1. giải phương trình: y(x-1)=x2+2
2. x6+x3-15x2z=3x2y2z - (y2+5)3
3. tìm nghiệm nguyên tố: y2-2x2=1
Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên: (y2+1)(2x2+x+1)=x+5
Do \(2x^2+x+1>0;\forall x\) nên pt tương đương:
\(y^2+1=\dfrac{x+5}{2x^2+x+1}\)
Ta có: \(6-\dfrac{x+5}{2x^2+x+1}=\dfrac{12x^2+5x+1}{2x^2+x+1}=\dfrac{12\left(x+\dfrac{5}{24}\right)^2+\dfrac{23}{48}}{2\left(x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{7}{8}}>0\) ; \(\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x+5}{2x^2+x+1}< 6\Rightarrow y^2+1< 6\)
\(\Rightarrow y^2< 5\) \(\Rightarrow y^2=\left\{0;1;4\right\}\)
- Với \(y^2=0\Rightarrow y=0\Rightarrow2x^2+x+1=x+5\Rightarrow x^2=2\) (ko tồn tại x nguyên thỏa mãn) \(\Rightarrow\) loại
- Với \(y^2=1\Rightarrow2\left(2x^2+x+1\right)=x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+x-3=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=\dfrac{3}{4}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
- Với \(y^2=4\Rightarrow5\left(2x^2+x+1\right)=x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10x^2+4x=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-\dfrac{2}{5}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt có 4 cặp nghiệm nguyên:
\(\left(x;y\right)=\left(-1;-1\right);\left(-1;1\right);\left(0;-2\right);\left(0;2\right)\)
1) Tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình : x2= 2y2+2013
2) Giải phương trình x3+2x2- 4x +\(\dfrac{8}{3}\)=0
Ta có \(2y^2⋮2\Rightarrow x^2\equiv1\left(mod2\right)\Rightarrow x^2\equiv1\left(mod4\right)\Rightarrow2y^2⋮4\Rightarrow y⋮2\Rightarrow x^2\equiv5\left(mod8\right)\) (vô lí).
Vậy pt vô nghiệm nguyên.
2: \(PT\Leftrightarrow3x^3+6x^2-12x+8=0\Leftrightarrow4x^3=\left(x-2\right)^3\Leftrightarrow\sqrt[3]{4}x=x-2\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{-2}{\sqrt[3]{4}-1}\).
Bài 1: Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử
a)x2-y2-2x+2y e)x4+4y4
b)x2(x-1)+16(1-x) f)x4-13x2+36
c)x2+4x-y2+4 g) (x2+x)2+4x2+4x-12
d)x3-3x2-3x+1 h)x6+2x5+x4-2x3-2x2+1
a.
$x^2-y^2-2x+2y=(x^2-y^2)-(2x-2y)=(x-y)(x+y)-2(x-y)=(x-y)(x+y-2)$
b.
$x^2(x-1)+16(1-x)=x^2(x-1)-16(x-1)=(x-1)(x^2-16)=(x-1)(x-4)(x+4)$
c.
$x^2+4x-y^2+4=(x^2+4x+4)-y^2=(x+2)^2-y^2=(x+2-y)(x+2+y)$
d.
$x^3-3x^2-3x+1=(x^3+1)-(3x^2+3x)=(x+1)(x^2-x+1)-3x(x+1)$
$=(x+1)(x^2-4x+1)$
e.
$x^4+4y^4=(x^2)^2+(2y^2)^2+2.x^2.2y^2-4x^2y^2$
$=(x^2+2y^2)^2-(2xy)^2=(x^2+2y^2-2xy)(x^2+2y^2+2xy)$
f.
$x^4-13x^2+36=(x^4-4x^2)-(9x^2-36)$
$=x^2(x^2-4)-9(x^2-4)=(x^2-9)(x^2-4)=(x-3)(x+3)(x-2)(x+2)$
g.
$(x^2+x)^2+4x^2+4x-12=(x^2+x)^2+4(x^2+x)-12$
$=(x^2+x)^2-2(x^2+x)+6(x^2+x)-12$
$=(x^2+x)(x^2+x-2)+6(x^2+x-2)=(x^2+x-2)(x^2+x+6)$
$=[x(x-1)+2(x-1)](x^2+x+6)=(x-1)(x+2)(x^2+x+6)$
h.
