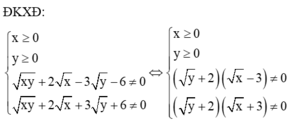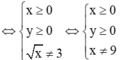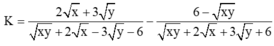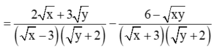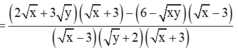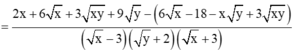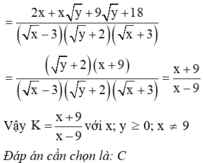6-2x
NH
Những câu hỏi liên quan
|2x+6|-x3
TH1 |2x+6|2x+6
khi
2x+60hayx -3ta có dạng pt2x+6-x3x+63x-3TMTH2|2x+6|-2x-6
khi
2x+6 0hay
x-3ta có dạng pt -2x-6-x3-3x-63-3x9x-3TMmọi người xem hộ em đúng không ạ
Đọc tiếp
\(|2x+6|-x=3
\)
TH1 \(|2x+6|=2x+6
khi
2x+6>=0hayx< =-3\)
ta có dạng pt
2x+6-x=3
<=>x+6=3
<=>x=-3TM
TH2\(|2x+6|=-2x-6
khi
2x+6< 0hay
x>-3\)
ta có dạng pt
-2x-6-x=3
<=>-3x-6=3
<=>-3x=9
<=>x=-3TM
mọi người xem hộ em đúng không ạ
ngược dấu hai chỗ điều kiện rồi bạn
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Cho biểu thức:
K
2
x
+
3
y
xy
+
2
x
-
3
y
-
6
-
6
-
xy
xy
+...
Đọc tiếp
Cho biểu thức: K = 2 x + 3 y xy + 2 x - 3 y - 6 - 6 - xy xy + 2 x + 3 y + 6
A. K = x + 9 x - 9
B. K = x - 9 x + 9
C. K = x + 9 x - 9
D. K = 1 x + 3
Tính:
a) \(\dfrac{x+1}{2x-6}+\dfrac{2x+3}{x^2+3x}\)
b) \(\dfrac{3}{2x+6}-\dfrac{x-6}{3x^2+6}\)
c) \(\dfrac{2x+6}{3x^2-x}:\dfrac{x^2+3x}{1-3x}\)
c: \(=\dfrac{2\left(x+3\right)}{x\left(3x-1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{-\left(3x-1\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{-2}{x^2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình sau
1/ 2x( x+3) - 6 (x-3) =0
2/ 2x^2( 2x+3) +(2x+3) =0
3/ (x-2) (x+1) -(x-2) 4x =0
4/ 2x ( x-5) -3x +15=0
5/ 3x(x+4) -2x-8 =0
6/ x^2 (2x-6) + 2x -6 =0
1: Ta có: \(2x\left(x+3\right)-6\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+6x-6x+18=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+18=0\left(loại\right)\)
2: Ta có: \(2x^2\left(2x+3\right)+\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+3=0\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
3: Ta có: \(\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)-4x\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(1-3x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
4: Ta có: \(2x\left(x-5\right)-3x+15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(2x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
5: Ta có: \(3x\left(x+4\right)-2x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\x=\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
6: Ta có: \(x^2\left(2x-6\right)+2x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-6=0\)
hay x=3
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
cho đa thức p(x)=|2x-6|-|2x-2| tìm x sao cho|2x-6|-|2x-2|=6
và để P() mìn
giải phương trình sau
\(\dfrac{2x+5}{95}+\dfrac{2x+6}{94}+\dfrac{2x+7}{93}=\dfrac{2x+93}{7}+\dfrac{2x+94}{6}\dfrac{2x+95}{5}\)
Ta có : \(\dfrac{2x+5}{95}+\dfrac{2x+6}{94}+\dfrac{2x+7}{93}=\dfrac{2x+93}{7}+\dfrac{2x+94}{6}+\dfrac{2x+95}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+5}{95}+\dfrac{2x+6}{94}+\dfrac{2x+7}{93}-\dfrac{2x+93}{7}-\dfrac{2x+94}{6}-\dfrac{2x+95}{5}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+5}{95}+1+\dfrac{2x+6}{94}+1+\dfrac{2x+7}{93}+1-\dfrac{2x+93}{7}-1-\dfrac{2x+94}{6}-1-\dfrac{2x+95}{5}-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+100}{95}+\dfrac{2x+6}{94}+\dfrac{2x+7}{93}-\dfrac{2x+100}{7}-\dfrac{2x+100}{6}-\dfrac{2x+100}{5}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+100\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{95}+\dfrac{1}{94}+\dfrac{1}{93}-\dfrac{1}{7}-\dfrac{1}{6}-\dfrac{1}{5}\right)=0\)
Thấy : \(\dfrac{1}{95}+\dfrac{1}{94}+\dfrac{1}{93}-\dfrac{1}{7}-\dfrac{1}{6}-\dfrac{1}{5}\ne0\)
\(\Rightarrow2x+100=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-50\)
Vậy ...
