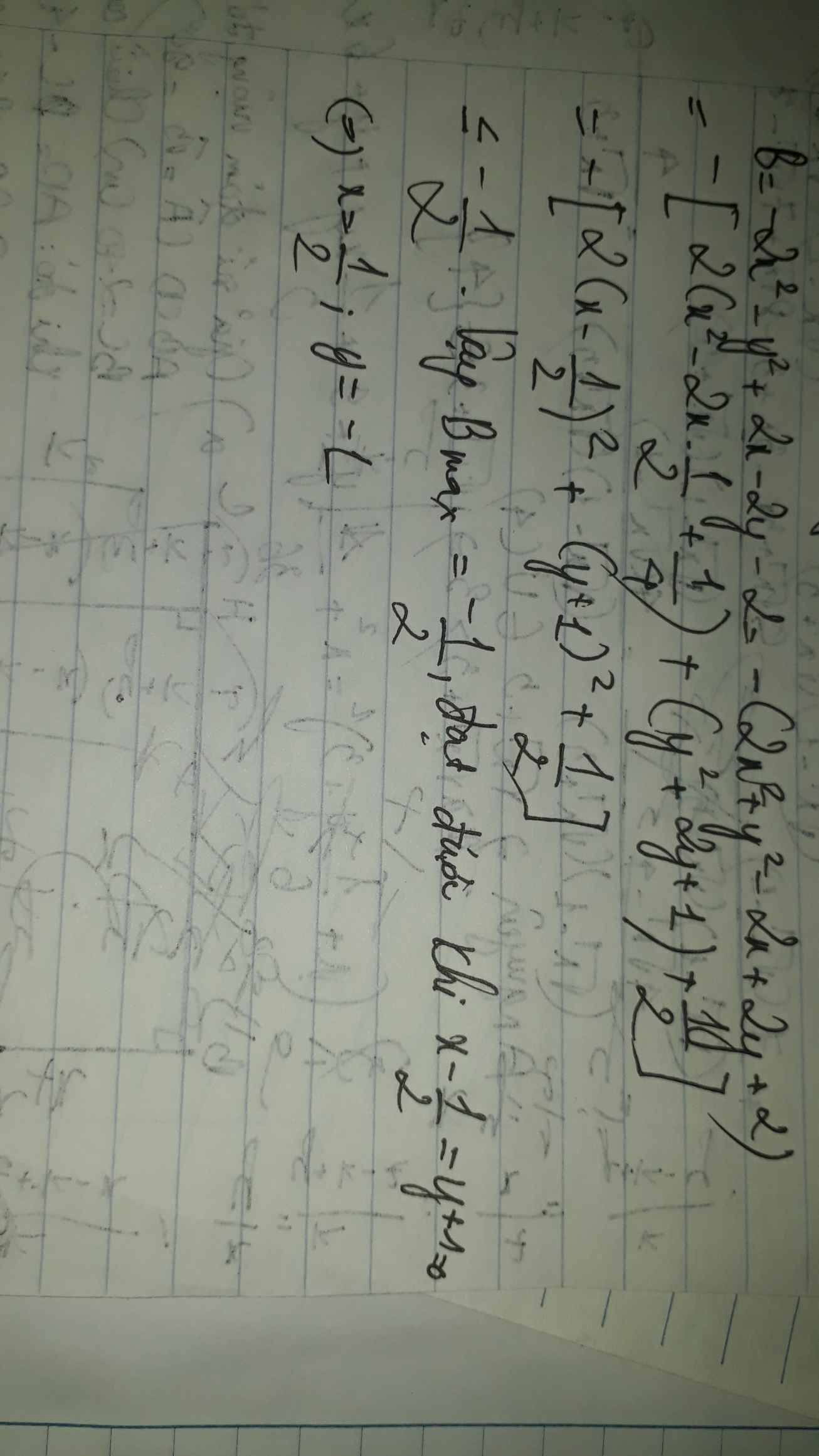2x2-2x+2y+y2-4x+7=0
H3
Những câu hỏi liên quan
Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a,x3+4x-5
b,x3-3x2+4
c,x3+2x2+3x+2
d,x2+2xy+y2+2x-2y-3
e,(x2+3x)2-2(x2+3x)-8
f,(x2+4x+10)2-7(x2+4x+11)+7
a) x3+4x-5 = x3-x2+x2+4x-5=(x3-x2)+(x2-x)+(5x-5)=x2(x-1)+x(x-1)+5(x-1)=(x2+x+5)(x-1)
b) x3-3x2+4=x3-2x2-x2+4=(x3-2x2)-(x2-4)=x2(x-2)-(x-2)(x+2)=(x2-x+2)(x-2)
c) x3+2x2+3x+2=x3+x2+x2+x+2x+2=(x3+x2)+(x2+x)+(2x+2)=x2(x+1)+x(x+1)+2(x+1)=(x2+x+2)(x+1)
d) bạn xem lại đề đúng ko
e) (x2+3x)2-2(x2+3x)-8=x4+6x3+9x2-2x2-6x-8=x4+6x3+7x2-6x-8=x4-x3+7x3-7x2+14x2-14x+8x-8=(x4-x3)+(7x3-7x2)+(14x2-14x)+(8x-8)=x3(x-1)+7x2(x-1)+14x(x-1)+8(x-1)=(x3+7x2+14x+8)(x-1)=(x3+x2+6x2+6x+8x+8)(x-1)=\(\left[\left(x^3+x^2\right)+\left(6x^2+6x\right)+\left(8x+8\right)\right]\left(x-1\right)\)\(=\left[x^2\left(x+1\right)+6x\left(x+1\right)+8\left(x+1\right)\right]\left(x-1\right)\)\(=\left(x^2+6x+8\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\)\(=\left(x^2+2x+4x+8\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\)\(=\left[\left(x^2+2x\right)+\left(4x+8\right)\right]\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\)\(=\left[x\left(x+2\right)+4\left(x+2\right)\right]\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\)=\(\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+4\right)\)
f) (x2+4x+10)2-7(x2+4x+11)+7=(x2+4x+10)2-\(\left[7\left(x^2+4x+11\right)-7\right]\)\(=\left(x^2+4x+10\right)^2-7\left(x^2+4x+10\right)\)\(=\left(x^2+4x+10\right)\left(x^2+4x+3\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a) Ta có: \(x^3+4x-5\)
\(=x^3-x+5x-5\)
\(=x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)+5\left(x-1\right)\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+5\right)\)
b) Ta có: \(x^3-3x^2+4\)
