cho hai sốx;y>0.biết x:y=4:5 và x.y=5 tìm hai số đó
cho các sốx= 1+2+22+...+22012+22013; y=22014. Chứng minh x, y là hai số tự nhiên liên tiếp
Minh hoạ tập nghiêm phương trình sau bằng đồ thị hàm số
x+y=3
giải BPT sau rồi biểu diễn tập nghiệm trên trục số
x + 2 / x - 3 < 0
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x+2}{x-3}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2>0\\x-3< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow-2< x< 3\)
Vậy: S={x|-2<x<3}
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2< 0\\x-3>0\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2>0\\x-3< 0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< -2\\x>3\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>-2\\x< 3\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2< x< 3\)
Vậy ...
Giải bất phương trình sau và biểu diễn nghiệm trên trục số
X-2/6-x-1/6
Giải bất phương trình sau và biểu diễn nghiệm trên trục số
x-2/6 - x-1/3 < x/2
`(x-2)/6 -(x-1)/3 < x/2`
`<=> (x-2)/6 -(2(x-1))/6 < (3x)/6`
`<=> x-2 - (2x-2) <3x`
`<=> x-2-2x+2<3x`
`<=> -x <3x`
`<=> -x-3x<0`
`<=> -4x<0`
`<=> x>0`
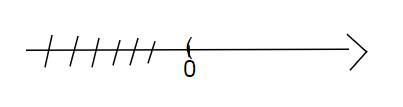
\(\dfrac{x-2}{6}\)-\(\dfrac{x-1}{3}\)<\(\dfrac{x}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{x-2}{6}\)-\(\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)}{6}\)<\(\dfrac{6x}{6}\)
<=>x-2-2x+2<6x
<=>-7x<0
<=>x>0
vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là
\(\left\{x|x>0\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x-2}{6}-\dfrac{x-1}{3}< \dfrac{x}{2}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-2}{6}-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)2}{3.2}< \dfrac{x.3}{2.3}\\ \Leftrightarrow x-2-2x+2< 3x\\ \Leftrightarrow x-2x-3x< -2\\ \Leftrightarrow-4x< -2\\ \Leftrightarrow x>\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy bất phương trình có tập nghiệm là:
\(S=\left\{x|x>\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
Biểu diễn:
giải bất phương trình sau và biểu diễn trên trục số
x\(-\)5 \(\ge\) 8\(-\)3x
x\(-\)3 < x\(-\)5
Giải :
\(x-5\ge8-3x\\ \Leftrightarrow x+3x\ge8+5\\ \Leftrightarrow4x\ge13\\ \Leftrightarrow x\ge\dfrac{13}{4}\)
Biểu diễn :
b,
\(x-3< x-5\\ \Leftrightarrow-3< -5\left(voli\right)\)
Cho 2 sốx,y thỏa mãn:2(x2+y2)=2025 Giá trị lớn nhất của x+y là
may ban giup minh voi
Bạn may đấy...
----------------
Ta có: \(2\left(x^2+y^2\right)\ge\left(x+y\right)^2\)
nên \(2025\ge\left(x+y\right)^2\) (do \(2\left(x^2+y^2\right)=2025\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\sqrt{2025}\ge x+y\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(45\ge x+y\) với mọi \(x;y\)
Vậy, Giá trị lớn nhất của \(x+y\) là \(45\)
Tìm phần nguyên của hỗn số
x và 4/15 biết 5 và 1/5 bé hơn x và 4/5 bé hơn 9 và 4/13
Ta có: \(5\dfrac{1}{5}< x\dfrac{4}{15}< 9\dfrac{4}{13}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{26}{5}< \dfrac{15x+4}{15}< \dfrac{131}{13}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1014}{195}< \dfrac{13\left(15x+4\right)}{195}< \dfrac{1965}{195}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1014< 195x+52< 1965\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}195x>962\\195x< 2017\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{962}{195}< x< \dfrac{2017}{195}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{5;6;7;8;9;10\right\}\)
1. Tính:a) A=1253.24; b) B=\(\frac{1}{49^4}\).77; c) C=\(\frac{27^3+9^5}{81^3+3^{11}}\); d) D=\(\frac{\frac{4}{9}+\frac{28}{15}-\frac{12}{4}}{\frac{5}{9}+\frac{35}{15}-\frac{15}{4}}\)
2. a) Tìm GTNN của A= (2x-3)2-7; b) Tìm GTLN của 3- giá trị tuyệt đối của 3x-2
3. Tìm sốx nguyên để các số sau là số nguyên: a)A= 2+\(\frac{3}{x+1}\);b) B=\(\frac{3x-1}{x-1}\)