2x+ 5y=1
2x+y=-4 Giải hệ pt
giải hệ pt sau
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{5x^2+2xy+2y^2}+\sqrt{2x^2+2xy+5y^2}=3\left(x+y\right)\\\sqrt{x+2y+1}+2\sqrt[3]{12x+7y+8}=2xy+x+5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{5x^2+2xy+2y^2}+\sqrt{2x^2+2xy+5y^2}=3\left(x+y\right)\\\sqrt{2x+y+1}+2\sqrt[3]{7x+12y+8}=2xy+y+5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Xét \(pt\left(1\right)\) dễ dàng suy ra \(x+y\ge0\)
\(VT=\sqrt{\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(2x+y\right)^2}+\sqrt{\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(2y+x\right)^2}\)
\(\ge\left|2x+y\right|+\left|2y+x\right|\ge3\left(x+y\right)\)
Đẳng thức xảy ra khi \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=y\\x,y\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay vào \(pt\left(2\right)\) ta được:
\(\sqrt{3x+1}+2\sqrt[3]{19x+8}=2x^2+x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\sqrt{3x+1}-\left(x+1\right)\right]+2\left[\sqrt[3]{19x+8}-\left(x+2\right)\right]=2x^2-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-x^2\right)\left[\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3x+1}+x+1}+2\cdot\dfrac{x+7}{\sqrt[3]{\left(19x+8\right)^2}+\left(x+2\right)\sqrt[3]{19x+8}+\left(x+2\right)^2}+2\right]=0\)
Do \(x;y\ge0\) nên pt trong ngoặc luôn dương
\(\Rightarrow x-x^2=0\Rightarrow x\left(1-x\right)=0\Rightarrow\)\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Mà \(x=y\)\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=y=0\\x=y=1\end{matrix}\right.\) là nghiệm của hpt
thanks b đã chỉ giúp mình.tại đánh máy nên mình ko để ý^^
pt(1): 5x2+2xy+2y2>=(2x+y)2 nên \(\sqrt{5x^{2^{ }}+2xy+2y^2}\ge\:\)trị tuyệt đối 2x+y.
cmtt>\(\sqrt{2x^2+2xy+5y^2}\ge\)trị tuyệt đối x+ 2y.
>mà tt đối 2x+y cộng ttđ x+2y>= 3(x+y).
>(1)>=3(x+y).
đâu = xảy ra khi và chỉ khi x=y.
thay x=y >=0 vào (2):
\(\sqrt{3x+1}+2\sqrt[3]{19x+8}\) = 2x2+x+5.
<=>\(\left(\sqrt{3x+1}-\left(x+1\right)\right)\)+\(\left(2\sqrt[3]{19x+8}-\left(x+2\right)\right)\)= 2x2- 2x.
nhân liên hợp ta đc:
(x2-x)*(\(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3x+1}+x+1}+2\dfrac{x+7}{\sqrt[3]{19x+18}+\left(x+2\right)\left(\sqrt[3]{19x+18}\right)+\left(x+2\right)^2}=0\)
dễ thấy phần *>0 với mọi x,ytheo đk của (1)
>(x2 -x)=0
>x=0 hoặc x=1
>(x,y)=(0,0); (1,1).
vậy....
giải hệ pt a)2x+3y=5 và 4x-5y=1
b)xy-x-y=3 và x^2+y^2-xy=1
c)x+2y+3z=4 và 2x+3y-4z=-3 và 4x+y-z=-4
a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+3y=5\\4x-5y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+6y=10\\4x-5y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+3y=5\\11y=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+3\cdot\dfrac{9}{11}=5\\y=\dfrac{9}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+\dfrac{27}{11}=5\\y=\dfrac{9}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=\dfrac{28}{11}\\y=\dfrac{9}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{14}{11}\\y=\dfrac{9}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(x=\dfrac{14}{11};y=\dfrac{9}{11}\)
giải hệ phương trình
\(\begin{cases}8\sqrt{2x-1}\left(2x-\sqrt{2x-1}\right)=y\left(y^2-2y+4\right)\\4xy+2\sqrt{\left(y+2\right)\left(y+2x\right)}=5y+12x-6\end{cases}\)(x;y thuộc R)
Giải hệ pt
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{4x+10y}-\sqrt{2x+2y}=4\\x+2y+\dfrac{2\sqrt{2x^2+7xy+5y^3}}{3}=24\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đề có vẻ sai sai. Bạn xem lại đề xem có đúng không?
1) Cho hệ phương trình:
(k+1)x + (3k+1)y = 2-k
(2x + (k+2)y = 4. Tìm k để x và y thuộc Z
2) giải pt
a) x² - 4x - 6= √2x²-8x-12
b) (4x+1)(12x-1)(3x+2)(x+1)=4
2)
a) ĐK: \(2x^2-8x-12\ge0\)(1)
Nhân 2 cả hai vế ta có:
\(2x^2-8x-12=2\sqrt{2x^2-8x-12}\)
Đặt: \(\sqrt{2x^2-8x-12}=t\left(t\ge0\right)\)
Ta có phương trình: \(t^2=2t\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}t=0\\t=2\end{cases}}\)(tm)
+) Với t=0 ta có:\(\sqrt{2x^2-8x-12}=0\Leftrightarrow2x^2-8x-12=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x-6=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2+\sqrt{10}\\x=2-\sqrt{10}\end{cases}}\)( thỏa mãn đk (1))
+) Với t=2 ta có: \(\sqrt{2x^2-8x-12}=2\Leftrightarrow2x^2-8x-12=4\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x-8=\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2+2\sqrt{3}\\x=2-2\sqrt{3}\end{cases}}\)( THỎA MÃN đk (1))
vậy ...
b) pt <=> \(\left(4x+1\right)\left(3x+2\right)\left(12x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=4\)
<=> \(\left(12x^2+11x+2\right)\left(12x^2+11x-1\right)=4\)
Đặt :\(12x^2+11x+2=t\)
Ta có pt: \(t\left(t-3\right)=4\Leftrightarrow t^2-3t-4=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}t=4\\t=-1\end{cases}}\)
Với t=4 ta có: ....
Với t=-1 ta có:...
Em tự làm tiếp nhé
giải hệ pt :
\(\frac{x+3}{9}+\frac{2x-y}{12}=4và\frac{2x-5y}{3}-\frac{3x-7}{11}=-55\)
Giải các hệ phương trình sau bằng phương pháp thế: 3 x + 5 y = 1 2 x - y = - 8
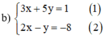
Từ (2) ta rút ra được y = 2x + 8 (*)
Thế (*) vào phương trình (1) ta được :
3x + 5(2x + 8) = 1 ⇔ 3x + 10x + 40 = 1 ⇔ 13x = -39 ⇔ x = -3.
Thay x = - 3 vào (*) ta được y = 2.(-3) + 8 = 2.
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (-3 ; 2).
Giải các hệ phương trình: 5 x + 2 y = 3 x - 1 2 x + 4 = 3 x - 5 y - 12
Giải các hệ phương trình sau:
b) 5 x + 2 y = 4 x - 1 2 x + 4 = 3 x - 5 y - 20
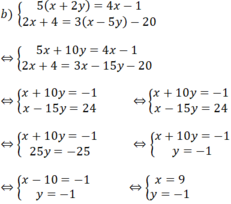
Vậy hệ phương trình đã cho có nghiệm (x; y) = (9; -1).