\(=x^3+x^2-4x^2+4\)
\(=x^2\left(x+1\right)-4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-4x+4\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\cdot\left(x-2\right)^2\)
c) Ta có: \(x^3+2x^2+3x+2\)
\(=x^3+x^2+x^2+x+2x+2\)
\(=x^2\left(x+1\right)+x\left(x+1\right)+2\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+2\right)\)
d) Ta có: \(x^2+2xy+y^2+2x+2y-3\)
\(=\left(x+y\right)^2+2\left(x+y\right)-3\)
\(=\left(x+y\right)^2+3\left(x+y\right)-\left(x+y\right)-3\)
\(=\left(x+y\right)\left(x+y+3\right)-\left(x+y+3\right)\)
\(=\left(x+y+3\right)\left(x+y-1\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
e) Ta có: \(\left(x^2+3x\right)^2-2\left(x^2+3x\right)-8\)
\(=\left(x^2+3x\right)^2-4\left(x^2+3x\right)+2\left(x^2+3x\right)-8\)
\(=\left(x^2+3x\right)\left(x^2+3x-4\right)+2\left(x^2+3x-4\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+3x-4\right)\left(x^2+3x+2\right)\)
\(=\left(x+4\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\)
f) Ta có: \(\left(x^2+4x+10\right)^2-7\left(x^2+4x+11\right)+7\)
\(=\left(x^2+4x+10\right)^2-7\left(x^2+4x+10\right)-7+7\)
\(=\left(x^2+4x+10\right)\left(x^2+4x+10-7\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+4x+3\right)\left(x^2+4x+10\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+4x+10\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Hãy cho biết phương trình nào trong các phương trình sau đây là phương trình đường tròn:
2x2 + y2 – 8x + 2y – 1 = 0;
x2 + y2 + 2x – 4y – 4 = 0;
x2 + y2 – 2x – 6y + 20 = 0;
x2 + y2 + 6x + 2y + 10 = 0.
+ 2x2 + y2 – 8x + 2y – 1 = 0 không phải phương trình đường tròn vì hệ số của x2 khác hệ số của y2.
+ Phương trình x2 + y2 + 2x – 4y – 4 = 0 có :
a = –1; b = 2; c = –4 ⇒ a2 + b2 – c = 9 > 0
⇒ phương trình trên là phương trình đường tròn.
