Giải các phương trình sau:
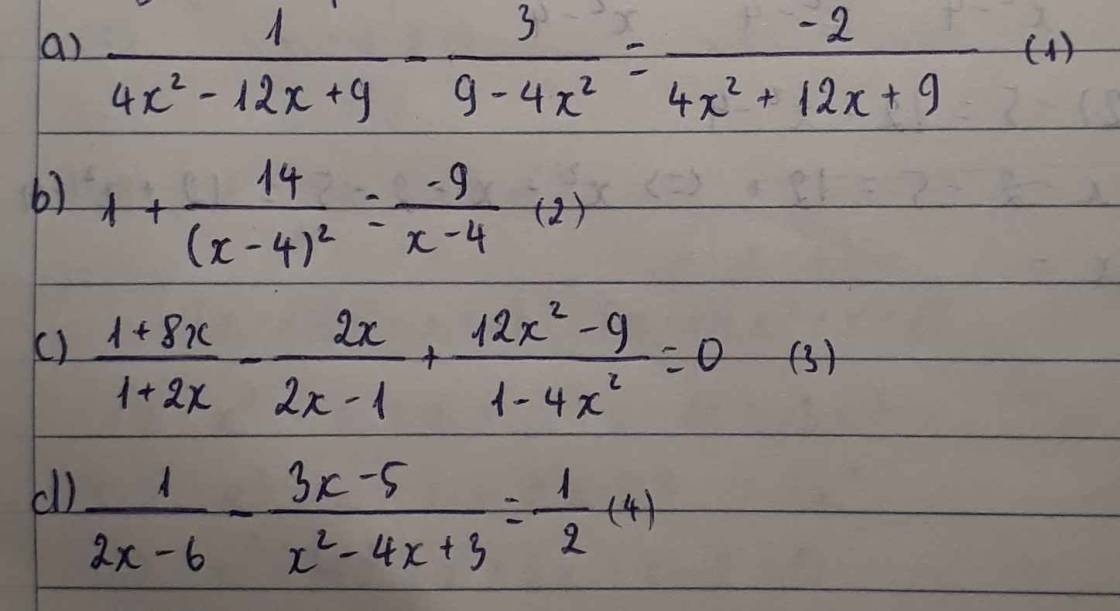
Giải các phương trình sau:
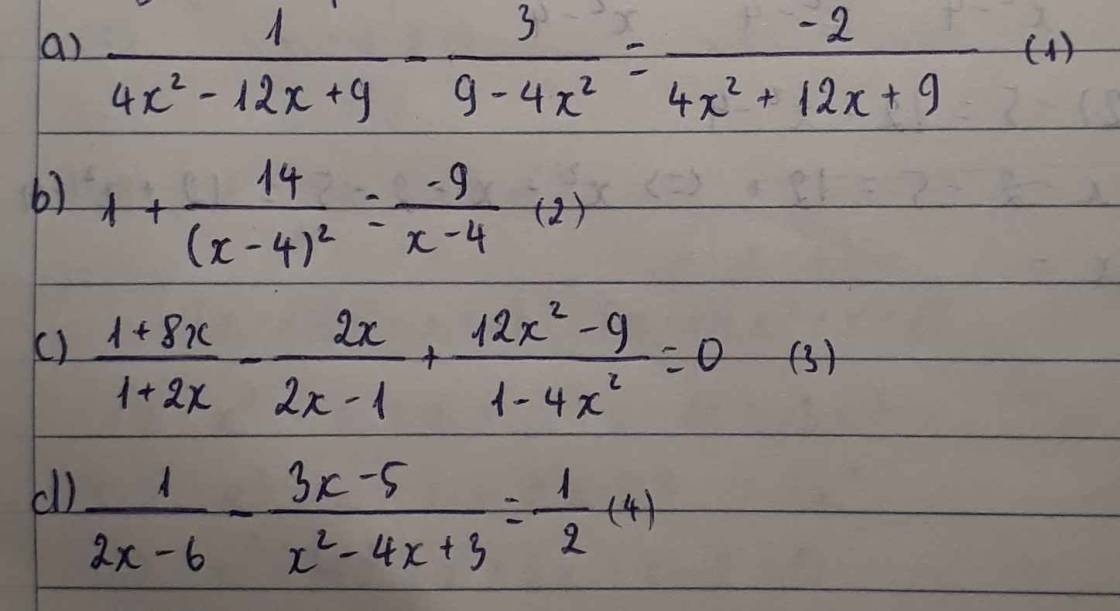
a) \(\dfrac{1}{\left(2x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{3}{\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)}+\dfrac{2}{\left(2x+3\right)^2}=0\left(Đk:x\ne\pm\dfrac{2}{3}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{1}{2x-3}+\dfrac{1}{2x+3}\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{2x-3}+\dfrac{2}{2x+3}\right)=0\)
+) \(\dfrac{1}{2x-3}=-\dfrac{1}{2x+3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+3=3-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
+) \(\dfrac{1}{2x-3}=-\dfrac{2}{2x+3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+3=2\left(3-2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
b) \(1+\dfrac{14}{\left(x-4\right)^2}=-\dfrac{9}{x-4}\left(Đk:x\ne4\right)\)
\(\left(x-4\right)^2+14+9\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(x^2-8x+16+14+9x-36=0\)
\(x^2+x-6=0\)
\(\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(\dfrac{1+8x}{1+2x}-\dfrac{2x}{2x-1}+\dfrac{12x^2-9}{1-4x^2}=0\left(Đk:x\ne\pm\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\)
\(\left(1+8x\right)\left(1-2x\right)+2x\left(1+2x\right)+12x^2-9=0\)
\(1-2x+8x-16x^2+2x+4x^2+12x^2-9=0\)
\(8x-8=0\)
\(x=1\)
d) \(\dfrac{1}{2\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{3x-5}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(Đk:x\ne1;x\ne3\right)\)
\(x-1+2\left(5-3x\right)=x^2-4x+3\)
\(9-5x=x^2-4x+3\)
\(x^2+x-6=0\)
\(\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải phương trình
360/x - 400/x+1 = 1
Giúp mik giải với ạ
