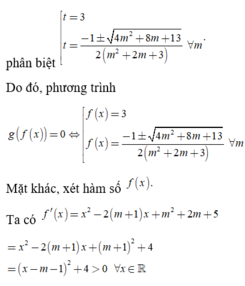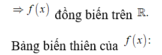(2x4 – 13x3 + 15x2 +11x - 3) : (x2 - 4x - 3)
GT
Những câu hỏi liên quan
tìm x nguyên để:
(2x4-13x3+15x2+11x-4)⋮(x2-4x-3)
Kiểm tra lại tích (x2 – 4x – 3)(2x2 – 5x + 1) có bằng (2x4 - 13x3 + 15x2 + 11x – 3) hay không.
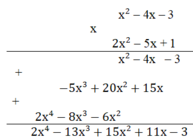
Vậy (x2 – 4x – 3)(2x2 – 5x + 1) = 2x4 - 13x3 + 15x2 + 11x – 3
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Sắp xếp các đa thức theo luỹ thừa giảm dần của biến rồi tính:a) (
-
x
2
+
6
x
3
- 26x + 21): (3 - 2x);b) (
2
x
4
-
13
x
3
-15 + 5x + 21
x
2
): (4x -
x
2
- 3).
Đọc tiếp
Sắp xếp các đa thức theo luỹ thừa giảm dần của biến rồi tính:
a) ( - x 2 + 6 x 3 - 26x + 21): (3 - 2x);
b) ( 2 x 4 - 13 x 3 -15 + 5x + 21 x 2 ): (4x - x 2 - 3).
a) Kết quả -3 x 2 – 4x + 7. b) Kết quả -2 x 2 + 5x + 5.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm a và b để đa thức A chia hết cho đa thức B với:a) A
4
x
3
+
15
x
2
+ 24x + 3 + a và B
x
2
+ 4x + 7;b) A
x
4
+
3
x
3
-
x
2
+ (2a - 3)x +...
Đọc tiếp
Tìm a và b để đa thức A chia hết cho đa thức B với:
a) A = 4 x 3 + 15 x 2 + 24x + 3 + a và B = x 2 + 4x + 7;
b) A = x 4 + 3 x 3 - x 2 + (2a - 3)x + 3b + a và B = x 2 + 3x - 1.
a. (2x4 - x3 + 4x - 2) : (2x-1)
b. (2x3 - x2 -5x - 2) : (x-2)
c. (-6a3 + a2 + 26a – 21): (2a – 3)
d. (x4 - 3x2 - 10x - 6) : (x2 - 2x +3)
a: \(=\dfrac{x^3\left(2x-1\right)+2\left(2x-1\right)}{2x-1}=x^3+2\)
b: \(=\dfrac{2x^3-4x^2+3x^2-6x+x-2}{x-2}=2x^2+3x+1\)
d: \(=\dfrac{x^4-2x^3+3x^2+2x^3-4x^2+6x-x^2+2x-3}{x^2-2x+3}=x^2+2x-1\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a) Thực hiện phép chia đa thức (2x4 - 6x3 +12x2 - 14x + 3) cho đa thức (x2 – 4x +1)
b) Thực hiện phép chia đa thức (2x4 – 5x3 + 2x2 +2x - 1) cho đa thức (x2 – x - 1)
Bài 2:
a) Tìm a để đa thức (2x4 + x3 - 3x2 + 5x + a) chia hết cho đa thức (x2 - x +1)
Bài 1:
a: \(=\dfrac{2x^4-8x^3+2x^2+2x^3-8x^2+2x+18x^2-72x+18+56x-15}{x^2-4x+1}\)
\(=2x^2+2x+18+\dfrac{56x-15}{x^2-4x+1}\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình:
a) x4 - 2x3 + x2 - 4x +4 = 0
b) x4 + 2x3 - 3 = 0
c) 2x4 - 100x + 98 = 0
d) (x + 1)(x + 2)(x + 3)(x + 4) = 24
d: Ta có: \(\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)=24\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+5x+4\right)\left(x^2+5x+6\right)-24=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
bài 1:phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử
a,x4 +5x2 +9
b,x4 + 3x2 +4
c,2x4 - x2 -1
Bài 2:tìm x biết
a,(x+1) (x+2)(x+3)(x+4)= 120
b,(x-4x+3)(x2+6x +8) +24
Bài 1:
\(a,x^4+5x^2+9\\=(x^4+6x^2+9)-x^2\\=[(x^2)^2+2\cdot x^2\cdot3+3^2]-x^2\\=(x^2+3)^2-x^2\\=(x^2+3-x)(x^2+3+x)\)
\(b,x^4+3x^2+4\\=(x^4+4x^2+4)-x^2\\=[(x^2)^2+2\cdot x^2\cdot2+2^2]-x^2\\=(x^2+2)^2-x^2\\=(x^2+2-x)(x^2+2+x)\)
\(c,2x^4-x^2-1\\=2x^4-2x^2+x^2-1\\=2x^2(x^2-1)+(x^2-1)\\=(x^2-1)(2x^2+1)\\=(x-1)(x+1)(2x^2+1)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (2)
Bài 2:
\(a,\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)=120\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\left(x+1\right)\left(x+4\right)\right]\cdot\left[\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\right]=120\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+5x+4\right)\left(x^2+5x+6\right)=120\) (1)
Đặt \(x^2+5x+5=y\), khi đó (1) trở thành:
\(\left(y-1\right)\left(y+1\right)=120\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y^2-1=120\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y^2=121\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=11\\y=-11\end{matrix}\right.\)
+, TH1: \(y=11\Leftrightarrow x^2+5x+5=11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+5x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x+6x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)+6\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\left(\text{nhận}\right)\)
+, TH2: \(y=-11\Leftrightarrow x^2+5x+5=-11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+5x+16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[x^2+2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{5}{2}+\left(\dfrac{5}{2}\right)^2\right]-\dfrac{25}{4}+16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+\dfrac{5}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{39}{4}=0\)
Ta thấy: \(\left(x+\dfrac{5}{2}\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+\dfrac{5}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{39}{4}\ge\dfrac{39}{4}>0\forall x\)
Mà \(\left(x+\dfrac{5}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{39}{4}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) loại
Vậy \(x\in\left\{1;-6\right\}\).
\(b,\) Đề thiếu vế phải rồi bạn.
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Cho hai hàm số:
f
(
x
)
1
3
x
3
-
m
+
1
x
2
+
m
2
+
2
m
+
5
x
-
2019
và...
Đọc tiếp
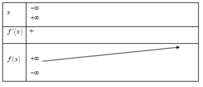
Cho hai hàm số: f ( x ) = 1 3 x 3 - m + 1 x 2 + m 2 + 2 m + 5 x - 2019 và g ( x ) = ( m 2 + 2 m + 3 ) x 3 - ( 3 m 2 + 6 m + 8 ) x 2 - 4 x + 3 với m là tham số.
Phương trình g(f(x)) = 0 có bao nhiêu nghiệm?
A. 9
B. 6
C. 3
D. 1