+ Phương trình x2 + y2 – 2x – 6y + 20 = 0 có :
a = 1; b = 3; c = 20 ⇒ a2 + b2 – c = –10 < 0
⇒ phương trình trên không là phương trình đường tròn.
+ Phương trình x2 + y2 + 6x + 2y + 10 = 0 có :
a = –3; b = –1; c = 10 ⇒ a2 + b2 – c = 0 = 0
⇒ phương trình trên không là phương trình đường tròn.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1. Tìm x,y:
a) (x+2)2 + (x-3)2 = 2x ( x+ 7)
b) x3- 3x2 + 3x - 126 = 0
c) x2 + y2 - 2x + 4y + 5 = 0
d) 2x2 - 2xy + y2 + 4x + 4 = 0
\(a.\left(x^2+4x+4\right)+\left(x^2-6x+9\right)=2x^2+14x\)
\(x^2+4x+4+x^2-6x+9-2x^2-14x=0\)
\(-18x+13=0\)
\(x=\dfrac{13}{18}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\dfrac{13}{18}\right\}\)
\(b.\left(x-1\right)^3-125=0\)
\(\left(x-1\right)^3=125\)
\(x-1=5\)
\(x=6\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{6\right\}\)
\(c.\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y +2\right)^2=0\)
\(Do\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\forall x;\left(y+2\right)^2\ge0\forall y\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y+2\right)^2\ge0\forall x,y\)
Mà \(\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y+2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-1\right)^2=0\\\left(y+2\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\y+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{1;-2\right\}\)
\(d.x^2-4x+4+x^2-2xy+y^2=0\)
\(\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(x-y\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-2\right)^2=0\\\left(x-y\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x-y=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{2;2\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải hệ phương trình
2
x
2
−
y
2
+
x
y
−
5
x
+
y
+
2
y...
Đọc tiếp
Giải hệ phương trình 2 x 2 − y 2 + x y − 5 x + y + 2 = y − 2 x + 1 − 3 − 3 x x 2 − y − 1 = 4 x + y + 5 − x + 2 y − 2
ĐK: y − 2 x + 1 ≥ 0 , 4 x + y + 5 ≥ 0 , x + 2 y − 2 ≥ 0 , x ≤ 1
T H 1 : y − 2 x + 1 = 0 3 − 3 x = 0 ⇔ x = 1 y = 1 ⇒ 0 = 0 − 1 = 10 − 1 ( k o t / m ) T H 2 : x ≠ 1 , y ≠ 1
Đưa pt thứ nhất về dạng tích ta được
( x + y − 2 ) ( 2 x − y − 1 ) = x + y − 2 y − 2 x + 1 + 3 − 3 x ( x + y − 2 ) 1 y − 2 x + 1 + 3 − 3 x + y − 2 x + 1 = 0 ⇒ 1 y − 2 x + 1 + 3 − 3 x + y − 2 x + 1 > 0 ⇒ x + y − 2 = 0
Thay y= 2-x vào pt thứ 2 ta được x 2 + x − 3 = 3 x + 7 − 2 − x
⇔ x 2 + x − 2 = 3 x + 7 − 1 + 2 − 2 − x ⇔ ( x + 2 ) ( x − 1 ) = 3 x + 6 3 x + 7 + 1 + 2 + x 2 + 2 − x ⇔ ( x + 2 ) 3 3 x + 7 + 1 + 1 2 + 2 − x + 1 − x = 0
Do x ≤ 1 ⇒ 3 3 x + 7 + 1 + 1 2 + 2 − x + 1 − x > 0
Vậy x + 2 = 0 ⇔ x = − 2 ⇒ y = 4 (t/m)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Chứng minh rằng không có các số x, y thỏa mãn
a) 2x2 +2x +1 = 0
b) x2 + y2 + 2xy +2y +2x +2 =0
a: \(2x^2+2x+1=0\)
\(\text{Δ}=2^2-4\cdot2\cdot1=4-8=-4< 0\)
Vì Δ<0 nên phương trình vô nghiệm
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a) \(2x^2+2x+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow2x^2+2x=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow2x\left(x+1\right)=-1\)