$x^6+2x^5+x^4-2x^3-2x^2+1$
$=(x^6+2x^5+x^4)-(2x^3+2x^2)+1$
$=(x^3+x^2)^2-2(x^3+x^2)+1=(x^3+x^2-1)^2$
giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên : x2-x=y2-1
giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên:
a,2x2+4x=19-3y2
b,y2=-2(x2-x3y-32)
a)2x2+4x=19-3y2
⇔2x2+4x+2=21-3y2
⇔2(x+1)2=3(7-y2)Ta có 2(x+1)2⋮2⇒3(7-y2)⋮2
⇒7-y2⋮2
⇒y lẻ (1)
Ta lại có 2(x+1)2≥0
⇒3(7-y2)≥0
⇒7-y2≥0
⇒y2≤7
⇒y2∈{1;4} (2)
Từ (1),(2)⇒y2∈{1}
⇒y∈{-1;1}
Ta có y2=1⇒2(x+1)2=3(7-y2)=18⇒(x+1)2=9
⇒x+1=3 hoặc x+1=-3
⇒x=2 hoặc x=-4
Vậy {x,y}={(-1;2);(-1;-4);(1;2);(1;-4)}
gọi x1,x2 là 2 nghiệm của phương trình \(3x^2+5X-6=0\) không giải phương trình hãy lập phương trình bậc hai ẩn y có 2 nghiệm y1,y2 thỏa mãn y1=2x1-x2 và y2=2x2-x1
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{5}{3}\\x_1x_2=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y_1+y_2=2x_1-x_2+2x_2-x_1\\y_1y_2=\left(2x_1-x_2\right)\left(2x_2-x_1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y_1+y_2=x_1+x_2\\y_1y_2=-2x_1^2-2x_2^2+5x_1x_2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y_1+y_2=-\dfrac{5}{3}\\y_1y_2=-2\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2+9x_1x_2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y_1+y_2=-\dfrac{5}{3}\\y_1y_2=-2.\left(-\dfrac{5}{3}\right)^2+9.\left(-2\right)=-\dfrac{212}{9}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow y_1;y_2\) là nghiệm của:
\(y^2+\dfrac{5}{3}y-\dfrac{212}{9}=0\Leftrightarrow9y^2+10y-212=0\)
Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a) 3x - 3y + x 2 - y 2 ; b) x 2 -4 x 2 y 2 + y 2 + 2xy
c) x 6 - x 4 + 2 x 3 + 2 x 2 ; d) x 3 - 3x 2 +3x - 1 - y 3 .
a) (x - y)(x + y + 3). b) (x + y - 2xy)(2 + y + 2xy).
c) x 2 (x + l)( x 3 - x 2 + 2). d) (x – 1 - y)[ ( x - 1 ) 2 + ( x - 1 ) y + y 2 ].
a) 3x(x+1)-x(3x+2)
b) 2x(x2-5x+6)+(x-1)(x+3)
c) (x2-xy+y2)-(x2+2xy+y2)
d) (2/5xy+x-y)-(3x+4y)-2/5xy
e) 2xy(x2-4xy+4y2)
f) (x+y)(xy+5)
g) (x3-2x2-x+2):(x-1)
h) (2x2+3x-2):(2x-1)
Giải pt nghiệm nguyên:
1. x2+y2=(x-y)(xy+2)+9
2. xy=p(x+y) với p là số nguyên tố
3. x3+y3=2022
\(pt< =>\left(x-y\right)^2+xy=\left(x-y\right)\left(xy+2\right)+9\)
\(< =>\left(y-x\right)\left(xy+2+y-x\right)+xy+2+y-x-\left(y-x\right)=11\)
\(< =>\left(y-x+1\right)\left(xy+2+y-x\right)-\left(y-x+1\right)=10\)
\(< =>\left(x-y+1\right)\left(x-y-1-xy\right)=10\)
đến đây giải hơi bị khổ =))
giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên: x+y+xy=x2+y2
\(x+y+xy=x^2+y^2\)
⇔ \(2xy+2x+2y=2x^2+2y^2\)
⇔ \(\left(x^2+y^2-2xy\right)+\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+\left(y^2-2y+1\right)=2\)
⇔ \(\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y-1\right)^2=2\)
⇔ 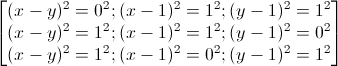
⇔ 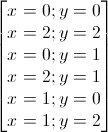
Các cặp số nguyên (x, y) thỏa mãn phương trình là : (0; 0); (2; 2); (0; 1); (2; 1); (1; 0);(1;2).