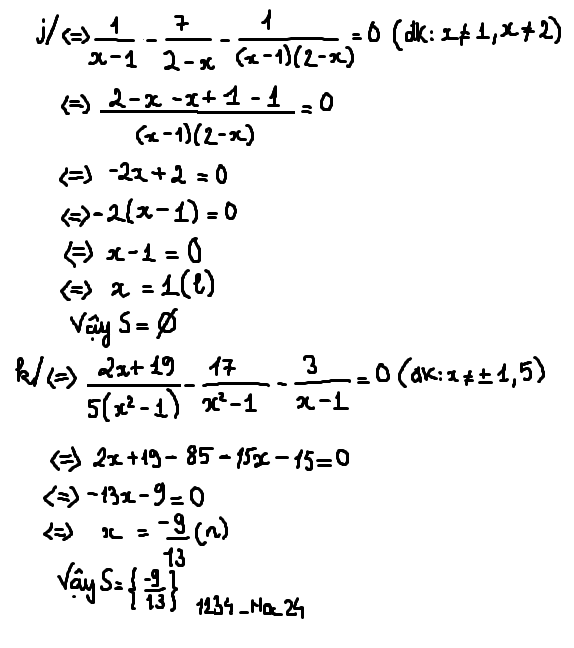giải phương trình \(\dfrac{1}{x^2-1}+\dfrac{5}{x+1}-\dfrac{1}{x-1}=1\)
H24
Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải các phương trình sau:
\(a.\dfrac{4x-5}{x-1}=2+\dfrac{x}{x-1}\)
\(b.\dfrac{7}{x+2}=\dfrac{3}{x-5}\)
\(c.\dfrac{14}{3x-12}-\dfrac{2+x}{x-4}=\dfrac{3}{8-2x}-\dfrac{5}{6}\)
\(d.\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}=\dfrac{16}{x^2-1}\)
TK
https://lazi.vn/edu/exercise/giai-phuong-trinh-4x-5-x-1-2-x-x-1-7-x-2-3-x-5
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a: \(\Leftrightarrow4x-5=2x-2+x\)
=>4x-5=3x-2
=>x=3(nhận)
b: =>7x-35=3x+6
=>4x=41
hay x=41/4(nhận)
c: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{14}{3\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{x+2}{x-4}=\dfrac{-3}{2\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{5}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{28}{6\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{6\left(x+2\right)}{6\left(x-4\right)}=\dfrac{-9}{6\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{5\left(x-4\right)}{6\left(x-4\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow28-6x-12=-9-5x+20\)
=>-6x+16=-5x+11
=>-x=-5
hay x=5(nhận)
d: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+1-\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=16\)
hay x=4(nhận)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
\(j.\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{7}{x-2}=\dfrac{1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(2-x\right)}\)
\(k.\dfrac{2x+19}{5x^2-5}-\dfrac{17}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{3}{1-x}\)
\(l.\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x^2+5}{x^3-1}=\dfrac{4}{x^2+x+1}\)
giải phương trình chứa ẩn ở mẫua/dfrac{5}{3}dfrac{5-3x}{2x}b/dfrac{x-4}{x+1}+dfrac{x-1}{x}2c/dfrac{x+2}{x-2}-dfrac{1}{x}dfrac{2}{xleft(x-2right)}d/dfrac{1}{x}+dfrac{3}{x+1}dfrac{2}{xleft(x+1right)}e/dfrac{x}{x-3}+dfrac{x}{x+1}dfrac{2x}{left(x-3right)left(x+1right)}f/dfrac{2}{x-3}-dfrac{4}{x+3}dfrac{5}{x^2-9}
Đọc tiếp
giải phương trình chứa ẩn ở mẫu
a/\(\dfrac{5}{3}\)=\(\dfrac{5-3x}{2x}\)
b/\(\dfrac{x-4}{x+1}\)+\(\dfrac{x-1}{x}\)=2
c/\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-2}\)-\(\dfrac{1}{x}\)=\(\dfrac{2}{x\left(x-2\right)}\)
d/\(\dfrac{1}{x}\)+\(\dfrac{3}{x+1}\)=\(\dfrac{2}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
e/\(\dfrac{x}{x-3}\)+\(\dfrac{x}{x+1}\)=\(\dfrac{2x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
f/\(\dfrac{2}{x-3}\)-\(\dfrac{4}{x+3}\)=\(\dfrac{5}{x^2-9}\)
a: =>10x=3(5-3x)
=>10x=15-9x
=>19x=15
=>x=15/19
b: =>\(\dfrac{x\left(x-4\right)+x^2-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}=2\)
=>2x^2+2x=x^2-4x+x^2-1=2x^2-4x-1
=>2x=-4x-1
=>6x=-1
=>x=-1/6
c:=>x(x+2)-x+2=2
=>x^2+2x-x=0
=>x(x+1)=0
=>x=0(loại) hoặc x=-1(nhận)
d: =>x+1+3x=2
=>4x=1
=>x=1/4
e: =>x(x+1)+x(x-3)=2x
=>x^2+x+x^2-3x=2x
=>2x^2-4x=0
=>x=0(nhận) hoặc x=2(nhận)
f: =>2x+6-4x+12=5
=>-2x=-13
=>x=13/2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình: \(\dfrac{x^2+1}{x} + \dfrac{x}{x^2+1}=\dfrac{5}{2} \)
=>(x^2+1)^2+x^2/x*(x^2+1)=5/2
=>\(\dfrac{\left(x^2+1\right)^2+x^2}{x\left(x^2+1\right)}=\dfrac{5}{2}\)
