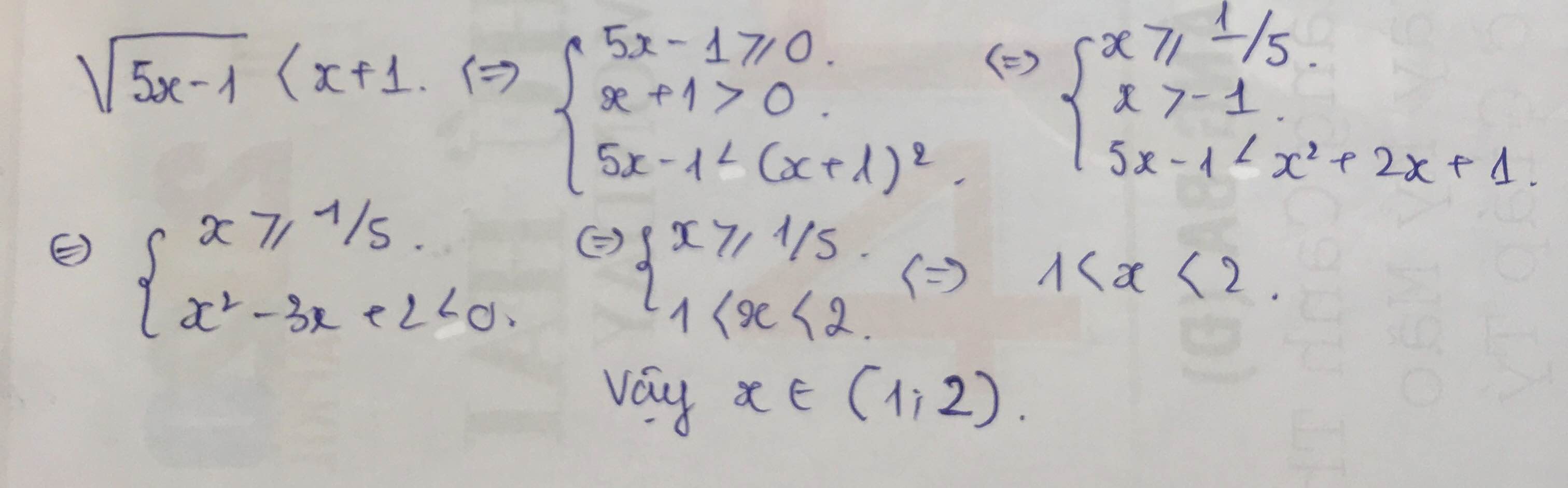giải phương trình căn ( 2x-1) + căn (x-2) = căn (x+1) (bằng cách liên hợp hoặc đặt ẩn phụ)
H24
Những câu hỏi liên quan
giải pt bằng cách đặt ẩn phụ:
5.căn(2x^3+16)=2(x^2+8)
\(5\sqrt{2x^3+16}=2\left(x^2+8\right)\left(x>-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow20\sqrt{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}=2\left(x^2+8\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2+8\right)-20\sqrt{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+8-10\sqrt{x+2}\sqrt{x^2-2x+4}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+4+2x+4-10\sqrt{x+2}\sqrt{x^2-2x+4}=0\)
Đặt a = \(\sqrt{x^2-2x+4}\left(a>0\right)\)
b = \(\sqrt{x+2}\left(b\ge0\right)\)
=> pt có dạng:
\(a^2-10ab+b^2=0\)
bạn phân tích rồi làm tiếp nhá
GIẢI HỆ PHƯƠNG TRÌNH:(đặt ẩn phụ)
a) 1/x -1/y-2 =-1
4/x + 3/y-2 =5
b)2/x +5/(x+y) =2
3/x +1/(x+y) =17/10
c) 2/(x-1) +1 /(y+1) =7
5/(x-1) - 2/(y-1) =4
d) 2/ (căn x-1) -1/ (căn y-1) =1
1/ (căn x-1) +1 / (căn y-1) =2
\(a.\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}-2=-1\\\dfrac{4}{x}+\dfrac{3}{y}-2=5\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a-b-2=-1\\4a+3b-2=5\end{matrix}\right.\) (với \(\dfrac{1}{x}=a-\dfrac{1}{y}=b\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{10}{7}\\b=\dfrac{3}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{10}{7}\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{7}{10}\\\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{3}{7}\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{7}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b.\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x}+\dfrac{5}{\left(x+y\right)}=2\\\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+y\right)}=\dfrac{17}{10}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a+5b=2\\3a+b=\dfrac{17}{10}\end{matrix}\right.\) (với \(\dfrac{1}{x}=a-\dfrac{1}{x+y}=b\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{1}{2}\\b=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow x=2\\\dfrac{1}{x+y}=\dfrac{1}{5}\Rightarrow y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c.\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x-1}+\dfrac{1}{y+1}=7\\\dfrac{5}{x-1}-\dfrac{2}{y+1}=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a+b=7\\5a-2b=4\end{matrix}\right.\) (với \(\dfrac{1}{x-1}=a-\dfrac{1}{y+1}=b\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\\b=3\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x-1}=2\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\\dfrac{1}{y+1}=3\Rightarrow y=-\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(d.\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x-1}}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{y-1}}=1\\\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x-1}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{y-1}}=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a-b=1\\a+b=2\end{matrix}\right.\) (với \(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x-1}}=a-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{y-1}}=b\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\b=1\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x-1}}=1\Rightarrow x=2\\\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{y-1}}=1\Rightarrow y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 4
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình 6x^2 +7x căn x+1=24(x+1)
dùng phương pháp đặt ẩn
giải pt bằng phương pháp đặt ẩn phụ :
căn (x^2-3x+2) = x^2-3x-4
giải pt bằng phương pháp đặt ẩn phụ :
căn (x^2-3x+2) = x^2-3x-4
Lời giải:
ĐKXĐ: $x\geq 2$ hoặc $x\leq 1$
Đặt $\sqrt{x^2-3x+2}=a(a\geq 0)\Rightarrow x^2-3x-4=a^2-6$
Phương trình đã cho trở thành:
\(a=a^2-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2-a-6=0\Leftrightarrow a(a-3)+2(a-3)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (a-3)(a+2)=0\Rightarrow a=3\) (do $a\geq 0$)
\(\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{x^2-3x+2}=3\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-3x+2=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-7=0\Rightarrow x=\frac{3\pm \sqrt{37}}{2}\) (đều thỏa mãn)
Vậy.........