\(\dfrac{360}{x}-\dfrac{400}{x+1}=1\) (ĐK: \(x\ne0,x\ne-1\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{360\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{400x}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow360\left(x+1\right)-400x=x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow360x+360-400x=x^2+x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-40x+360=x^2+x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+40x+x-360=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+41x-360=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta=41^2-4\cdot1\cdot\left(-360\right)=3121>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-41+\sqrt{3121}}{2\cdot1}\approx7\left(tm\right)\\x_2=\dfrac{-41-\sqrt{3121}}{2\cdot1}\approx-48\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{360}{x}-\dfrac{400}{x+1}=1\)
Điều kiện: \(x\ne0;x\ne-1\)
PT \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{360\left(x+1\right)-400x}{x\left(x+1\right)}=1\)
\(\Rightarrow-40x+360=x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-40x+360=x^2+x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+41x-360=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2.\dfrac{41}{2}.x+\dfrac{1681}{4}=\dfrac{3121}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+\dfrac{41}{2}\right)^2=\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{3121}}{2}\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+\dfrac{41}{2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3121}}{2}\) hoặc \(x+\dfrac{41}{2}=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3121}}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\sqrt{3121}}{2}-\dfrac{41}{2}\) hoặc \(x=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3121}}{2}-\dfrac{41}{2}\)
Vậy...
3/(2-x)>0
\(\dfrac{3}{2-x}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2-x>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 2\)
Vậy: ..
