Giải phương trình:
(x2+3x+2).(x2+7x+12)=24
Giải phương trình: (3x – 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x – 1)(7x – 10).
(3x – 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x – 1)(7x – 10)
⇔ (3x – 1)(x2 + 2) – (3x – 1)(7x – 10) = 0
⇔ (3x – 1)(x2 + 2 – 7x + 10) = 0
⇔ (3x – 1)(x2 – 7x + 12) = 0
⇔ (3x – 1)(x2 – 4x – 3x + 12) = 0
⇔ (3x – 1)[(x2 – 4x) – (3x - 12)] = 0
⇔ (3x – 1)[x(x – 4) – 3(x – 4)] = 0
⇔ (3x – 1)(x – 3)(x – 4) = 0
⇔ 3x – 1 = 0 hoặc x – 3 = 0 hoặc x – 4 = 0
+ 3x – 1 = 0 ⇔ 3x = 1 ⇔ x = 1/3.
+ x – 3 = 0 ⇔ x = 3.
+ x – 4 = 0 ⇔ x = 4.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là 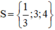
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 2 x − 1 2 + x − 3 2 x − 1 = 0 ;
b) 3 − 2 x 2 + 4 x 2 − 9 = 0 ;
c) 7 − x 2 + 2 3 x − 7 x − 3 = 0 ;
d) 4 3 x − 2 − 3 x − 2 3 = 0 .
Giải các phương trình sau:
1/x2+5x+6 + 1/x2+7x+12 + 1/x2+9x+20 + 1/x2+11x+30 = 1/8
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)}+...+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x+6\right)}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{x+2}-\dfrac{1}{x+3}+\dfrac{1}{x+3}-\dfrac{1}{x+4}+...+\dfrac{1}{x+5}-\dfrac{1}{x+6}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>1/x+2-1/x+6=1/8
=>\(\dfrac{x+6-x-2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+6\right)}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>x^2+8x+12=32
=>x^2+8x-20=0
=>(x+10)(x-2)=0
=>x=-10 hoặc x=2
Bài 2: Giải các phương trình sau:
a. (3x + 2)(x2 – 1) = (9x2 – 4)(x + 1)
b. x(x + 3)(x – 3) – 5(x + 2)(x2 – 2x + 4) = 0
c. x(x + 3)(x – 3) + 5(x – 3) = 0
d. (3x – 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x – 1)(7x – 10)
\(a.\left(3x+2\right)\left(x^2-1\right)=\left(9x^2-4\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)=\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=3x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c: =>x-3=0
hay x=3
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\cdot\left(x^2+2-7x+10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{\dfrac{1}{3};3;4\right\}\)
Bài 2: Giải các phương trình sau:
a. (3x + 2)(x2 – 1) = (9x2 – 4)(x + 1)
b. x(x + 3)(x – 3) – 5(x + 2)(x2 – 2x + 4) = 0
c. x(x + 3)(x – 3) + 5(x – 3) = 0
d. (3x – 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x – 1)(7x – 10)
\(\left(3x+2\right)\left(x^2-1\right)=\left(9x^2-4\right)\left(x+1\right).\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)=0.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1-3x+2\right)=0.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(-2x+1\right)=0.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+2=0.\\x+1=0.\\-2x+1=0.\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{2}{3}.\\x=-1.\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}.\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: =>(x-3)(x2+3x+5)=0
=>x-3=0
hay x=3
d: =>(3x-1)(x2+2-7x+10)=0
=>(3x-1)(x-3)(x-4)=0
hay \(x\in\left\{\dfrac{1}{3};3;4\right\}\)
Giải phương trình :
1) √x2+x+2 + 1/x= 13-7x/2
2) x2 + 3x = √1-x + 1/4
3) ( x+3)√48-x2-8x= 28-x/ x+3
4) √-x2-2x +48= 28-x/x+3
5) 3x2 + 2(x-1)√2x2-3x +1= 5x + 2
6) 4x2 +(8x - 4)√x -1 = 3x+2√2x2 +5x-3
7) x3/ √16-x2 + x2 -16 = 0
Giải các phương trình sau:
g/ x(x + 3)(x – 3) – (x + 2)(x2 – 2x + 4) = 0
h/ (3x – 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x – 1)(7x – 10)
i/ (x + 2)(3 – 4x) = x2 + 4x + 4
k/ x(2x – 7) – 4x + 14 = 0
m/ x2 + 6x – 16 = 0
n/ 2x2 + 5x – 3 = 0
\(m,x^2+6x-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+8x-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)+8\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+8\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+8=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(n,2x^2+5x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-x+6x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x-1\right)+3\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\2x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(k,x\left(2x-7\right)-4x+14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-4x-7x+14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-2\right)-7\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-7\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-7=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải các phương trình sau bằng cách đặt ẩn số phụ x 2 + 3 x - 1 2 +2( x 2 +3x -1) -8 =0
Đặt m = x 2 +3x -1
Ta có: x 2 + 3 x - 1 2 +2( x 2 +3x -1) -8 =0 ⇔ m 2 +2m -8 =0
∆ ’ = 1 2 -1.(-8) =1 +8 =9 > 0
∆ ' = 9 =3
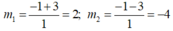
Với m = 2 thì : x 2 +3x - 1 = 2 ⇔ x 2 + 3x - 3 = 0
∆ ’ = 3 2 -4.1.(-3 )=9 +12=21 > 0
∆ ' = 21
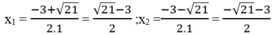
Với m = -4 ta có: x 2 +3x -1 = -4 ⇔ x 2 +3x +3 = 0
∆ = 3 2 -4.1.3=9 -12 = -3 < 0
Phương trình vô nghiệm
Vậy phương trình đã cho có 2 nghiệm :
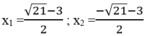
Giải các phương trình: (2 x 2 + 7x - 8) (2 x 2 + 7x - 3) - 6 = 0
Giải phương trình : ( 3x-1) ( x2+ 9) = (3x-1) (7x-10)
Giải chi tiết hộ mình nhe . MInh cám unn
( 3x-1) ( x2+ 9) = (3x-1) (7x-10)
⇒( 3x-1) ( x2+ 9) - (3x-1) (7x-10) = 0
⇒( 3x-1) (( x2+ 9)-(7x-10)) = 0
⇒( 3x-1)(x2+9-7x+10)=0
⇒( 3x-1)(x2-7x+19)=0
⇒\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=0\\x^2-7x+19=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
3x-1=0
⇒x=\(\dfrac{1}{3}\)
x2-7x+19=0
⇒ \(x^2-\dfrac{7}{2}x-\dfrac{7}{2}x+\left(\dfrac{7}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{27}{4}=0\)
⇒ \(\left(x-\dfrac{7}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{27}{4}=0\)
vì \(\left(x-\dfrac{7}{2}\right)^2\ge0\); \(\dfrac{27}{4}>0\)
⇒ \(\left(x-\dfrac{7}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{27}{4}>0\)
⇒ x vô nghiệm
Vậy x= \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\left(3x-1\right)\left(x^2+9\right)=\left(3x-1\right)\left(7x-10\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x^2+9\right)-\left(3x-1\right)\left(7x-10\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x^2-7x+12\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x^2-4x-3x+12\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left[x\left(x-4\right)-3\left(x-4\right)\right]=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=0\\x-3=0\\x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=3\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(\left(3x-1\right)\left(x^2+9\right)=\left(3x-1\right)\left(7x-10\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x^2+9-7x+10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x^2-7x+19\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-1=0\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)