=>\(2\left(x^4+2x^2+1+x^2\right)=5\left(x^3+x\right)\)
=>2x^4+6x^2+2-5x^3-5x=0
=>2x^4-5x^3+6x^2-5x+2=0
=>2x^4-2x^3-3x^3+3x^2+3x^2-3x-2x+2=0
=>(x-1)(2x^3-3x^2+3x-2)=0
=>(x-1)(2x^3-2x^2-x^2+x+2x-2)=0
=>(x-1)^2*(2x^2-x+2)=0
=>x-1=0
=>x=1
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải bất phương trình:
\(\dfrac{1}{x^2}+\dfrac{x^2}{1-x^2}+\dfrac{5}{2}\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{1-x^2}}{x}+\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}\right)+2>0\)
giải/hệ/phương/trình:\(\dfrac{1}{x-2}+\dfrac{5}{2y-1}=3\)
\(\dfrac{3}{x-2}-\dfrac{1}{2y-1}=1\)
`đk:x ne 2,y ne 1/2`
ĐẶt `a=1/(x-2),b=1/(2y-1)`
`hpt<=>` $\begin{cases}a+5b=3\\3a-b=1\\\end{cases}$
`<=>` $\begin{cases}3a+15b=9\\3a-b=1\\\end{cases}$
`<=>` $\begin{cases}16b=8\\a=3-5b\\\end{cases}$
`<=>` $\begin{cases}b=\dfrac12\\a=\dfrac12\\\end{cases}$
`<=>` $\begin{cases}x-2=2\\2y-1=2\\\end{cases}$
`<=>` $\begin{cases}x=4\\y=\dfrac32\\\end{cases}$
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Đk: \(x\ne2;y\ne\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Đặt \(a=\dfrac{1}{x-2},b=\dfrac{1}{2y-1}\) (a,b khác 0)
Có hệ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+5b=3\\3a-b=1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+5b=3\\15a-5b=5\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}16a=8\\3a-b=1\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{1}{2}\\b=3a-1=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)(tm)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x-2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\\\dfrac{1}{2y-1}=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\y=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)(tm)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình sau: \(1+\dfrac{x-2}{1-x}+\dfrac{2x^2-5}{x^3-1}=\dfrac{4}{x^2+x+1}\)
`1+(x-2)/(1-x)+(2x^2-5)/(x^3-1)=4/(x^2+x+1)(x ne 1)`
`<=>(x^3-1)/(x^3-1)-((x-2)(x^2+x+1))/(x^3-1)+(2x^2-5)/(x^3-1)=(4(x-1))/(x^3-1)`
`<=>x^3-1-(x-2)(x^2+x+1)+2x^2-5=4(x-1)`
`<=>x^3-1-(x^3-x^2-x-2)+2x^2-5=4x-4`
`<=>x^3-1-x^3+x^2+x+2+2x^2-5-4x+4=0`
`<=>3x^2-3x+2=0`
`<=>x^2-2/3 x+2/3=0`
`<=>x^2-2.x. 1/3+1/9+5/9=0`
`<=>(x-1/3)^2=-5/9` vô lý
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne1\)
Ta có: \(1+\dfrac{x-2}{1-x}+\dfrac{2x^2-5}{x^3-1}=\dfrac{4}{x^2+x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^3-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}+\dfrac{2x^2-5}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}=\dfrac{4\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(x^3-1-\left(x^3+x^2+x-2x^2-2x-2\right)+2x^2-5=4x-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-1-x^3+x^2+x+2+2x^2-5-4x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x-1\right)=0\)
mà 3>0
nên x(x-1)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(nhận\right)\\x=1\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={0}
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
giải các phương trình sau
1, \(\dfrac{5x^2-12}{x^2-1}+\dfrac{3}{x-1}=\dfrac{5x}{x+1}\)
2, \(\dfrac{3}{x-5}-\dfrac{15-3x}{x^2-25}=\dfrac{3}{x+5}\)
3, \(\dfrac{-3}{x-4}-\dfrac{3-5x}{x^2-16}=\dfrac{1}{x+4}\)