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x}\)-\(\dfrac{1}{x+1}\)=\(\dfrac{2x-1}{x^2+x}\)
Giải phương trình giúp mình với
ĐKXĐ: x<>0; x<>-1
PT =>(x-1)(x+1)-x=2x-1
=>x^2-1-x=2x-1
=>x^2-x-2x=0
=>x(x-3)=0
=>x=0(loại) hoặc x=3(nhận)
\(ĐK: x\ne 0; x\ne-1\)
Khi đó:
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}=\dfrac{2x-1}{x^2+x}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{1.x}{\left(x+1\right).x}-\dfrac{2x-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{x}{x\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{2x-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-1-x-2x+1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(loại\right)\\x=3\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy PT có nghiệm duy nhất \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(ĐKXĐ:x\ne0;x\ne-1\)
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}=\dfrac{2x-1}{x^2+x}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{1.x}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\\ \Rightarrow x^2-x+x-1-x=2x-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-x+x-x-2x=-1+1\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(ktm\right)\\x=3\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
x-1/x+2 + x+1/x-2 = 6/4-x^2
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x+2}+\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}=\dfrac{6}{4-x^2}\left(dkxd:x\ne\pm2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{x+2}+\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}=-\dfrac{6}{x^2-4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{x+2}+\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}+\dfrac{6}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)+\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)+6}{x^2-4}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-x+2+x^2+2x+x+2+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+10=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=-5\left(ktm\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\varnothing\)
Cho phương trình
\(\dfrac{x-a}{x+a}-\dfrac{x+a}{x-a}+\dfrac{3a^2+a}{3a^2-a^2}=0\)
a, Giải phương trình với a=3
b, Giải PT với a=1
c, Xác định a để PT có nghiệm x=0,5
a) Khi $a=3$, ta có phương trình:
$$x-3x+3-x+3x-3+3^2+3^3-3^2=0$$
$$\Leftrightarrow 6x=51 \Leftrightarrow x=\frac{17}{2}$$
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là $x=\frac{17}{2}$.
b) Khi $a=1$, ta có phương trình:
$$x-x+1-x+1x-1+3+1-1=0$$
$$\Leftrightarrow x=0$$
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là $x=0$.
c) Để phương trình có nghiệm $x=0,5$, ta cần giải phương trình:
$$0,5-a(0,5)+a-0,5+a(0,5)-a+3a^2+a^3-a^2=0$$
$$\Leftrightarrow a^3+3a^2-2a=0$$
$$\Leftrightarrow a(a-1)(a+2)=0$$
Vậy các giá trị của $a$ để phương trình có nghiệm $x=0,5$ là $a=0,1$ hoặc $a=-2$.
x/x+4 + x-3/x-4 - 5x-12/ x^2-15
Sửa đề: x^2-16
\(\dfrac{x}{x+4}+\dfrac{x-3}{x-4}-\dfrac{5x-12}{x^2-16}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-4x+x^2+x-12-5x+12}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2-8x}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)}=\dfrac{2x}{x+4}\)
Điều kiện xác định của phương trình x/2 +x+1/3-x giải giúp tuii với c.ơn nhìuuu
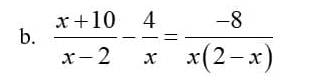 giúp mình với ạ
giúp mình với ạ
\(\dfrac{x+10}{x-2}-\dfrac{4}{x}=-\dfrac{8}{x\left(2-x\right)}\)
`<=>`\(\dfrac{x+10}{x-2}-\dfrac{4}{x}=\dfrac{8}{x\left(x-2\right)}\)
ĐKXĐ : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne0\\x-2\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne0\\x\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có :\(\dfrac{x+10}{x-2}-\dfrac{4}{x}=\dfrac{8}{x\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+10\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{4\left(x-2\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{8}{x\left(x-2\right)}\)
`=> x^2 +10x -4x+8 =8`
`<=> x^2 + 6x=0`
`<=> x(x+6)=0`
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(l\right)\\x=-6\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt có nghiệm `x=-6`
=>x(x+10)-4(x-2)=8
=>x^2+10x-4x+8=8
=>x^2+6x=0
=>x=0(loại) hoặc x=-6(nhận)
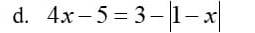 giúp ạ
giúp ạ
\(4x-5=3-\left|1-x\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3-\left|1-x\right|=4x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left|1-x\right|=4x-5-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left|1-x\right|=4x-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|1-x\right|=-\left(4x-8\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|1-x\right|=-4x+8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}1-x=-4x+8\\1-x=-\left(-4x+8\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-x+4x=8-1\\1-x=4x-8\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-x+4x=7\\-x-4x=-8+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x=7\\-5x=-7\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7}{3}\\x=\dfrac{7}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)