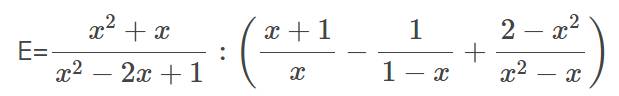Đk: \(x\ne1;x\ne0\)
a) \(E=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}:\left[\dfrac{x+1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{x-1}+\dfrac{2-x^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}\right]\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}:\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)+x+2-x^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}.\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}\)
b) \(E>1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}>1\) \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x-1}>0\) \(\Leftrightarrow x-1>0\)
( do \(x^2-x+1=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}>0\forall x\) )
\(\Leftrightarrow x>1\)
Vậy để E>1 thì x>1
c) \(E=\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}=\dfrac{x^2-1+1}{x-1}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)+1}{x-1}=x+1+\dfrac{1}{x-1}\)
\(E\in Z\Leftrightarrow x+1+\dfrac{1}{x-1}\in Z\) mà \(x\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1\inƯ\left(1\right)=\left\{-1;1\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\left(ktm\right);x=2\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy \(x=2\) thì \(E\in Z\).