Giải các phương trình sau: 13 x - 3 2 x + 7 + 1 2 x + 7 = 6 x 2 - 9
Tuyển Cộng tác viên Hoc24 nhiệm kì 26 tại đây: https://forms.gle/dK3zGK3LHFrgvTkJ6
PB
Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải các phương trình sau bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích x + 1 3 –x +1 = (x -1)(x -2)
Ta có: x + 1 3 –x +1 = (x -1)(x -2)
⇔ x 3 +3 x 2 +3x +1 –x +1 = x 2 -2x –x +2
⇔ x 3 +2 x 2 +5x = 0 ⇔ x( x 2 + 2x + 5) =0
⇔ x =0 hoặc x 2 +2x +5 =0
Giải phương trình x 2 +2x +5 =0
∆ ’ = 1 2 - 1.5 = 1 - 5 = -4 < 0 ⇒ phương trình vô nghiệm
Vậy phương trình đã cho có 1 nghiệm : x=0
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:a)
2
x
−
1
3
+
6
3
x
−
1
2
2
x
+
1
3
+
6...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 2 x − 1 3 + 6 3 x − 1 2 = 2 x + 1 3 + 6 x + 2 3 ;
b) x − 2 2 + 3 − 2 x 2 − 4 x − 4 x − 5 = x + 3 2 ;
c) x − 3 + 2 x − 3 − 1 3 = 3 − x 4 ;
d) x + 4 3 − 1 7 = 2 − x 7 + x 3 + x + 1 .
Giải các phương trình sau:
1
3
-
x
-
1
x
+
1
x
x
-
3
-
(
x
-
1
)
2
x
2
-
2...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau: 1 3 - x - 1 x + 1 = x x - 3 - ( x - 1 ) 2 x 2 - 2 x - 3
ĐKXĐ: x ≠ - 1;x ≠ 3.
Ta có: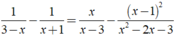
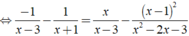
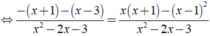
![]()
⇔ -2x + 2 = 3x - 1
⇔ 5x = 3 ⇔ x = 3/5.
Kết hợp điều kiện, vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm là x = 3/5.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
1
3
-
x
-
1
x
+
1
x
x
-
3
-
(
x
-
1
)
2
x
2
-
2...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau: 1 3 - x - 1 x + 1 = x x - 3 - ( x - 1 ) 2 x 2 - 2 x - 3
Giải các phương trình sau
a) x^4 – 3x^2 + 6x + 13 = 0
b) x^6 + x^5 + x^4 + x^3 + x^2 + x + 1 = 0
Giải các bất phương trình sau và viết tập nghiệm bằng kí hiệu tập hợp:a)
x
+
2
7
−
1
21
3
x
+
1
3
;
b)
1
+
x
−
2
3
5...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các bất phương trình sau và viết tập nghiệm bằng kí hiệu tập hợp:
a) x + 2 7 − 1 21 > 3 x + 1 3 ; b) 1 + x − 2 3 > 5 − x + 3 ( x − 2 ) 3
giải các phương trình sau
1/ 7x-5=13-5x
2/ 19+3x=5-18x
3/ x^2+2x-4=-12+3x+x^2
4/ -(x+5)=3(x-5)
5/ 3(x+4)=(-x+4)
1/ \(7x-5=13-5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
==========
2/ \(19+3x=5-18x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow21x=-14\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{2}{3}\right\}\)
==========
3/ \(x^2+2x-4=-12+3x+x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x=-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=8\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{8\right\}\)
===========
4/ \(-\left(x+5\right)=3\left(x-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x-5=3x-15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x=-10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{5}{2}\right\}\)
==========
5/ \(3\left(x+4\right)=\left(-x+4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x+12=-x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-2\right\}\)
[----------]
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1. \(7x-5=13-5x\) \(\Leftrightarrow12x=18\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
2. \(19+3x=5-18x\Leftrightarrow21x=-14\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
3. \(x^2+2x-4=-12+3x+x^2\Leftrightarrow-x=-8\Leftrightarrow x=8\)
4. \(-\left(x+5\right)=3\left(x-5\right)\Leftrightarrow-x-5=3x-15\Leftrightarrow4x=10\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\)
5. \(3\left(x+4\right)=-x+4\Leftrightarrow3x+12=-x+4\Leftrightarrow4x=-8\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1) Ta có: \(7x-5=13-5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x=18\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
2) Ta có: \(19+3x=5-18x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow21x=-14\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
