìm giá trị nguyên của x để A nhận giá trị nguyên
3.Cho 2 đa thức
A= 2x3 + 5x2 - 2x + a
B = 2x2 - x + 1
a.Tính giá trị của B tại x = -1
b.Tìm a để A ⋮ B
c.Tìm x để B = 1
1, a, để A có giá trị xác định <=> 5x-5y \(\ne\) 0 => 5x\(\ne\)5y =>x\(\ne\)y b, A=\(\dfrac{x^2-y^2}{5x-5y}=\dfrac{\left(x+y\right)\left(x-y\right)}{5\left(x-y\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x+y\right)}{5}\) 2, a,
A=\(\dfrac{2x^3+4x}{x^3-4x}+\dfrac{x^2-4}{x^2+2x}+\dfrac{2}{2-x}\) =\(\dfrac{2x\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(x^2-4\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}{x\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{2}{x-2}\) =\(\dfrac{2x\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{x-2}{x}-\dfrac{2}{x-2}\) =\(\dfrac{2x}{x\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{x\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{2x}{x\left(x-2\right)}\) =\(\dfrac{2x+\left(x-2\right)^2-2x}{x\left(x-2\right)}\) =\(\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{x\left(x-2\right)}\) =\(\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)}{x}\)
b, thay x=4 vào A ta có : A=\(\dfrac{4-2}{4}\) =\(\dfrac{2}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c, để A \(\in\) Z => (x-2)\(⋮\)x mà x\(⋮\)x =>-2\(⋮\)x => x\(\in\){ \(\pm1;\pm2\)} mà x\(\ne\)\(\pm2\) => x\(\in\left\{-1,+1\right\}\)
Bài 3 : a, Ta có B= 2.(-1)2+-(-1)+1 =2+1+1=4 b, Ta có A=2x3 +5x2 -2x +a =(2x3 -x2 +x )+(6x2-3x +3) +(a-3) \(⋮\) 2x2-x+1 => x(2x2-x+1)+3(2x2-x+1) +(a-3)\(⋮\) 2x2-x+1
=>a-3=0 (vì a-3 là số dư )=>a-3 Vậy a=3 thì A\(⋮\)B c,B=1 => 2x2 -x+1=1 =>x(2x-1)=0 => x=0 hoặc 2x-1 =0 => x=0 hoặc x=\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho biểu thức K=\(\left(\dfrac{a}{a-1}-\dfrac{1}{a^2-a}\right):\left(\dfrac{1}{a+1}+\dfrac{2}{a^2-1}\right)\)
a)Tìm điều kiện của a để biểu thức K xác ddinhjj và rút gọn biểu thức K
b)Tính giá trị biểu thức K khi a=\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
a: ĐKXĐ: a<>0; a<>1; a<>-1
\(K=\dfrac{a^2-1}{a\left(a-1\right)}:\dfrac{a-1+2}{\left(a-1\right)\left(a+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{a+1}{a}\cdot\dfrac{\left(a-1\right)\left(a+1\right)}{a+1}=\dfrac{a^2-1}{a}\)
b: Khi a=1/2 thì K=(1/4-1):1/2=-3/4*2=-3/2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)