Đúng 1
Bình luận (2)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{2x+5}{95}+\dfrac{2x+6}{94}+\dfrac{2x+7}{93}=\dfrac{2x+93}{7}+\dfrac{2x+94}{6}+\dfrac{2x+95}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+5}{95}+1+\dfrac{2x+6}{94}+1+\dfrac{2x+7}{93}+1=\dfrac{2x+93}{7}+1+\dfrac{2x+94}{6}+1+\dfrac{2x+95}{5}+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+100}{95}+\dfrac{2x+100}{94}+\dfrac{2x+100}{93}=\dfrac{2x+100}{7}+\dfrac{2x+100}{6}+\dfrac{2x+100}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+100\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{95}+\dfrac{1}{94}+\dfrac{1}{93}\right)=\left(2x+100\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{7}+\dfrac{1}{6}+\dfrac{1}{5}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+100\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{95}+\dfrac{1}{94}+\dfrac{1}{93}\right)-\left(2x+100\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{7}+\dfrac{1}{6}+\dfrac{1}{5}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+100\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{95}+\dfrac{1}{94}+\dfrac{1}{93}-\dfrac{1}{7}-\dfrac{1}{6}-\dfrac{1}{5}\right)=0\)
mà \(\dfrac{1}{95}+\dfrac{1}{94}+\dfrac{1}{93}-\dfrac{1}{7}-\dfrac{1}{6}-\dfrac{1}{5}\ne0\)
nên 2x+100=0
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-100\)
hay x=-50
Vậy: S={-50}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
rút gọn: P=(2x+3y)/(xy+2x-3y-6) - (6-xy)/(xy+2x+3y+6) - (x^2 +9)/( x^2 -9)
Điều kiện \(x\ne\pm3;y\ne-2\):
\(P=\frac{2x+3y}{xy+2x-3y-6}-\frac{6-xy}{xy+2x+3y+6}-\frac{x^2+9}{x^2-9}.\)
=> \(P=\frac{2x+3y}{\left(y+2\right)\left(x-3\right)}-\frac{6-xy}{\left(y+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}-\frac{x^2+9}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{\left(2x+3y\right)\left(x+3\right)-\left(6-xy\right)\left(x-3\right)-\left(x^2+9\right)\left(y+2\right)}{\left(y+2\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{2x^2+3xy+6x+9y-6x+x^2y+18-3xy-x^2y-9y-2x^2-18}{\left(y+2\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{0}{\left(y+2\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
=> P=0 (với mọi x khác 3, -3 và y khác -2)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(\sqrt{2x-2+2\sqrt{2x-3}}=4+\sqrt{2x-6-6\sqrt{2x-3}}\)
ĐỖ THỊ THANH HẬU: Dấu căn ở VP là \(\sqrt{2x+6-6\sqrt{2x-3}}\) chứ bạn nhỉ ? Nếu đề đúng thì ib nhé.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x từ phương trình (2x + 1) + (2x + 6) + (2x + 11) + ... + (2x + 96) = 1010 biết 1, 6, 11, ... là cấp số cộng.
Xét cấp số cộng 1, 6, 11, ..., 96.
Ta có: 96 = 1 + 5(n − 1) ⇒ n = 20
Suy ra
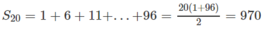
Và 2x.20 + 970 = 1010
Từ đó x = 1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1,Tìm x
5^x-5^x+2=650
2x-3/11+2x-4/12+2x-5/13=2x-6/14+2x-7/15+2x-8/6
5^x + 5^ ( x + 2 ) = 650
5x + 5x . 52 = 650
5x .( 1 + 25 ) = 650
5x . 26 = 650
5x = 650 : 26
5x = 25
5x = 52
=> x = 2
Vậy x = 2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
The Reflection Of Light~ Ủa đề là 5^x-5^x+2= 650 sao ông lại đổi thành 5^x-5^(x+2) zậy
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)