⇒ Pt vô nghiệm
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
b) \(x^2+y^2+2xy+2x+2y+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x^2+y^2+2xy\right)+\left(2x+2y+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+y\right)^2+2\left(x+y+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x+y\right)^2=0\\2\left(x+y+1\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=0\\x+y+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+y=0\\x+y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇒ Pt vô nghiệm
Đúng 0
Bình luận (2)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giúp mik nha
2x2+y2-2xy+2x+2y+5=0
\(2x^2\)+\(y^2\)-2xy+2x+2y+5=0
(\(x^2-2xy+y^2\))+2(x+y)+4+(\(x^2+1\))=0
(x-y)2 +2(x+y)+\(2^2\)+(\(x^2+1\))=0
(x-y+2)2 +(\(x^2+1\))=0
Với mọi x;y Thuộc R thì (x-y+2)2 >=0;\(x^2+1\)>0
suy ra (x-y+2)2 +\(x^2+1\)>0
Do đó không tìm được giá trị nào của x;y để 2x2 +\(y^2\)-2xy+2x+2y+5=0
Vậy không tìm đc giá trị nào của x;y thỏa mãn 2x2 +\(y^2\) -2xy+2x+2y+5=0
chúc bạn học tốt ạ
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Hãy giải các phương trình sau đây :
1, x2 - 4x + 4 = 0
2, 2x - y = 5
3, x + 5y = - 3
4, x2 - 2x - 8 = 0
5, 6x2 - 5x - 6 = 0
6,( x2 - 2x )2 - 6 (x2 - 2x ) + 5 = 0
7, x2 - 20x + 96 = 0
8, 2x - y = 3
9, 3x + 2y = 8
10, 2x2 + 5x - 3 = 0
11, 3x - 6 = 0
1) Ta có: \(x^2-4x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2=0\)
hay x=2
Vậy: S={2}
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1: Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử
a)x2-y2-2x+2y e)x4+4y4
b)x2(x-1)+16(1-x) f)x4-13x2+36
c)x2+4x-y2+4 g) (x2+x)2+4x2+4x-12
d)x3-3x2-3x+1 h)x6+2x5+x4-2x3-2x2+1
a.
$x^2-y^2-2x+2y=(x^2-y^2)-(2x-2y)=(x-y)(x+y)-2(x-y)=(x-y)(x+y-2)$
b.
$x^2(x-1)+16(1-x)=x^2(x-1)-16(x-1)=(x-1)(x^2-16)=(x-1)(x-4)(x+4)$
c.
$x^2+4x-y^2+4=(x^2+4x+4)-y^2=(x+2)^2-y^2=(x+2-y)(x+2+y)$
d.
$x^3-3x^2-3x+1=(x^3+1)-(3x^2+3x)=(x+1)(x^2-x+1)-3x(x+1)$
$=(x+1)(x^2-4x+1)$
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
e.
$x^4+4y^4=(x^2)^2+(2y^2)^2+2.x^2.2y^2-4x^2y^2$
$=(x^2+2y^2)^2-(2xy)^2=(x^2+2y^2-2xy)(x^2+2y^2+2xy)$
f.
$x^4-13x^2+36=(x^4-4x^2)-(9x^2-36)$
$=x^2(x^2-4)-9(x^2-4)=(x^2-9)(x^2-4)=(x-3)(x+3)(x-2)(x+2)$
g.
$(x^2+x)^2+4x^2+4x-12=(x^2+x)^2+4(x^2+x)-12$
$=(x^2+x)^2-2(x^2+x)+6(x^2+x)-12$
$=(x^2+x)(x^2+x-2)+6(x^2+x-2)=(x^2+x-2)(x^2+x+6)$
$=[x(x-1)+2(x-1)](x^2+x+6)=(x-1)(x+2)(x^2+x+6)$
h.
$x^6+2x^5+x^4-2x^3-2x^2+1$
$=(x^6+2x^5+x^4)-(2x^3+2x^2)+1$
$=(x^3+x^2)^2-2(x^3+x^2)+1=(x^3+x^2-1)^2$
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
tìm GTLN của B= -2x2-y2=2x-2y-2
Ta có: \(B=-2x^2-y^2+2x-2y-2\)
\(=-\left(2x^2+y^2-2x+2y+2\right)\)
\(=-\left(2x^2-2x+\dfrac{1}{2}+y^2+2y+1+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\)
\(=-2\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2-\left(y+1\right)^2-\dfrac{1}{2}\le\dfrac{1}{2}\forall x,y\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\) và y=-1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)