1: Ta có: \(\dfrac{5x^2-12}{x^2-1}+\dfrac{3}{x-1}=\dfrac{5x}{x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5x^2-12}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{3x+3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{5x^2-5x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(5x^2+3x-9=5x^2-5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x=9\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{9}{8}\left(tm\right)\)
2: Ta có: \(\dfrac{3}{x-5}-\dfrac{15-3x}{x^2-25}=\dfrac{3}{x+5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x+15}{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{3x-15}{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{3x-15}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(6x=3x-15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-15\)
hay \(x=-5\left(loại\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
2. ĐKXĐ: $x\neq \pm 5$
PT \(\Leftrightarrow \frac{3}{x-5}+\frac{3x-15}{x^2-25}=\frac{3}{x+5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{3}{x-5}+\frac{3(x-5)}{(x-5)(x+5)}=\frac{3}{x+5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{3}{x-5}+\frac{3}{x+5}=\frac{3}{x+5}\Leftrightarrow \frac{3}{x-5}=0\) (vô lý)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
3. ĐKXĐ: $x\neq \pm 4$
PT \(\Leftrightarrow \frac{-3(x+4)}{(x-4)(x+4)}-\frac{3-5x}{(x-4)(x+4)}=\frac{x-4}{(x-4)(x+4)}\)
\(\Rightarrow -3(x+4)-(3-5x)=x-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 2x-15=x-4\Leftrightarrow x=11\) (thỏa mãn)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình saua) dfrac{6x+1}{x^2-7x+10}+ dfrac{5}{x-2}dfrac{3}{x-5}b) dfrac{2}{x^2-4}-dfrac{x-1}{xleft(x-2right)}+dfrac{x-4}{xleft(x+2right)}c) dfrac{1}{3-x}-dfrac{1}{x+1}dfrac{x}{x-3}-dfrac{left(x-1right)^2}{x^2-2x-3}
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau
a) \(\dfrac{6x+1}{x^2-7x+10}\)+ \(\dfrac{5}{x-2}\)=\(\dfrac{3}{x-5}\)
b) \(\dfrac{2}{x^2-4}\)-\(\dfrac{x-1}{x\left(x-2\right)}\)+\(\dfrac{x-4}{x\left(x+2\right)}\)
c) \(\dfrac{1}{3-x}\)-\(\dfrac{1}{x+1}\)=\(\dfrac{x}{x-3}\)-\(\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{x^2-2x-3}\)
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;5\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{6x+1}{x^2-7x+10}+\dfrac{5}{x-2}=\dfrac{3}{x-5}\)
=>\(\dfrac{6x+1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}+\dfrac{5}{x-2}=\dfrac{3}{x-5}\)
=>\(6x+1+5\left(x-5\right)=3\left(x-2\right)\)
=>6x+1+5x-25-3x+6=0
=>8x-18=0
=>8x=18
=>\(x=\dfrac{9}{4}\left(nhận\right)\)
b: Đề thiếu vế phải rồi bạn
c: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-1;3\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3-x}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}=\dfrac{x}{x-3}-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{x^2-2x-3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-1}{x-3}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}-\dfrac{x}{x-3}=\dfrac{-\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+1}{x-3}+\dfrac{1}{x+1}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
=>\(\left(x+1\right)^2+x-3=\left(x-1\right)^2\)
=>\(x^2+2x+1+x-3=x^2-2x+1\)
=>\(3x-2=-2x+1\)
=>5x=3
=>\(x=\dfrac{3}{5}\left(nhận\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)