Giải pt sau (bằng 3 cách TẠO LŨY THỪA DƯỚI DẤU CĂN, ĐẶT ẨN PHỤ, DÙNG BĐT): \(x^2+6x-3=4x\sqrt{2x-1}\)
\(x^2+6x-3=4x\sqrt{2x-1}\left(1\right)\) ĐK: \(x\ge\frac{1}{2}\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{2x-1}=a\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow6x-3=3a^2\)
=> (1) <=> x^2 +3a^2 = 4ax
<=> x^2 -4ax +3a^2 =0
<=> x^2 -ax - 3ax + 3a^2 =0
<=> x(x-a) -3a(x-a) =0
<=> (x-a) ( x-3a ) =0
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=a\\x=3a\end{cases}}\)
TH1: x=a
\(\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{2x-1}\)\(\left(x\ge0\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
<=> x=1 (tm)
TH2: x= 3a
\(\Rightarrow x=3\sqrt{2x-1}\left(x\ge0\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=18x-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-18x+9=0\)
\(\Delta=288\)
=> pt có 2 nghiệm pb \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{18+12\sqrt{2}}{2}=9+6\sqrt{2}\left(tm\right)\\x=\frac{18-12\sqrt{2}}{2}=9-6\sqrt{2}\left(tm\right)\end{cases}}\)
Vậy ...
Giải phương trình sau: 3+căn(2x-3)=x
(Căn x+1)(2 căn x-3)-2x=-4
Căn (2x+1)- x+1= 0
a: \(3+\sqrt{2x-3}=x\)
=>\(\sqrt{2x-3}=x-3\)
=>x>=3 và 2x-3=(x-3)^2
=>x>=3 và x^2-6x+9=2x-3
=>x>=3 và x^2-8x+12=0
=>x>=3 và (x-2)(x-6)=0
=>x>=3 và \(x\in\left\{2;6\right\}\)
=>x=6
b: \(\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(2\sqrt{x}-3\right)-2x=-4\)
=>\(2x-3\sqrt{x}+2\sqrt{x}-3-2x=-4\)
=>\(-\sqrt{x}-3=-4\)
=>\(-\sqrt{x}=-1\)
=>căn x=1
=>x=1(nhận)
c: \(\sqrt{2x+1}-x+1=0\)
=>\(\sqrt{2x+1}=x-1\)
=>x>=1 và (x-1)^2=2x+1
=>x>=1 và x^2-2x+1=2x+1
=>x>=1 và x^2-4x=0
=>x(x-4)=0 và x>=1
=>x=4
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình
căn x+3 - 2 căn x = căn 2x+2 - căn 3x+1
Em trục căn thức:
\(\sqrt{x+3}-2\sqrt{x}=\sqrt{2x+2}-\sqrt{3x+1}\)
<=> \(\frac{-3x+3}{\sqrt{x+3}+2\sqrt{x}}=\frac{-x+1}{\sqrt{2x+2}+\sqrt{3x+1}}\)
=> nhân tử chung là -x + 1 . Tự làm tiếp nhé!
làm như cô thì vẫn cần phải đánh giá rất khó chịu nhé
\(\sqrt{x+3}-2\sqrt{x}=\sqrt{2x+2}-\sqrt{3x+1}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ge0\right)\)
\(< =>\sqrt{x+3}-\sqrt{2x+2}+\sqrt{3x+1}-2\sqrt{x}=0\)
\(< =>\frac{\sqrt{x+3}^2-\sqrt{2x+2}^2}{\sqrt{x+3}+\sqrt{2x+2}}+\frac{\sqrt{3x+1}^2-4\sqrt{x}^2}{\sqrt{3x+1}+2\sqrt{x}}=0\)
\(< =>\frac{x+3-2x-2}{\sqrt{x+3}+\sqrt{2x+2}}+\frac{3x+1-4x}{\sqrt{3x+1}+2\sqrt{x}}=0\)
\(< =>\frac{1-x}{\sqrt{x+3}+\sqrt{2x+2}}+\frac{1-x}{\sqrt{3x+1}+2\sqrt{x}}=0\)
\(< =>\left(1-x\right)\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{x+3}+\sqrt{2x+2}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{3x+1}+2\sqrt{x}}\right)=0< =>x=1\)
Giải bất phương trình A) căn 5x-1< x+1 B) căn x^2 +2x+8 b< x+2 C) căn 2x^2 +4