giải pt chứa ẩn ở mẫu
4x2-2x/2x2+1=0
Giải phương trình chứa ẩn ở mẫu sau:
2 x − 1 x 2 + 4 x − 5 + x − 2 x 2 − 10 x + 9 = 3 x − 12 x 2 − 4 x − 45 .
Giải phương trình chứa ẩn ở mẫu sau:
1 2 x 2 + 5 x − 7 − 2 x 2 − 1 = 3 2 x 2 − 5 x − 7
Giải pt chứa ẩn ở mẫu sau :1/7-x=x-8/x-7-8
Giải pt chứa ẩn ở mẫu(làm J,k,l nha)
j: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)-x\left(x+2\right)=-5x+2\)
=>x^2-3x+2-x^2-2x=-5x+2
=>-5x+2=-5x+2
=>0x=0(luôn đúng)
k: =>(x-2)^2-3(x+2)=2x-22
=>x^2-4x+4-3x-6=2x-22
=>x^2-7x-2-2x+22=0
=>x^2-9x+20=0
=>x=4 hoặc x=5
Giải pt bằng delta và tìm nghiệm:
a) 2x2 - 5x + 1 = 0
b) 4x2 + 4x + 1 =0
c) 5x2 - x + 2 =0
a) \(2x^2-5x+1=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac\Rightarrow\left(-5\right)^2-4.2.1=17>0\)
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt:
\(x_1=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-\left(-5\right)+\sqrt{17}}{2.2}=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{17}}{4}\)
\(x_2=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-\left(-5\right)-\sqrt{17}}{2.2}=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{17}}{4}\)
___________________________________________________
b) \(4x^2+4x+1=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac\Rightarrow4^2-4.4.1=0\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm kép:
___________________________________________________
c) \(5x^2-x+2=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4a\Rightarrow\left(-1\right)^2-4.5.2=-39\)
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.
\(a,2x^2-5x+1=0\)
\(\Delta=-b^2-4ac\)
\(\Delta=25-8\)
\(\Delta=17\)
Vậy phương trình có `2` nghiệm phân biệt :
\(x_1=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{17}}{4} \)
\(x_2=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{17}}{4}\)
\(b,4x^2+4x+1=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac\)
\(\Delta=16-16=0\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm kép :
\(x=\dfrac{-b}{2a}=-\dfrac{4}{8}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(c,5x^2-x+2=0\)
\(\Delta=1-40\)
\(\Delta=-39\)
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm .
Giải các pt chứa ẩn ở mẫu:
a) \(\frac{x+2}{x-2}-\frac{1}{x}=\frac{2}{x^2-2x}\)
b) \(\frac{2x-5}{x+5}=3\)
c) \(\frac{\left(x^2+2x\right)-\left(3x+6\right)}{x-3}=0\)
a, Ta có: \(\frac{x+2}{x-2}-\frac{1}{x}=\frac{2}{x^2-2x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+2}{x-2}-\frac{2}{x^2-2x}=\frac{1}{x}\)
\(Đkxđ:\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne2\\x\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(Pt\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+2\right)-2=x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(ktm\right)\\x=-1\left(tmđk\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy .........
\(b,Đkxđ:x\ne-5\)
Ta có: \(\frac{2x-5}{x+5}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-5=3\left(x+5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=20\left(tmđk\right)\)
Vậy .........
c, \(Đkxđ:x\ne3\)
Ta có: \(\frac{\left(x^2+2x\right)-\left(3x+6\right)}{x-3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-3x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)+2\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\left(tm\right)\\x=3\left(ktmđk\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ............
`4x=2+xx+1x<=>4x=2+3x<=>4x-3x=2<=>1x=2<=>x=2`
Giải phương trình bằng cách đặt ẩn phụ:
2 x 2 - 2 x 2 + 3 x 2 - 2 x + 1 = 0
2(x2 – 2x)2 + 3(x2 – 2x) + 1 = 0 (1)
Đặt x2 – 2x = t,
(1) trở thành : 2t2 + 3t + 1 = 0 (2).
Giải (2) :
Có a = 2 ; b = 3 ; c = 1
⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có nghiệm t1 = -1; t2 = -c/a = -1/2.
+ Với t = -1 ⇒ x2 – 2x = -1 ⇔ x2 – 2x + 1 = 0 ⇔ (x – 1)2 = 0 ⇔ x = 1.
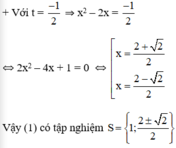
X/x+1-2x-3/x-1=2x+3/x^2-1 giải phương trình chứa ẩn ở mẫu!!😀😀
\(\frac{x}{x+1}-\frac{2x-3}{x-1}=\frac{2x+3}{x^2-1}\) ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 1; x ≠ -1
⇔x(x - 1) - (2x - 3)(x + 1) = 2x + 3
⇔ x2 - x - 2x2 + 3x - 2x + 3 = 2x + 3
⇔ -x2 - 2x = 0
⇔ -x(x + 2) = 0
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\) (TM)
Vậy nghiệm của pt là x = 0; x = -2
ĐKXĐ: x≠1; x≠-1
Ta có: \(\frac{x}{x+1}-\frac{2x-3}{x-1}=\frac{2x+3}{x^2-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}-\frac{\left(2x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\frac{2x+3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-\left(2x^2+2x-3x-3\right)-\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-2x^2+x+3-2x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^2-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: x∈{0;-2}