3) Ta có: \(x^2+2x-4=x^2+3x-12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-12=2x-4\)
hay x=8
4) Ta có: \(-\left(x+5\right)=3\left(x-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x-5-3x+15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x=-10\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{5}{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau
a) x^4 – 3x^2 + 6x + 13 = 0
b) x^6 + x^5 + x^4 + x^3 + x^2 + x + 1 = 0
a, pt <=> (x^4-4x+4)+(x^2+6x+9) = 0
<=> (x^2-2)^2+(x+3)^2=0
<=> x^2-2=0 và x+3=0
=> pt vô nghiệm
b, pt <=> (x-1).(x^6+x^5+x^4+x^3+x^2+x+1) = 0
<=> x^7+x^6+x^5+x^4+x^3+x^2+x-x^6-x^5-x^4-x^3-x^2-x-1 = 0
<=> x^7-1=0
<=> x^7=1 = 1^7
=> x=1
Tk mk nha
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
3.15 giải các phương trình sau :
a) ( x - 6 ) ( 2x - 5 ) ( 3x + 9 ) = 0
b) 2x( x - 3 ) + 5( x - 3 ) = 0
c) ( x^2 - 4 ) - ( x - 2 ) ( 3 - 2x ) =0
3.16 tìm m để phương trình sau có nghiệm :
x=-7 ( 2m - 5 )x - 2m^2 + 8
3.17 giải các phương trình sau :
a) ( 2x - 1 )^2 - ( 2x + 1 ) = 0
\(a,\left(x-6\right)\left(2x-5\right)\left(3x+9\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\Leftrightarrow x=6\\2x-5=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\3x+9=0\Leftrightarrow x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,2x\left(x-3\right)+5\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+5\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\Leftrightarrow x=3\\2x+5=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,x^2-4-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2-3+2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x=-7\left(2m-5\right)x-2m^2+8\Leftrightarrow x+7\left(2m-5\right)=8-2m^2\Leftrightarrow x\left(14m-34\right)=8-2m^2\)
\(ycđb\Leftrightarrow14m-34\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne\dfrac{34}{14}\)\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{8-2m^2}{14m-34}\)
\(3.17\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1-2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow4x^2-6x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(4x-6\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
3.15:
a, \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\\2x-5=0\\3x+9=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{9}{3}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(2x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\2x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2-3+2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\3x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
3.16
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m-5\right).-7-2m^2+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14m+35-2m^2+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14m-2m^2+43=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2\left(7m+m^2\right)=-43\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(7-m\right)=\dfrac{43}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{m\left(7-m\right)}{1}-\dfrac{43}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{14m-2m^2}{2}-\dfrac{43}{2}=0\)
pt vô nghiệm
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau theo phương pháp đặt ẩn phụ:
a.{\(\dfrac{12}{x-3}-\dfrac{5}{y+2}=63\)
\(\dfrac{8}{x-3}+\dfrac{15}{y+2}=-13\)
b.{\(4\sqrt{x+3}-9\sqrt{y+1}=2\)
\(5\sqrt{x+3}+3\sqrt{y+1}=31\)
a: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{12}{x-3}-\dfrac{5}{y+2}=63\\\dfrac{8}{x-3}+\dfrac{15}{y+2}=-13\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{24}{x-3}-\dfrac{10}{y+2}=126\\\dfrac{24}{x-3}+\dfrac{45}{y+2}=-39\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{-55}{y+2}=165\\\dfrac{12}{x-3}-\dfrac{5}{y+2}=63\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y+2=\dfrac{-1}{3}\\\dfrac{12}{x-3}=48\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{7}{3}\\x=\dfrac{13}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)








